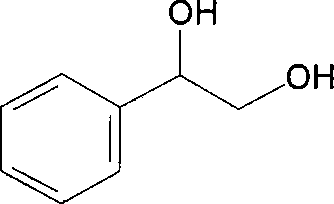
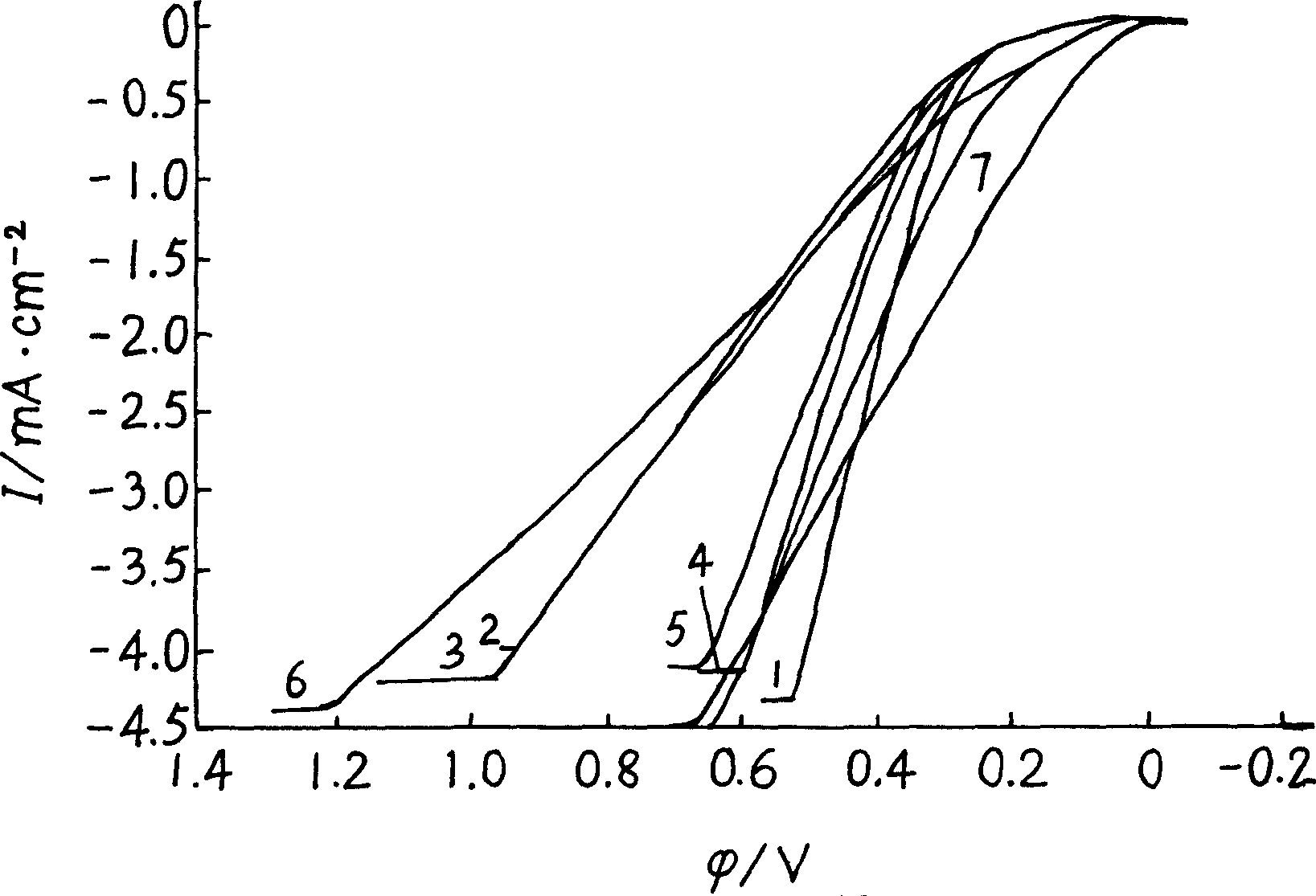
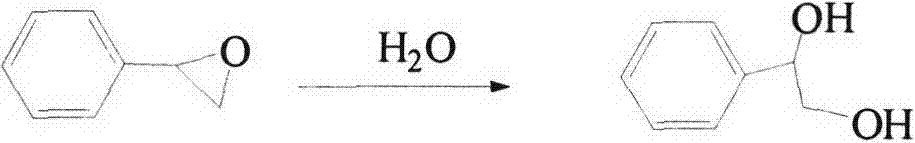Patents
Literature
65 results about "Phenylethylene glycol" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In total, 15 phenylethylene glycol derivatives with diverse Zn 2+-binding groups like carboxylate, hydrazide, carboxamide, sulfonamide, vicinal diol, thiol, thioester, and hydroxypyridinone moieties were prepared in divergent syntheses.
Method for preparing (R)-styrene glycol by employing asymmetric conversion of recombinant strain
ActiveCN101230363APromote conversionIncrease cell massBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliKetone
The invention relates to a method of using recombinant strain to asymmetrically transform and manufacture (R)-phenyl glycol, which belongs to the field of biological catalytic asymmetric transforming technique. The invention inserts the (R)-specific alcohol dehydrogenase gene rcr into the vector pET21c to construct a recombinant plasmid pET-RCR which is transformed to the E.coli to construct the recombinant plasmid E.coli BL21 / pET-RCR. The recombinant strain has the capability of asymmetrically catalyzing the 2-hydroxy phenyl ethyl ketone into (R)-phenyl ethylene glycol. Under optimized reaction condition, the 2.5-10 percent isopropanol is added to pH 8.0 Tris-HCL buffer as an auxiliary substrate, the 0.1-0.4g / ml recombinant cell solution is used for transforming the 0.5-5g / L 2-hydroxy phenyl ethyl ketone substrate for 48h, the product (R)-phenyl ethylene glycol with optical purity of 80-100 percent e.e. and productive rate of 70 to 100 percent is finally gained. The invention not only provides an effective way to manufacture (R)-phenyl ethylene glycol, but also makes sense for developing the biological catalyst for the chiral transformation.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
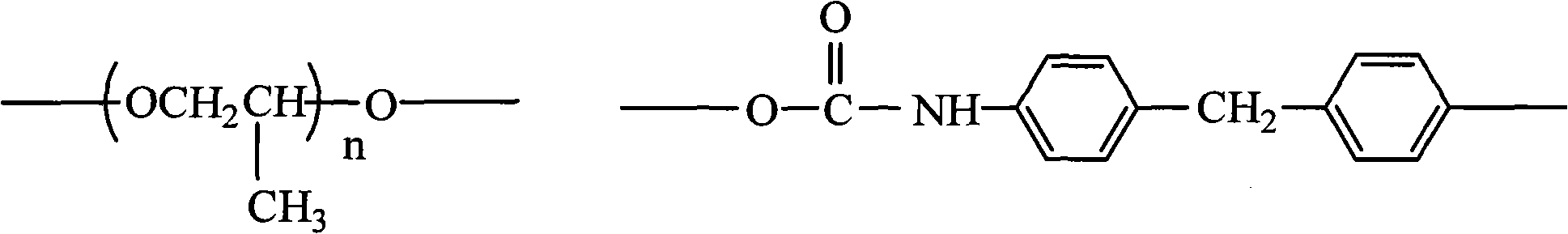
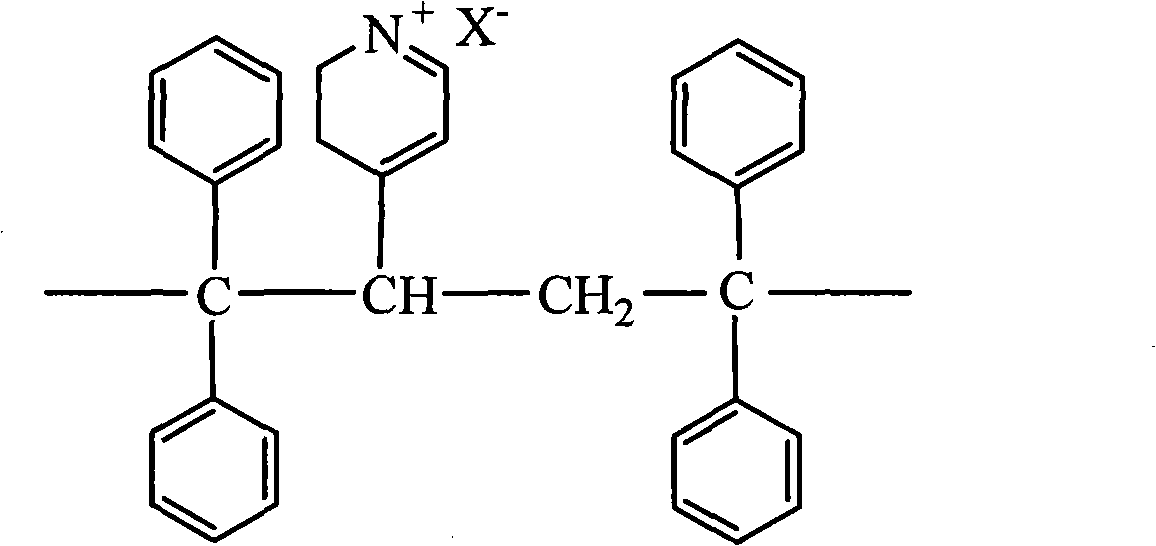
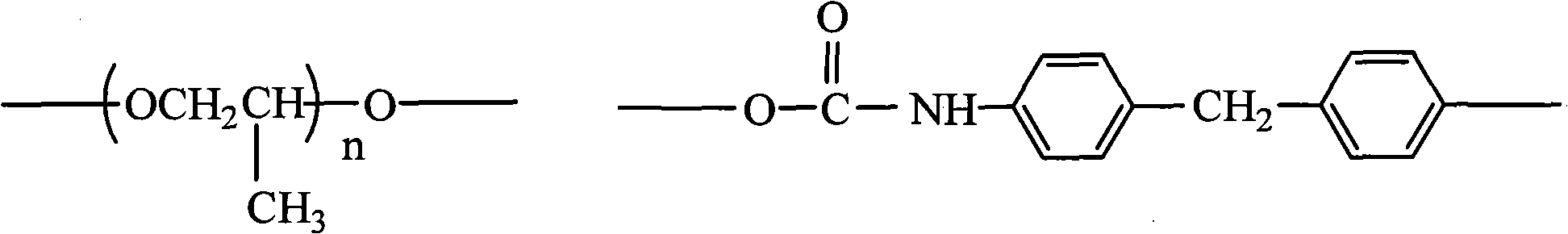
Pyridine quaternary ammonium salt polyurethane and preparation method thereof
The invention provides pyridine quaternary ammonium salt polyurethane, which comprises constitutional units shown in formulas 1, 2 and 3, wherein n is an integer from 20 to 80, and X is halogen atom; and the molecular weight of the pyridine quaternary ammonium salt polyurethane is 10,000 to 80,000. The invention also provides a preparation method for the pyridine quaternary ammonium salt polyurethane, which comprises the following steps of: performing condensation on polypropylene glycol and 4,4'-diphenylmethane diisocyanate to obtain prepolymer 1 taking isocyanate as a terminal group; performing chain extension on resin by adopting 1,1,2,2-tetraphenyl-1,2-ethanediol, and adding vinyl pyridine; and performing quaternary ammonium. The pyridine quaternary ammonium salt polyurethane has lipophilicity and hydrophily, and improves antibiotic property on the premise of keeping better ageing resistance and scratch resistance.
