A shale intercalation inhibitor prepared from branched tertiary amine type polyamine with ultralow molecular weight
A molecular weight, tertiary amine type technology, applied in the preparation of amino compounds from amines, organic chemistry, drilling compositions, etc., can solve problems such as the limitation of inhibition performance, and achieve improved inhibition performance, reduced probability of occurrence, and good water solubility. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Diethylenetriamine and dimethylallylamine are used as raw materials to prepare ultra-low molecular weight branched tertiary amine polyamines by step-by-step synthesis, and the specific steps are as follows:
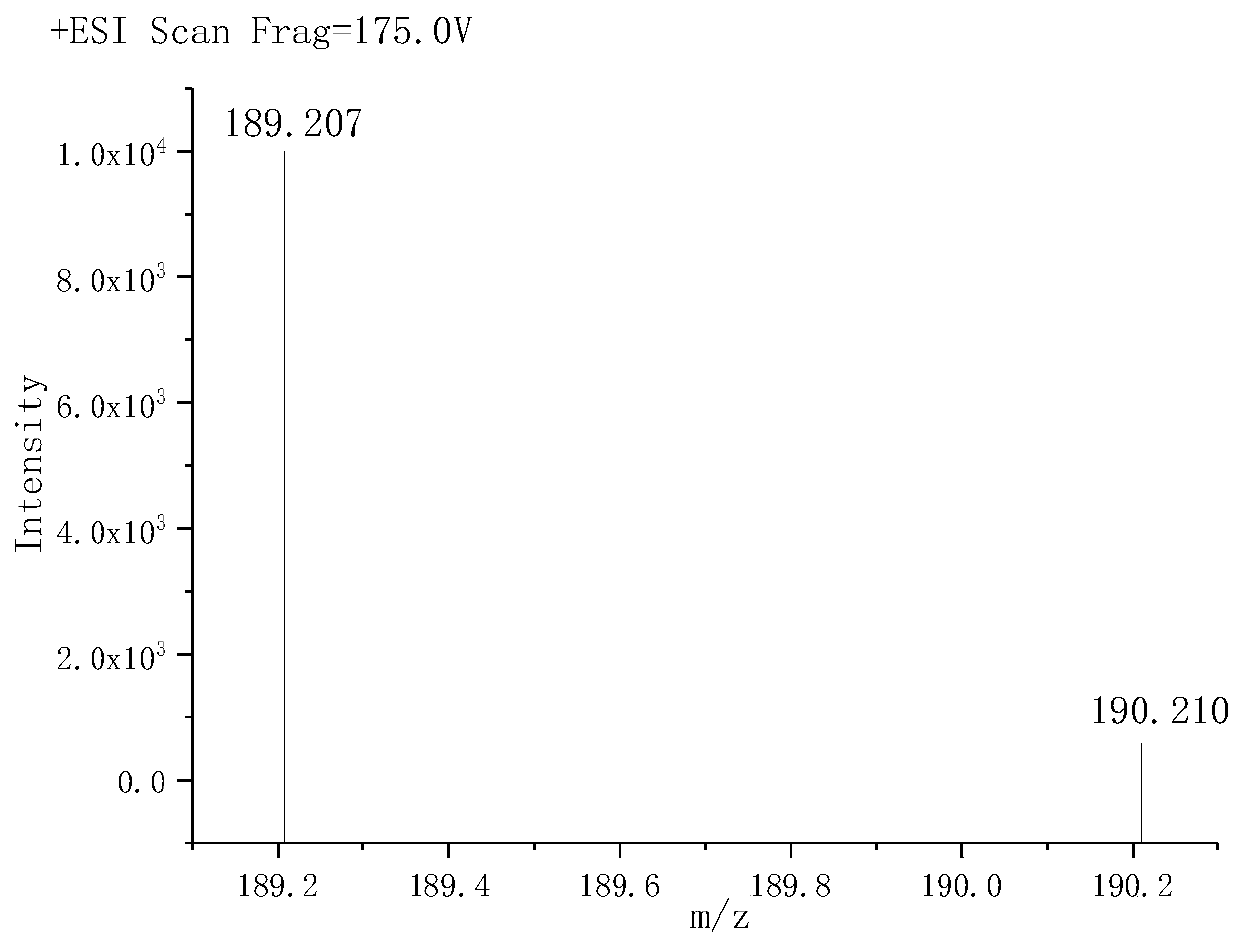