Owner:BYD CO LTD
Method for efficiently preparing (S)-styrene glycol from carbonyl reductase recombinant bacterium
The invention discloses a method for efficiently preparing (S)-styrene glycol from a carbonyl reductase recombinant bacterium, belonging to the technical field of biocatalysis asymmetric conversion. The invention provides a novel Candidaparapsiospis carbonyl group reductase gene scr II with Genbank sequence number of GQ411433; the scr II is inserted into a vector pET28a to construct a recombinant plasmid pETSCR II which is converted into E.coli BL21(DE3) competent cell; and a recombinant bacterium E.coli BL21 / pETSCR II with the preservation number of CCTCC NO:M209290 can be obtained by the screening of an LB flat plate containing 100 micrograms / ml kanamycin. The (S)-styrene glycol can be prepared by catalyzing 5g / L 2-carbonyl acetophenone obtained by asymmetrically reducing the recombinant bacterium; and the optical purity of products is 100 percent and the yield reaches 98.1 percent. The invention provides a novel functional gene and an effective path for efficiently preparing the (S)-styrene glycol.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
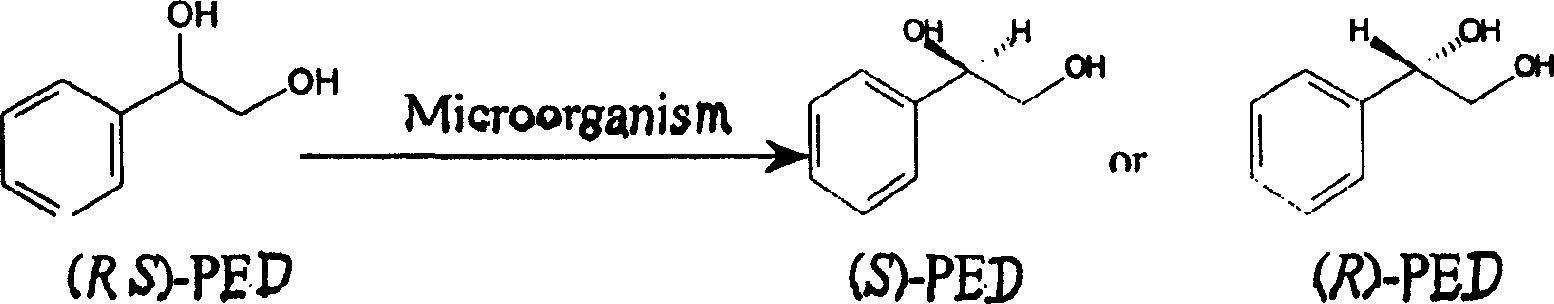
Method for preparing optical pure phenylethanediol by utilizing microbial stereoselectivity transformation and its special-purpose microbe
The present invention relates to a method for preparing optical pure phenyl ethanediol by utilizing microbial stereoselective conversion and its special-purpose microbe. It utilizes the screening process to obtain two strains of Candiba parapsilosis CCTCC M203011 and Bacillus polymyxa CCTCC M203010. Two strains can be used to make asymmetric conversion of racemic phenyl ethanediol so as to obtainthe product (S)-phenyl ethanediol, its optical purity is higher. Besides, it also provides optimized culture medium composition, culture condition, reaction system and reaction condition.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for improving transformation efficiency of (S)-phenyl glycol by coupling glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase and (S)-carbonyl reductase
The invention relates to a method for improving the transformation efficiency of (S)-phenyl glycol by coupling glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase and (S)-carbonyl reductase, belonging to the technical field of biological catalytic asymmetric transformation. The invention provides the method for preparing the (S)-phenyl glycol by recombinant Pichia pastoris with CGMCCNo.4198 and 2-hydroxyacetophenone catalyzed by the recombinant Pichia pastoris with CGMCCNo.4198 in multiple batches. In the invention, the Saccharomyces cerevisiae glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase gene and the Candida parapsilosis (S)-carbonyl reductase gene are simultaneously integrated into the Pichia pastoris genome, under the participation of 5% (w / v) glucose, the whole cells are reused for 10 batches, and the optical purity and yield of the (S)-phenyl glycol prepared by asymmetric transformation are maintained at 100% and higher than 85% all the time. The recombinant strain improves the batch stability of full cell transformation of the (S)-phenyl glycol by polygene coexpression, which well relieves the limit of coenzyme regenerative cycle in a biological transformation reaction; and simultaneously an efficient approach for preparing the (S)-phenyl glycol industrially in multiple batches at low cost is provided.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for preparing (R)-styrene glycol by changing coenzyme specificity and stereoselectivity via site-directed mutagenesis
ActiveCN101407780AUnderstanding StereoselectivityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliRecombinant escherichia coli
The invention discloses a (R)-styrene glycol preparation method that utilizes site-directed mutagenesis to alter coenzyme specificity and stereoselectivity, belongs to the technical field of biocatalytic asymmetric transformation, and provides a recombinant Escherichia coli strain BL21 / pETSCR6768 with the preservation CCTCC NO of M208079, and an asymmetric transforming preparation method of (R)-styrene glycol. The preparation method leads Ser in position 67 and His in position 68 of a (S)-specific carbonyl reductase to mutate to Asp, constructs recombinant plasmid pETSCR6768, and feeds the Escherichia coli, thus obtaining the recombinant strain E.coli BL21 / pETSCR6768 which leads the coenzyme specificity of (S)-specific carbonyl reductase to change from NADPH to NADH; furthermore, the stereoselectivity of the product is altered from (S)-styrene glycol to (R)-styrene glycol, and the preparation method provides an effective way for preparing (R)-styrene glycol in high efficiency and low cost and has significant meaning for recognizing the stereoselectivity of functional zymoprotein in the molecule and protein level.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Environmental protection type thread steel surface antirust treatment agent
ActiveCN103276383AGuaranteed performanceQuality assuranceMetallic material coating processesWater basedMaterials science
The present invention discloses an environmental protection type thread steel surface antirust treatment agent, which comprises, by weight, 5-15% of a zirconium salt, 2-8% of sodium hypophosphite, 0.5-5% of an alkali, 0.1-0.5% of a corrosion inhibitor, 0.1-0.5% of a stabilizer, 0.05-0.08% of nickel fluoride, 0.5-0.8% of phenyl ethylene glycol ether, 0.05-0.1% of tert-butylhydroquinone, 0.05-0.08% of glycerol monostearate, 0.05-0.08% of 4-sulfo phthalic acid, 0.02-0.05% of 2-sulfo phenylpropionic acid, and the balance of water. With the present invention, the commonly existing problem of easy rust during a storage and transportation process of the thread steel is solved, wherein a common water base antirust agent can heavily pollute an environment, and antirust oil can affect bounding stress between the thread steel and concrete. Compared with the antirust treatment agent in the prior art, the antirust treatment agent of the present invention has characteristics of significant antirust effect, long antirust time, low cost, no pollution and high safety.
Owner:合肥华清高科表面技术股份有限公司
Method for preparing optical pure phenylethanediol by utilizing microbial stereoselectivity transformation and its special-purpose microbe
The present invention relates to a method for preparing optical pure phenyl ethanediol by utilizing microbial stereoselective conversion and its special-purpose microbe. It utilizes the screening process to obtain two strains of Candiba parapsilosis CCTCC M203011 and Bacillus polymyxa CCTCC M203010. Two strains can be used to make asymmetric conversion of racemic phenyl ethanediol so as to obtain the product (S)-phenyl ethanediol, its optical purity is higher. Besides, it also provides optimized culture medium composition, culture condition, reaction system and reaction condition.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
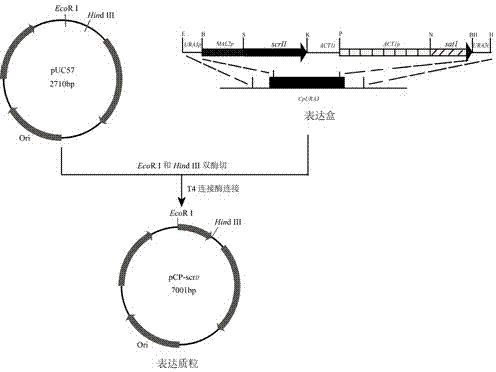
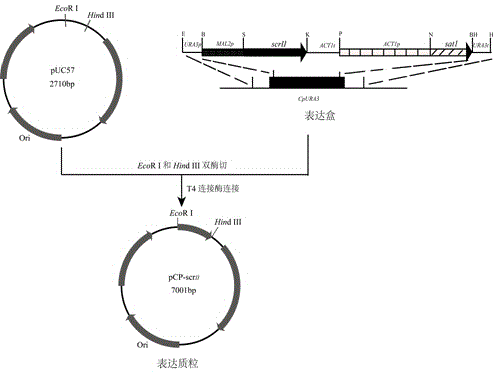
Method for using recombinant candida parapsilosis strain to efficiently prepare (S)-phenyl glycol
InactiveCN104774778AHelps understand the effect of stereoselectivityFungiMicroorganism based processesPhenyl glycolDrug biotransformation
The invention provides a method for using a recombinant candida parapsilosis strain to efficiently prepare (S)-phenyl glycol and belongs to the technical field of biological catalytic asymmetric transformation. The invention provides the recombinant candida parapsilosis strain Candida parapsilosis pCP-scrII preserved at the typical culture preservation center in China and marked with a preservation CCTCC NO: M2015107. According to the method, an expression plasmid of exogenous protein in candida parapsilosis is established, S-carbonyl reductase II is integrated to a candida parapsilosis genome to obtain the pCP-scrII, the candida parapsilosis is converted through electric shock to obtain the recombinant candida parapsilosis strain. By optimizing biotransformation reaction conditions, catalytic conversion is conducted on 2-hydroxyacetophenone through the recombinant strain to obtain the product S-phenyl glycol, the optical purity and yield of the product are up to 99.9%, an effective way is provided for efficient and low-cost preparation of the S-phenyl glycol, and a solid foundation is laid for industrial application of biological catalysis of chiral alcohol.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Synthesis of (R)-styrene glycol by coupling acceleration of (R)-carbonyl reduction enzyme and formic dehydrogenase
ActiveCN101469318AHigh optical purityHigh yieldBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliHigh concentration
The invention relates to promotion of synthesis of (R)-styrene glycol by coupling (R)-carbonyl reductase and formic dehydrogenase, which belongs to the technical field of asymmetrical transformation of biological catalysis. The invention provides a recombinant Escherichia coli, namely E.coli Rosetta / pETDuet-rcr-fdh, with a preservation number of CCTCC NO: M208123, wherein the (R)-special carbonyl reductasei and the formic dehydrogenase are coupled by a co-expression mode; asymmetrical transformation reaction is catalyzed by utilizing a cultured recombinant strain and taking 2-hydroxyacetophenone as a substrate; and the optical purity of the (R)-styrene glycol reaches 100 percent e.e., and the yield of the (R)-styrene glycol reaches 85.9 percent by optimizing the biotransformation reaction conditions. The invention utilizes double-enzyme coupling technology to solve the problem of limitation of regeneration cycle of coenzyme under the condition of high-concentration substrate, provides an effective path for high-efficiency and low-cost preparation of the (R)-styrene glycol, and lays a foundation for industrial application of the biosynthesized (R)-styrene glycol.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
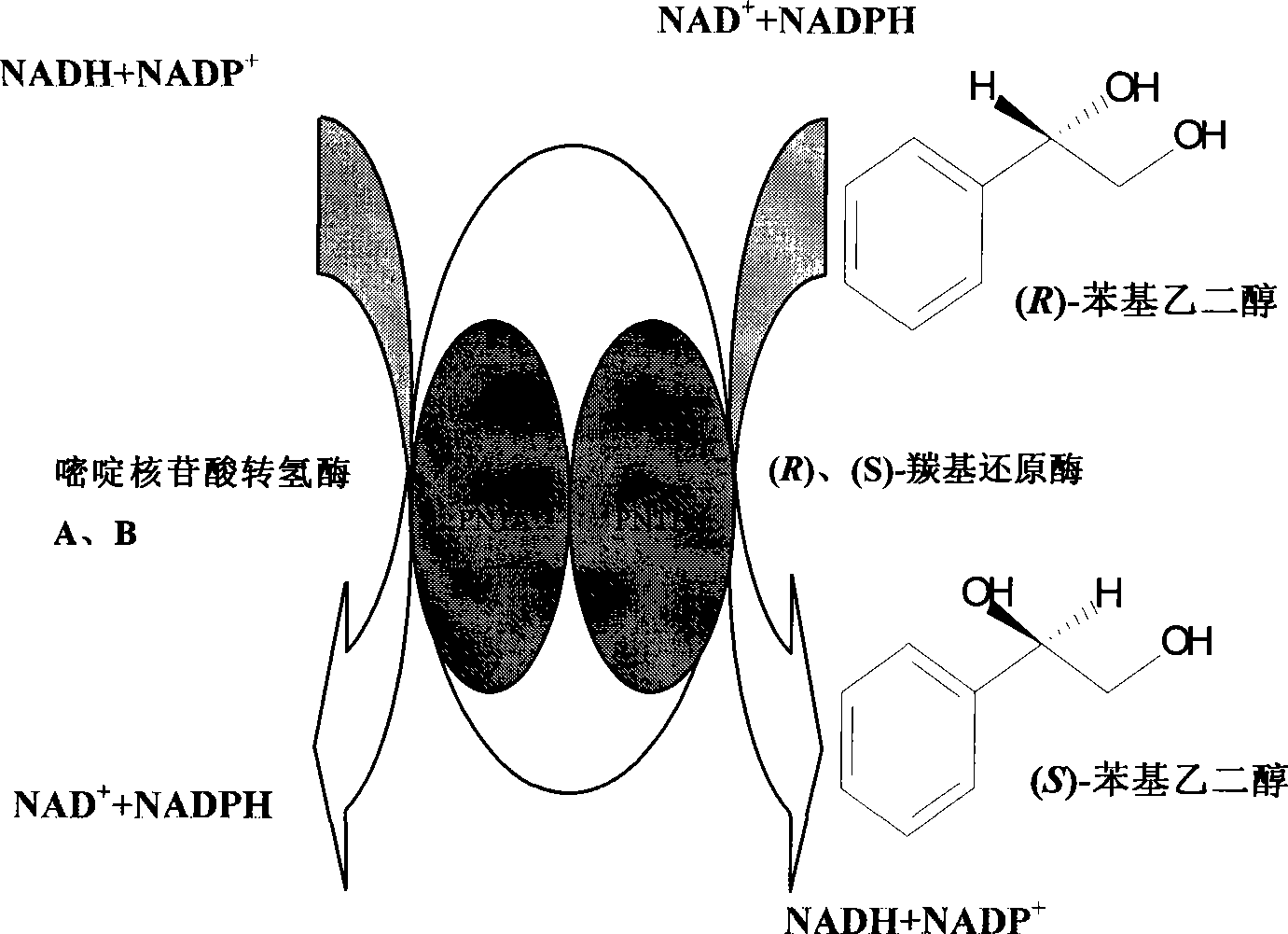
Method for preparing (S)-styrene glycol with carbonyl reduction enzyme and pyrimidine nucleoside acid transhydrogenase couplet
ActiveCN101368168AAchieve couplingSimplified chiral conversion pathwaysBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliAlcohol
A method for preparing (S)-phenylethylene glycol by coupling of carbonyl reductase and pyrimidine nucleotide transhydrogenase, which belongs to the technical field of biocatalysis asymmetric transformation. In the invention, (R)-carbonyl reductase, (S)-carbonyl reductase and pyrimidine nucleotide transhydrogenaseA, B are respectively constructed to two co-expression vectors, and the constructed recombinant plasmid pETDuet-rcr-scr and pACYCDuet-pnta-pntb are co-transformed into Escherichia coli to obtain recombinant strain E. Coli BL21(pETDuet-rcr-scr / pACYCDuet-pnta-pntb). The accession number is CCTCC NO: M208126. The recombinant strain not only realizes one-step transformation from substrate (R)-phenylethylene glycol to product (S)-phenylethylene glycol, but also removes a restriction of coenzyme regeneration cycle in a transformation reaction. The method provides an effective way for producing chiral alcohol through catalytic reaction of enzyme and regeneration of in-situ coenzyme under high substrate concentration.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
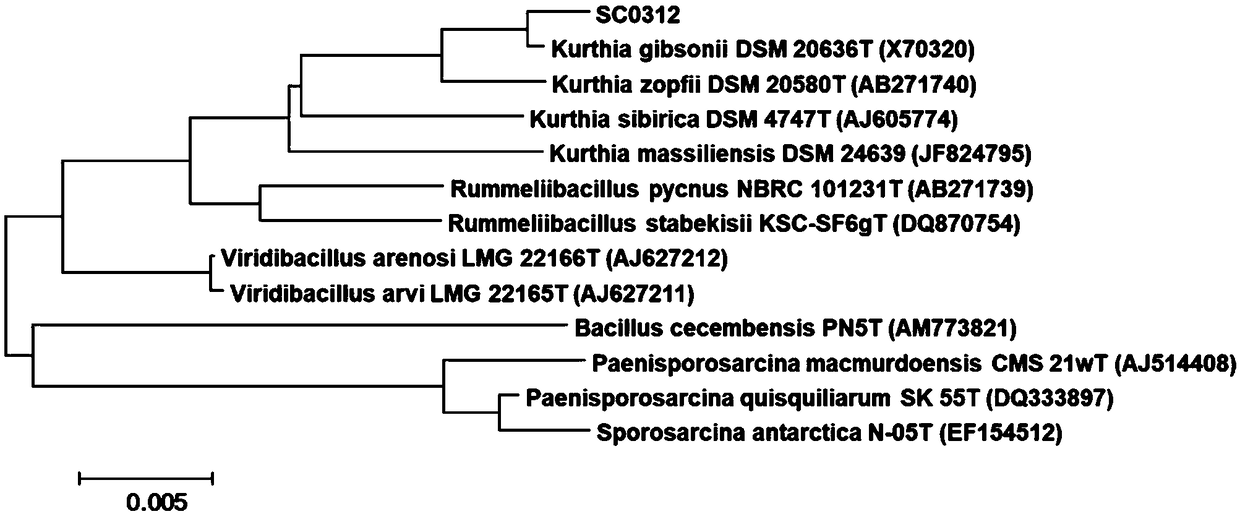
Kurthia gibsonii and application of Kurthia gibsonii in splitting of 1-phenyl-1,2-glycol
ActiveCN109294942AImprove catalytic selectivityHigh yieldBacteriaOrganic chemistry methodsPhenylethylene glycolBacterial strain
The invention discloses Kurthia gibsonii and an application of Kurthia gibsonii in splitting of 1-phenyl-1,2-glycol. The bacterial strain is Kurthia gibsonii SC0312, and a presevation number is CCTCCNO: M 2017157, The strain is preserved at the China Center for Type Culture Collection at Wuhan University, Wuhan, China on March 31st, 2017. The Kurthia gibsonii is capable of splitting racemic 1-phenyl-1,2-glycol to prepare (S)-1,2-diphenyl-1,2-ethanediol, has characteristics of high catalytic selectivity, high yield for product, simple conversion operation, safety, low cost, mild reaction conditions and environmental friendliness, can be applied to the fields of medicine, pesticides, cosmetics, liquid crystal materials, and the like, and has good application development prospects.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Multifunctional solution for cleaning and no-chromium deactivation of no-freon refrigerating pipe
InactiveCN1888137AMeet high cleanliness requirementsAvoid it happening againMetallic material coating processesPhenyl glycolTrichloroethylene
The present invention relates to deactivator for refrigerating part of copper, and is especially no-chromium deactivator for refrigerating part of copper. The no-chromium deactivator is the mixture of citric acid, sodium molybdate, urea, benzotriazole, ammonium acrylate, pyrrolidone, benzylalcohol, phenyl glycol ether, phenyl carbitol, amino trimethylene phosphonic acid and water. It is colorless, transparent, non-toxic and harmful multifunctional solution for cleaning and deactivating no Freon refrigerating pipe through soaking or spraying. It has simplified and environment friendly cleaning and deactivating process.
Owner:合肥华清方兴表面技术有限公司
Environment-friendly asymmetric synthetic method of (R)-phenyl ethylene glycol
InactiveCN104649865AEasy to separateAtom economy is highPreparation by hydroxy group additionChemical recyclingChemical industrySynthesis methods
The invention discloses an environment-friendly asymmetric synthetic method of (R)-phenyl ethylene glycol and belongs to the technical field of asymmetric synthesis. By taking styrene as a raw material, optically pure (R)-phenyl ethylene glycol is prepared by direct catalytic oxidization. The (R)-phenyl ethylene glycol has a relatively high atom economy. Moreover, by taking a low-toxicity harmless phosphotungstic chiral ionic liquid as a catalyst and H2O2 as a green oxidizing agent, the yield of the (R)-phenyl ethylene glycol is 67-82% and the enantiomeric purity is 96-100%e. e. After reaction, the catalyst is easily separated from byproducts, and the recovered catalyst precipitate can be recycled. The method disclosed by the invention is simple in process, high in production efficiency, low in cost and small in environmental risk and meets the requirements of environment-friendly chemical industry.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
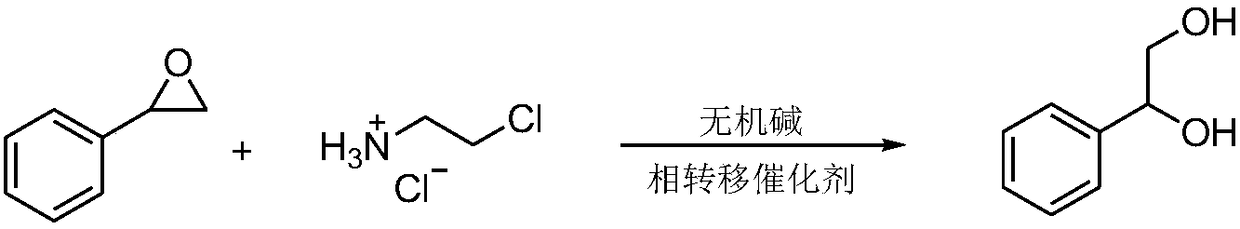
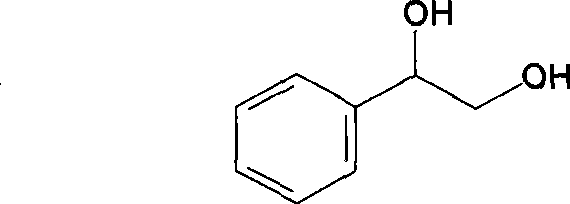
Synthetic method for 1-phenyl-1,2-ethanediol
ActiveCN108129260AHigh purityHigh yieldOrganic compound preparationPreparation by hydrolysisStyrene oxideOrganic layer
The invention provides a synthetic method for 1-phenyl-1,2-ethanediol. The synthetic method comprises the following steps: (1) performing a reaction: adding styrene oxide, a phase transfer catalyst, 2-chloroethylaminehydrochloride, an inorganic alkali and water into a flask with a thermometer and a reflux condenser pipe, performing stirring, and performing a heating reflux reaction; (2) performingend point monitoring: performing monitoring on the reaction of the step (1) by adopting an HPLC, and determining the reaction end point when the raw material styrene oxide disappears; and (3) performing extraction: when the reaction of the step (1) reaches the reaction end point, stopping heating, cooling the system to room temperature, performing extraction by using an organic solvent, separating and taking an organic layer, and performing decompression exsolution to obtain a white solid. The prepared product provided by the invention has high purity, a high yield and reduced three industrial waste (waste water, waste gas and solid waste), is friendly to the environment, and meets the requirements of the green chemistry process.
Owner:CHANGZHOU HIGH TECH RES INST OF NANJING UNIV
Method for preparing (R)-styrene glycol by changing coenzyme specificity and stereoselectivity via site-directed mutagenesis
The invention discloses a (R)-styrene glycol preparation method that utilizes site-directed mutagenesis to alter coenzyme specificity and stereoselectivity, belongs to the technical field of biocatalytic asymmetric transformation, and provides a recombinant Escherichia coli strain BL21 / pETSCR6768 with the preservation CCTCC NO of M208079, and an asymmetric transforming preparation method of (R)-styrene glycol. The preparation method leads Ser in position 67 and His in position 68 of a (S)-specific carbonyl reductase to mutate to Asp, constructs recombinant plasmid pETSCR6768, and feeds the Escherichia coli, thus obtaining the recombinant strain E.coli BL21 / pETSCR6768 which leads the coenzyme specificity of (S)-specific carbonyl reductase to change from NADPH to NADH; furthermore, the stereoselectivity of the product is altered from (S)-styrene glycol to (R)-styrene glycol, and the preparation method provides an effective way for preparing (R)-styrene glycol in high efficiency and low cost and has significant meaning for recognizing the stereoselectivity of functional zymoprotein in the molecule and protein level.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Epoxide hydrolase from rhodosporidium paludigenum and application of epoxide hydrolase
ActiveCN109355271AHigh catalytic activityImprove catalytic selectivityHydrolasesGenetic engineeringEpoxide hydrolase 3Phenyl glycol
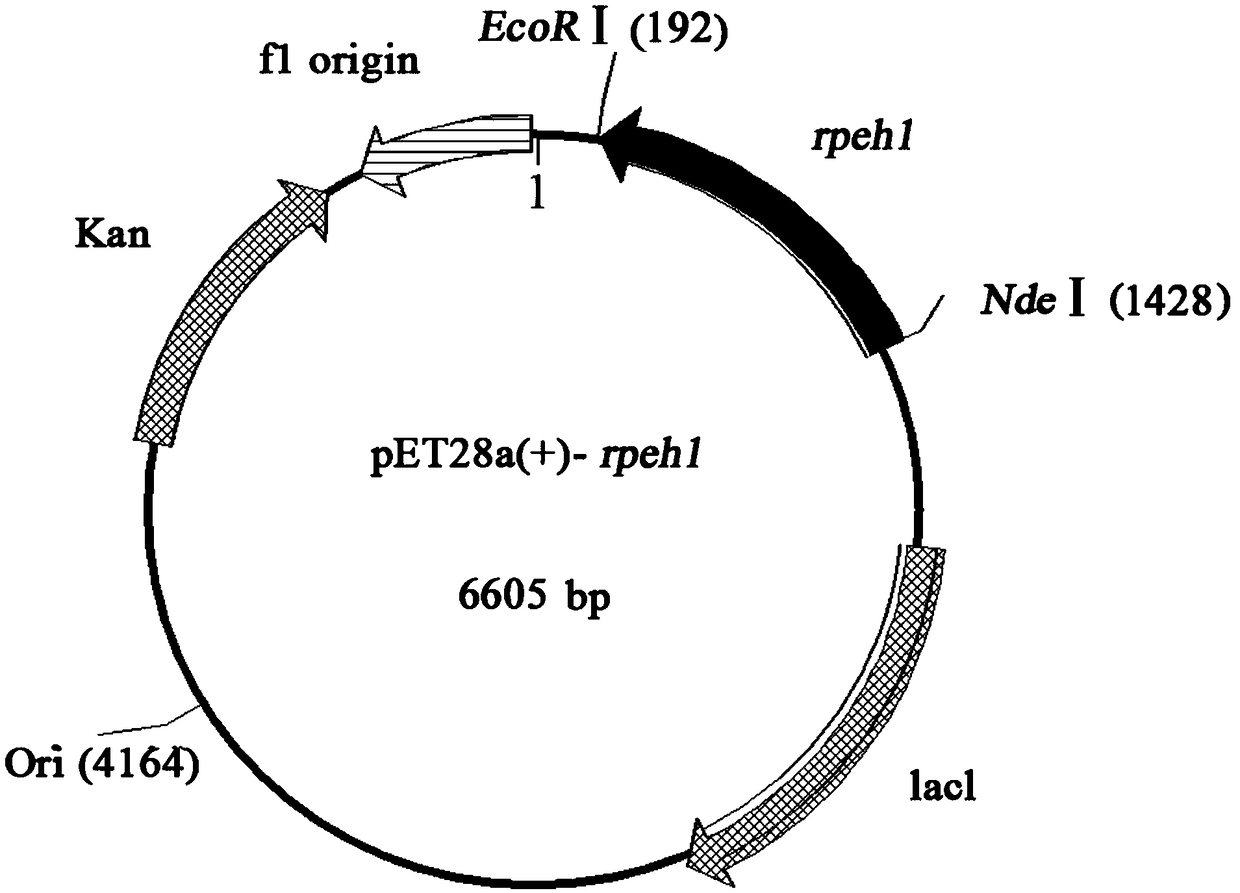
The invention discloses an epoxide hydrolase from rhodosporidium paludigenum and application of the epoxide hydrolase, and belongs to the technical field of biology. The epoxide hydrolase and the application have the advantages that epoxide hydrolase genes (rpeh1) from the rhodosporidium paludigenum R. paludigenum and corresponding amino acid sequences are provided; recombinant plasmids pET28a(+)-rpe1 with the genes and genetically engineered bacteria E. coli BL21 (DE3) / pET28a(+)-rpeh1 are constructed, and recombinant epoxide hydrolases are prepared by the aid of bacterial strains; biologicalcatalysis can be carried out by the constructed genetically engineered bacteria, and accordingly the ee of enantiomerically pure R-type phenyl glycol obtained by means of preparation is higher than 73%.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for preparing mandelic acid from styrene oxide
InactiveCN107162897ASimple preparation processMild reaction conditionsOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic compound preparationStyrene oxideActivated carbon
The invention provides a method for preparing mandelic acid from styrene oxide. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing phenyl glycol from styrene oxide through hydration under the catalysis of a NY-series catalyst; and introducing air for selective oxidation of mandelic acid from phenyl glycol under the action of an active carbon-loaded Pd-Au catalyst. The preparation method is characterized in that raw materials are mainly composed of styrene oxide, the NY-series catalyst and the active carbon-loaded Pd-Au catalyst. The preparation method for mandelic acid uses cheap and easily available raw materials and is simple in process, mild in conditions and high in product yield and product purity.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Chromium-free passivation liquid for cleaning of refrigerating pipe fitting
InactiveCN104988481AImprove corrosion resistanceImprove protectionMetallic material coating processesMethacrylatePyrazine
Disclosed is chromium-free passivation liquid for cleaning of a refrigerating pipe fitting. The chromium-free passivation liquid is formed by the following raw material formula components, by mass percentage, 10-15 parts of nonylphenol polyoxyethylene ether, 10-15 parts of dimethylformamide, 5-10 parts of 2-mercaptobenzothiazolyl, 5-8 parts of melamine, 10-20 parts of sodium sulfate, 8-10 parts of hexafluorozirconic acid, 25-30 parts of polymers with 2-methyl-2-[(1-oxo-2-propenyl)amino]-1-propanesulfonic acid monosodium salt, 10-15 parts of zinc methacrylate, 3-5 parts of benzilic acid, 50-80 parts of phenethyl alcohol, 50-80 parts of benzopinacole, 80-120 parts of pyrazine, 100-120 parts of polyethylene glycol octylphenol ether and 250-300 parts of deionized water. The chromium-free passivation liquid for cleaning of the refrigerating pipe fitting can meet the requirement for high cleanness, enables the refrigerating pipe fitting to have good corrosion resistance, and is beneficial to environmental protection and simplification of the operation technology.
Owner:谢伟杰
Method for producing 1, 2-alkamine compound by utilizing whole-cell transformation
InactiveCN110713965AIncrease enzyme activityRaise the ratioBacteriaTransferasesTransformation efficiencyGlycol synthesis
The invention discloses a method for producing a 1, 2-alkamine compound by utilizing whole-cell transformation, and belongs to the technical field of gene engineering and microbiology engineering. A bacillus subtilis engineering strain co-expresses alcohol dehydrogenase (MnADH) and w-transaminase (PAKw-TA), and can whole-cell catalyze phenyl-1, 2-ethylene glycol at one step so as to synthesize 2-amino-1-phenyethyl alcohol. By utilizing the method provided by the invention, the phenyl-1, 2-ethylene glycol can be used as a substrate, and whole-cell transformation is carried out to prepare the high-purity 2-amino-1-phenyethyl alcohol; and the method for producing the 1, 2-alkamine compound by utilizing whole-cell transformation is convenient to operate, cheap in substrate, and not only beneficial to improving the transformation efficiency but also beneficial to reducing the reaction cost, and has an important industrial application value.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for improving asymmetric conversion efficiency of (R)-phenyl glycol by recombination strains through cosubstrate coupling
ActiveCN101985647ASolve the regeneration bottleneck problemHigh substrate concentrationMicroorganism based processesFermentationGlycerolPhenyl glycol
The invention discloses a method for improving the asymmetric conversion efficiency of (R)-phenyl glycol by recombination strains through cosubstrate coupling, belonging to the technical field of biological catalysis asymmetric conversion. In the invention, a cosubstrate coupling system is built in rationality so as to realize good coenzyme regenerating cycle and greatly improve the preparation efficiency of the (R)-phenyl glycol; the recombinant Escherichia coli BL21 / pET32a-mrcr with the preservation number of CCTCCNO:M209289 serves as a biocatalyst after being optimized by the secondary structure of mRNA, and the cosubstrate glycerol and / or isopropanol with different ratios are added to improve the substrate dissolubility; and a substrate coupling coenzyme regenerating cycle system is built to shorten the reaction time from 48h to 1.5h and realize efficient conversion of the (R)-phenyl glycol under high substrate concentration. The economic and convenient whole cell coenzyme regenerating method provides an effective path for preparing the (R)-phenyl glycol with high efficiency and low cost and lays a solid foundation for industrial production of chiral alcohols.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for optimizing and improving biotransformation efficiency of (R)-carbonyl reductase by mRNA two-stage structure
ActiveCN101724597AImprove catalytic functionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliMrna secondary structure
The invention relates to a method for optimizing and improving biotransformation efficiency of (R)-carbonyl reductase by an mRNA two-stage structure, belonging to the technical field of biocatalysis asymmetric transformation. The invention optimizes an mRNA translation start area two-stage structure of (R)-carbonyl reductase and constructs a corresponding mutation recombination strain which is classified and named Escherichia coli BL21 / pET32a-mrcr with the CCTCC preservation No. M209289. The mutation strain not only realizes the efficient expression of the (R)-carbonyl reductase but also effectively improves the zymoprotein activity and biotransformation efficiency, and provides novel research idea and approach for efficiently preparing the (R)-phenylglycol in high substrate concentration.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Process of regenerating internal cell coenzyme NADP11 by pentose and its application
ActiveCN100999748AImprove stereoselective transformation abilityIncreased enantiomeric excessMicroorganism based processesChemical recyclingPhenylethylene glycolCellular metabolism
The present invention is the process of regenerating intracellular coenzyme NADPH with pentose and its application, and belongs to the field of biologically catalyzed asymmetrical conversion technology. Into the conversion reaction system, pentose as the auxiliary substrate for regenerating the coenzyme is added to raise the stereo selective conversion capacity of thallus. Adding pentose in 8 mg / ml can raise the enantiomeric excess value of the product (S)-phenyl ethylene glycol from 86 % to 98 % and the yield from 77 % to 85 %, and makes it possible to use the thallus for several times. The process regenerates great amount of NADPH and replenishes coenzyme for the conversion reaction. The present invention is helpful for understanding the cell metabolism mechanism related to coenzyme regeneration and is significant to the development of intracellular coenzyme regenerating system.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for efficiently preparing (S)-styrene glycol from carbonyl reductase recombinant bacterium
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Recombinant bacterium obtained by in-situ expression of (R)-carbonyl reductase in candida parapsilosis and method using same to produce (R)-phenyl glycol efficiently
InactiveCN104830704AHigh optical purityHigh yieldFungiMicroorganism based processesForeign proteinPhenyl glycol
The invention discloses a recombinant bacterium obtained by in-situ expression of (R)-carbonyl reductase in candida parapsilosis and a method using the same to produce (R)-phenyl glycol efficiently, and belongs to the technical field of bio-catalytic asymmetric conversion. The invention provides a strain of candida parapsilosis pCP-rcr, which has been preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC), and the preservation number is CCTCC No. M2015106. The expression plasmid pCP of foreign protein in candida parapsilosis is established, then (R)-carbonyl reductase is cloned to the plasmid to obtain recombinant plasmid pCP-rcr, and finally the recombinant plasmid pCP-rcr is electrically converted into candida parapsilosis to obtain the recombinant strain candida parapsilosis pCP-rcr. The recombinant bacterium can be used to catalyze 2-hydroxy acetophenone, by optimizing the biological conversion reaction conditions, the optical purity of the product namely (R)-phenyl glycol can reach 99.9%, the yield can reach 99.6%, the biological conversion time is shortened from 48 hours to 13 hours, and an efficient and low-cost method is provided for preparing (R)-phenyl glycol.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
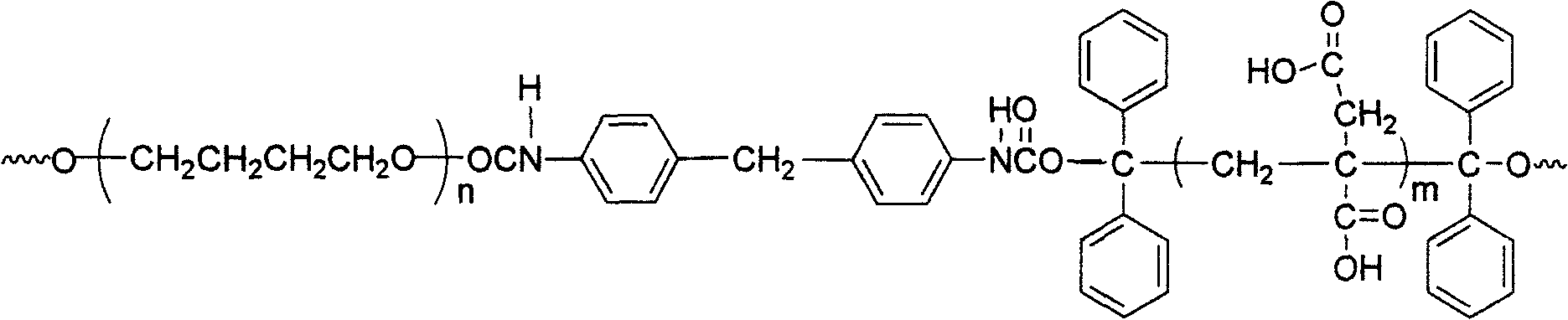
Fluorinated polyurethane and preparation method thereof
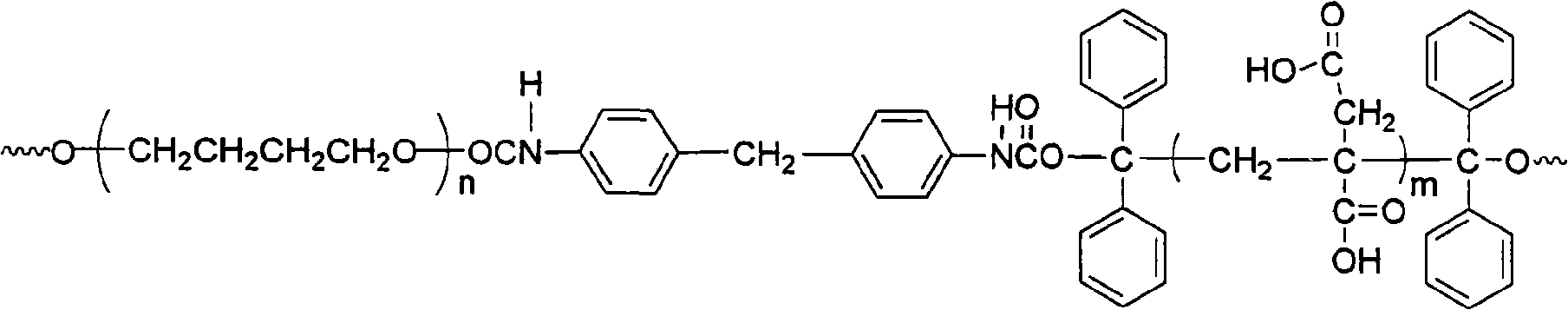
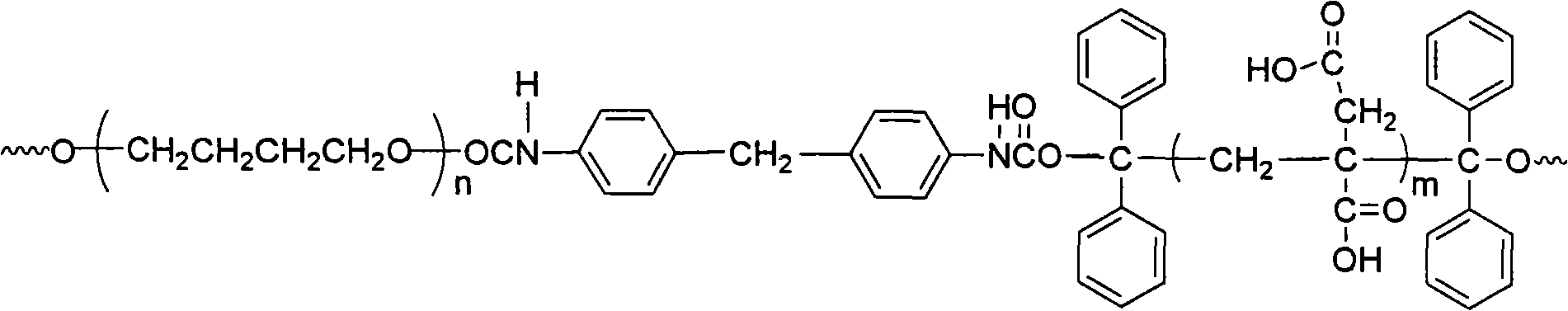
The invention relates to fluorinated polyurethane and a preparation method thereof and belongs to the technical field of polymer materials. A vinyl monomer is inserted in the main chain of the fluorinated polyurethane. The method adopts the following raw materials: benzophenone I, isopropanol II, polymeric diol III, diisocyanate IV, and or hexafluorobutyl acrylate V or hexafluorobutyl methacrylate VI. The method comprises: mixing the raw materials I and II and adding a first catalyst to perform a reaction under the radiation of ultraviolet light to obtain a product of 1,1,2,2-tetraphenylethylene glycol, performing recrystalization and purification by using acetic acid, mixing the III and the IV, adding the mixture of the III and the IV into a solvent, and stirring and mixing the mixture and the solvent to perform a reaction to obtain a prepolymer; and adding the 1,1,2,2-tetraphenylethylene glycol into the prepolymer to obtain reactants, adding a second catalyst into reactants and purifying to obtain a tetraphenylethylene glycol-terminated polyurethane, mixing the polyurethane with the V or the VI to perform a reaction and purifying to obtain the fluorinated polyurethane. The preparation method of the fluorinated polyurethane is simple and easy to implement. The synthesized fluorinated polyurethane has a good mechanical property and can be used in fields such as biomedical materials and paints.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Synthesis process of waterborne polyurethane
The invention belongs to the technical field of high molecular materials, and particularly relates to a synthesis process of waterborne polyurethane. The synthesis process includes following steps: step 1, adding a catalyst and a solvent into a mixed system of polyol, isophorone diisocyanate and 1, 1, 2, 2-tetraphenylglycol for reaction; step 2, after glycol and carboxymethyl chitosan are mixed well, adding into a mixture obtained in the step 1, and allowing reaction at 78-83 DEG C; step 3, adding a triethylamine-dichloromethane complex into a mixed system obtained in the step 2, and maintaining for 0.5h; step 4, adding the mixed system obtained in the step 3 into a water-diglycol mixed solution, and continuing to stir to obtain a waterborne polyurethane solution. High-stability waterbornepolyurethane is prepared under mild reaction conditions by introducing 1, 1, 2, 2-tetrapheneylglycol into raw materials and adding carboxymethyl chitosan into the step 2, few organic solvents are adopted in the process of reaction, and pollution is little.
Owner:南京宜凯瑞新材料有限公司
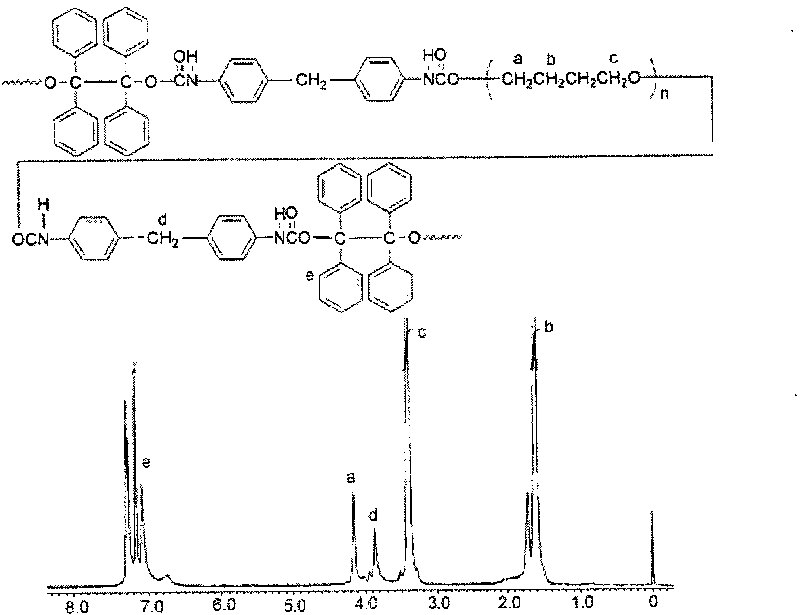
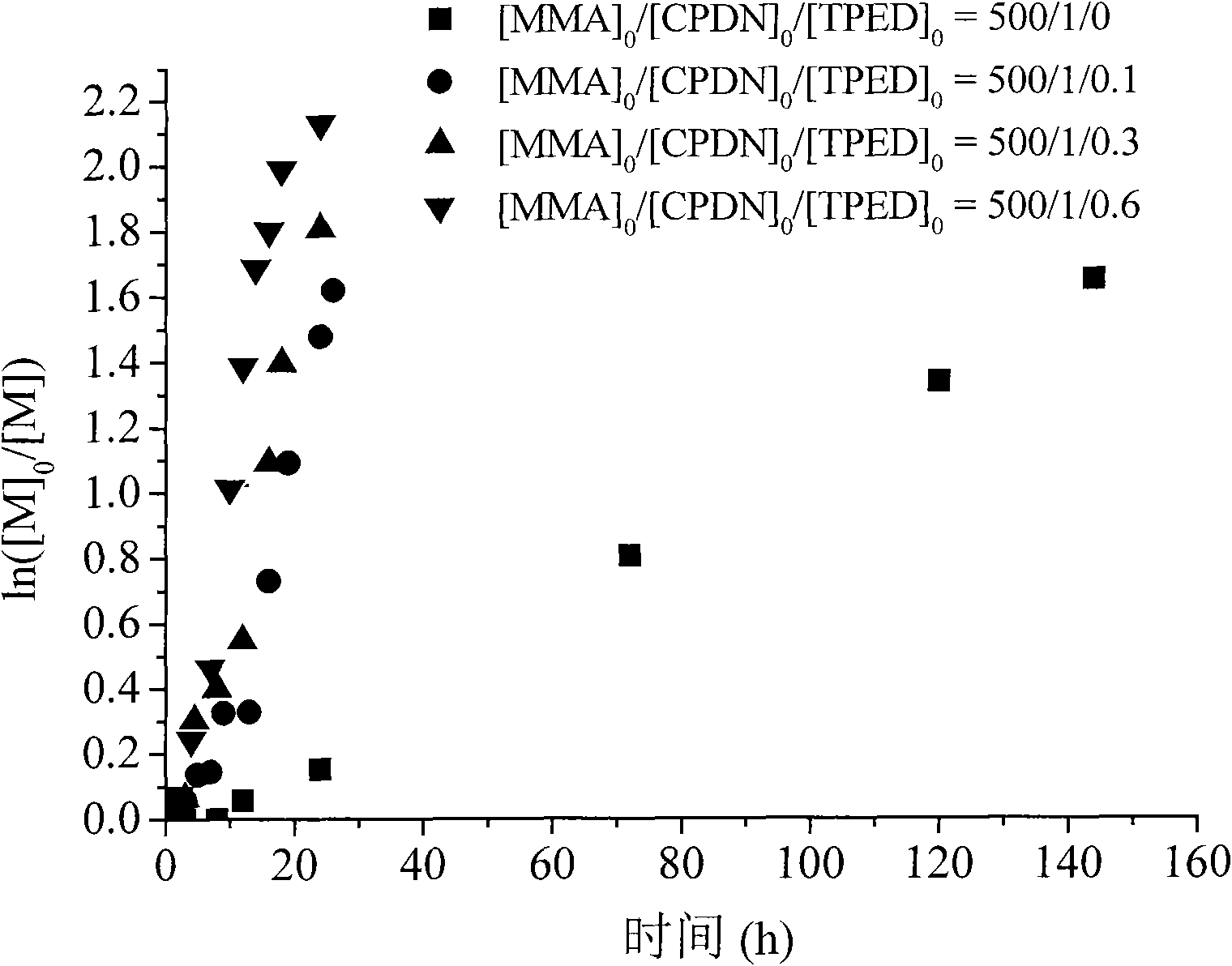
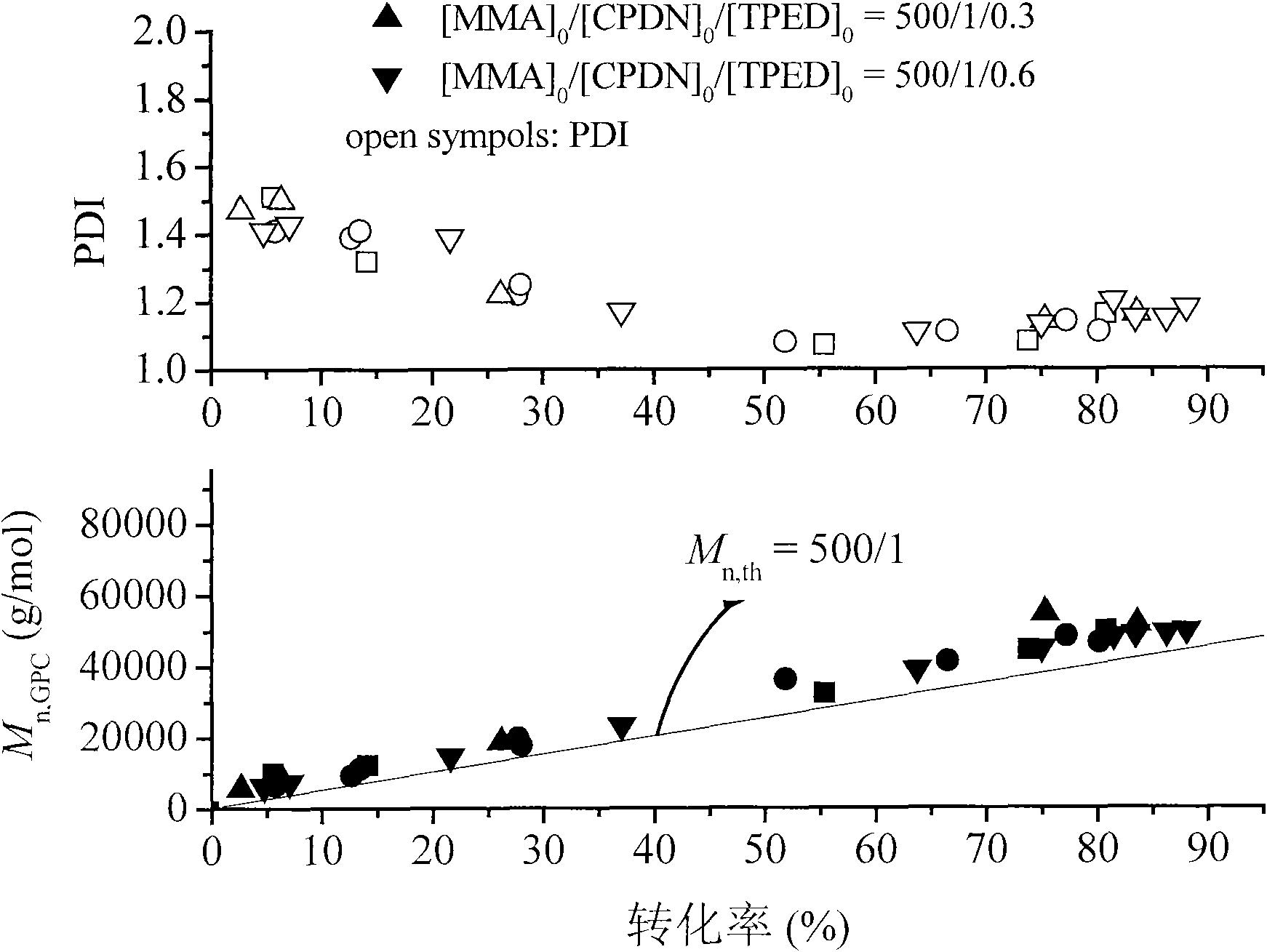
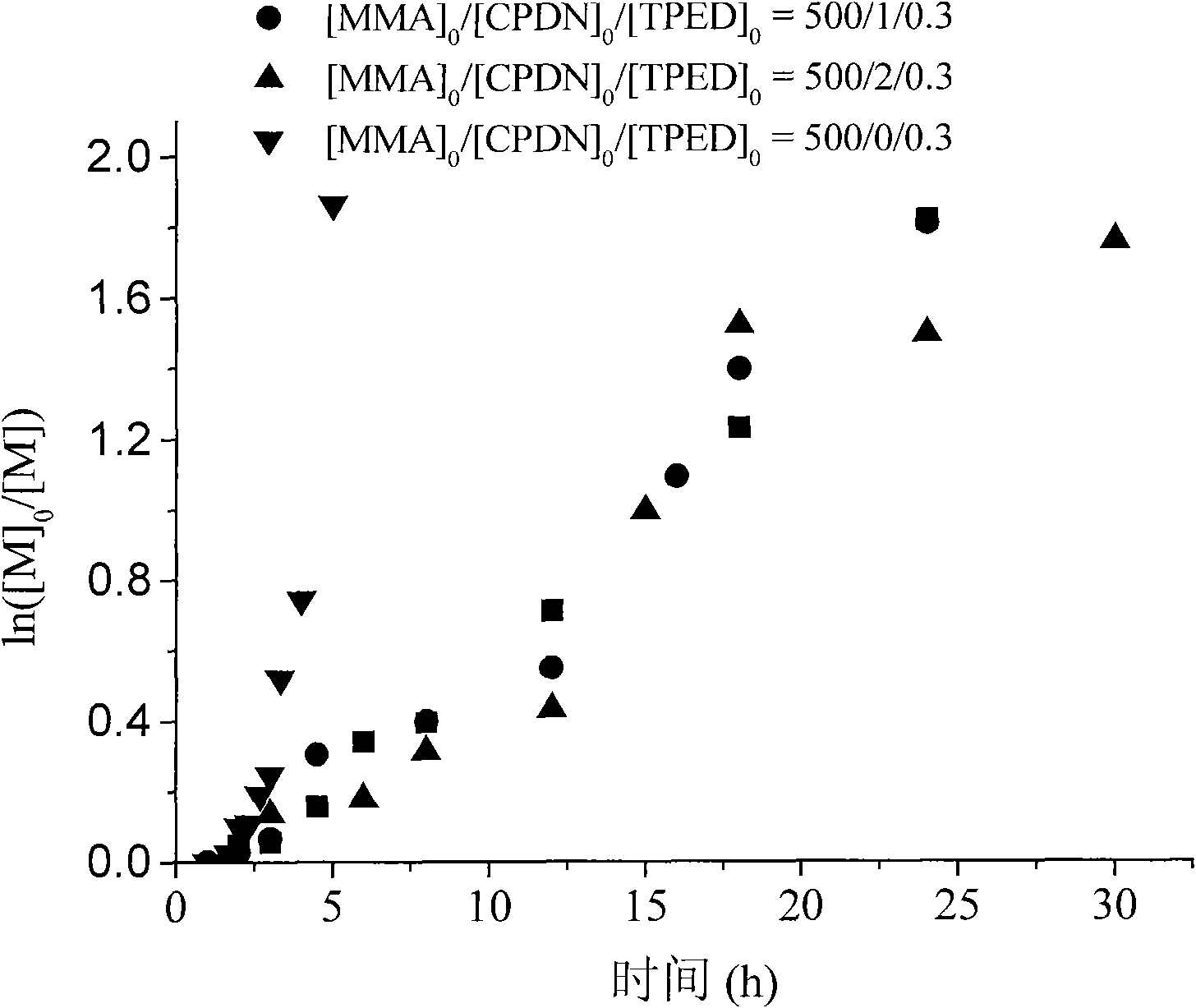
Application of 1,1,2,2-tetraphenylethylene glycol used as RAFT polymerization initiator
The invention discloses a new application of 1,1,2,2-tetraphenylethylene glycol used as RAFT polymerization initiator. The method of using 1,1,2,2-tetraphenylethylene glycol as RAFT polymerization initiator comprises the following steps: using monomer, initiator and chain transfer agent to form RAFT polymerization system in inert atmosphere and performing RAFT polymerization at 80-115 DEG C whilecontrolling the polymerization time to control the molecular weight of polymerization product. The molar ratio of monomer to initiator and chain transfer agent is 500:0.1-1:0.5-2, the chain transfer agent is one of CPDB and CPDN and the monomer is oil-soluble monomer corresponding to the chain transfer agent.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
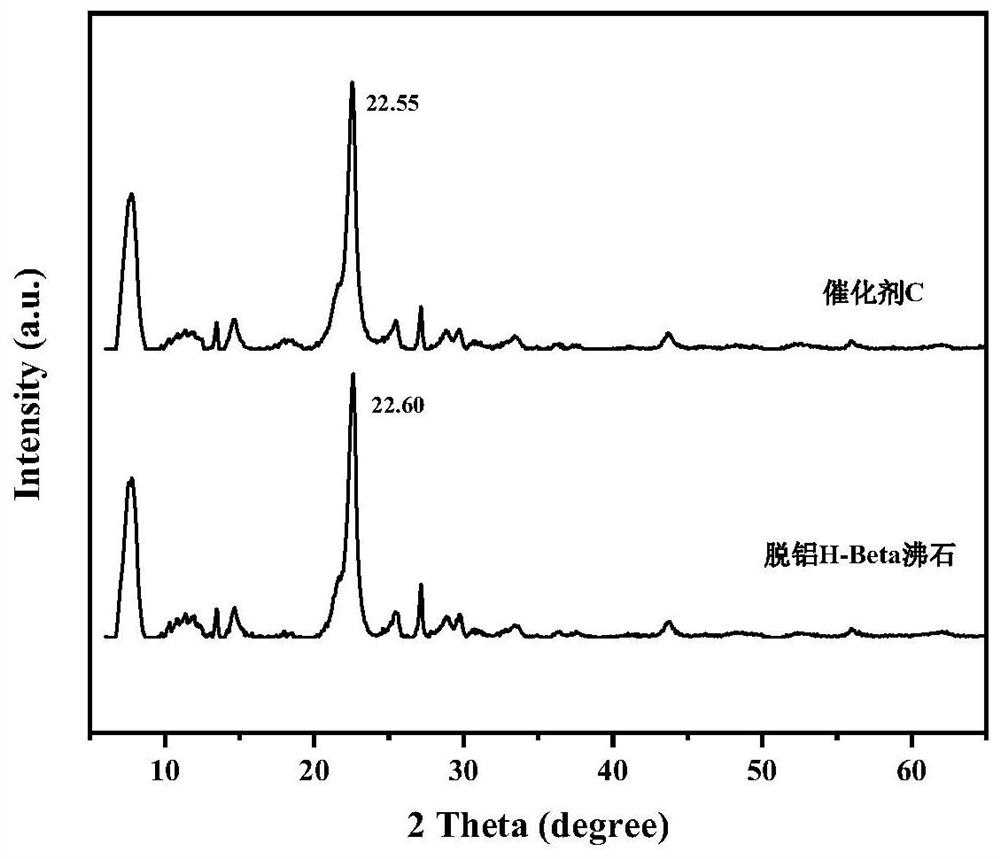
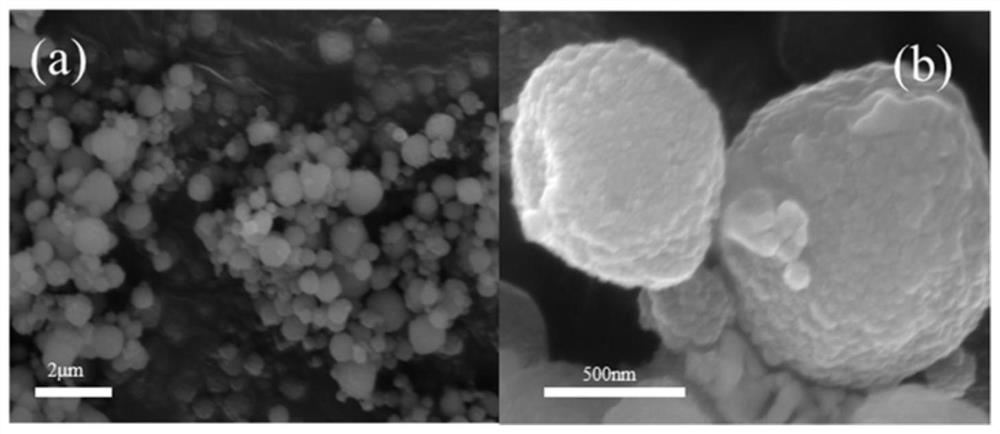
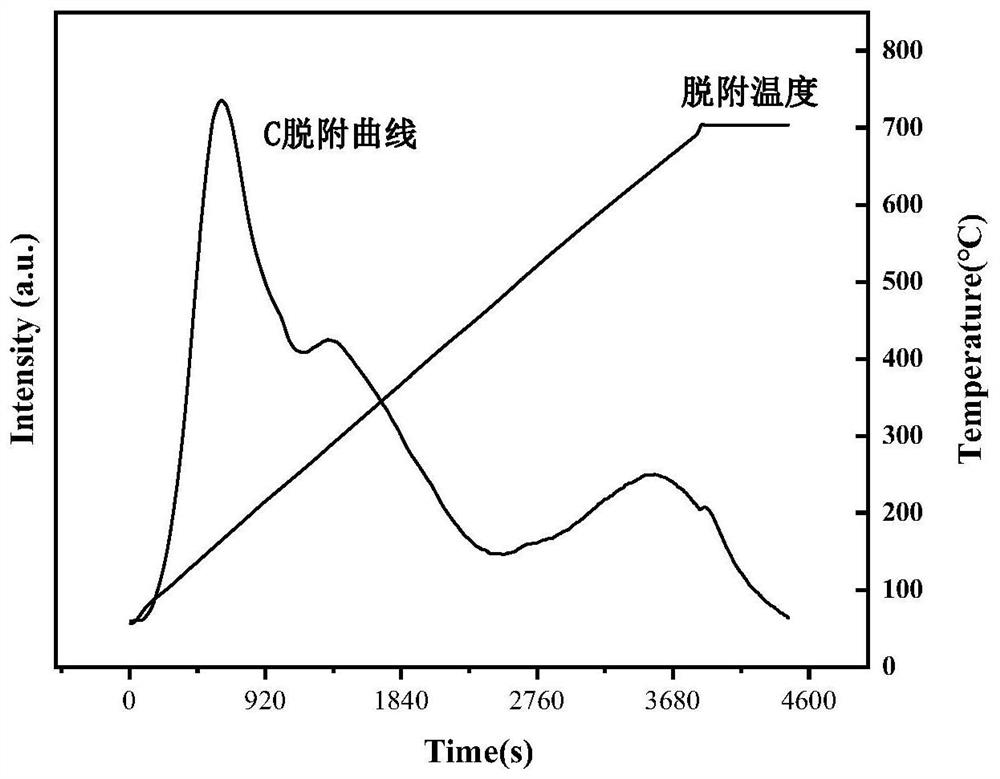
Biomass oxidative cracking catalyst based on modified H-Beta molecular sieve and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN113070096AIncrease the areaStrong ion exchangePreparation by oxidation reactionsMolecular sieve catalystsMolecular sievePtru catalyst
The invention discloses a biomass organic molecule oxidative cracking catalyst based on a modified H-Beta molecular sieve as well as a preparation method and application thereof. A metal component with better catalytic activity on ortho-diol is selected to be subjected to ion exchange with dealuminated H-Beta zeolite, so that the active component enters a framework of a dealuminated molecular sieve to serve as Lewis acid and an adsorption site in a reaction process, furthermore, the cracking activity and the reaction selectivity of the catalyst are effectively improved by utilizing the valence change of the metal ions and the synergistic effect of the metal ions and the H-Beta carrier, and the efficient and reusable catalyst meeting the ortho-diol C-C bond breakage is constructed. The prepared catalyst is used for the oxidative cracking reaction of phenyl glycol, the conversion rate of phenyl glycol is high, the yield of the oxidative cracking product reaches 95% or above, and the catalyst has unique advantages in the oxidative cracking reaction of biomass organic molecules.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Waterborne polyurethane and synthetic method thereof
The invention relates to waterborne polyurethane and a synthetic method thereof, belonging to the technical field of high polymer material. The material is polyurethane with a main chain inserted intohydrophilic vinyl monomers, and the raw materials adopted in the method of the invention comprise benzophenone, isopropanol, polymeric diol, diisocyanate, itaconic acid and vinyl pyrrolidone. The method comprises the following steps: firstly mixing the raw materials, then adding a first catalyst and reacting under ultraviolet irradiation to obtain product 1,1,2,2-tetraphenylglycol, then purifyingthrough the recrystallization with acetic acid, adding solvent after mixing, stirring and mixing to react and obtain prepolymer; then adding 1,1,2,2-tetraphenylglycol to mixing, adding a second catalyst to obtain a reactant, purifying to obtain polyurethane with terminal groups containing tetraphenylglycol, mixing the obtained polyurethane with the prepolymer to react, and purifying to obtain thewaterborne polyurethane material. The synthetic method of the invention is simple and easy to realize and the synthetic waterborne polyurethane can be used in the fields of coatings, bonding adhesives and elastomeric materials.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com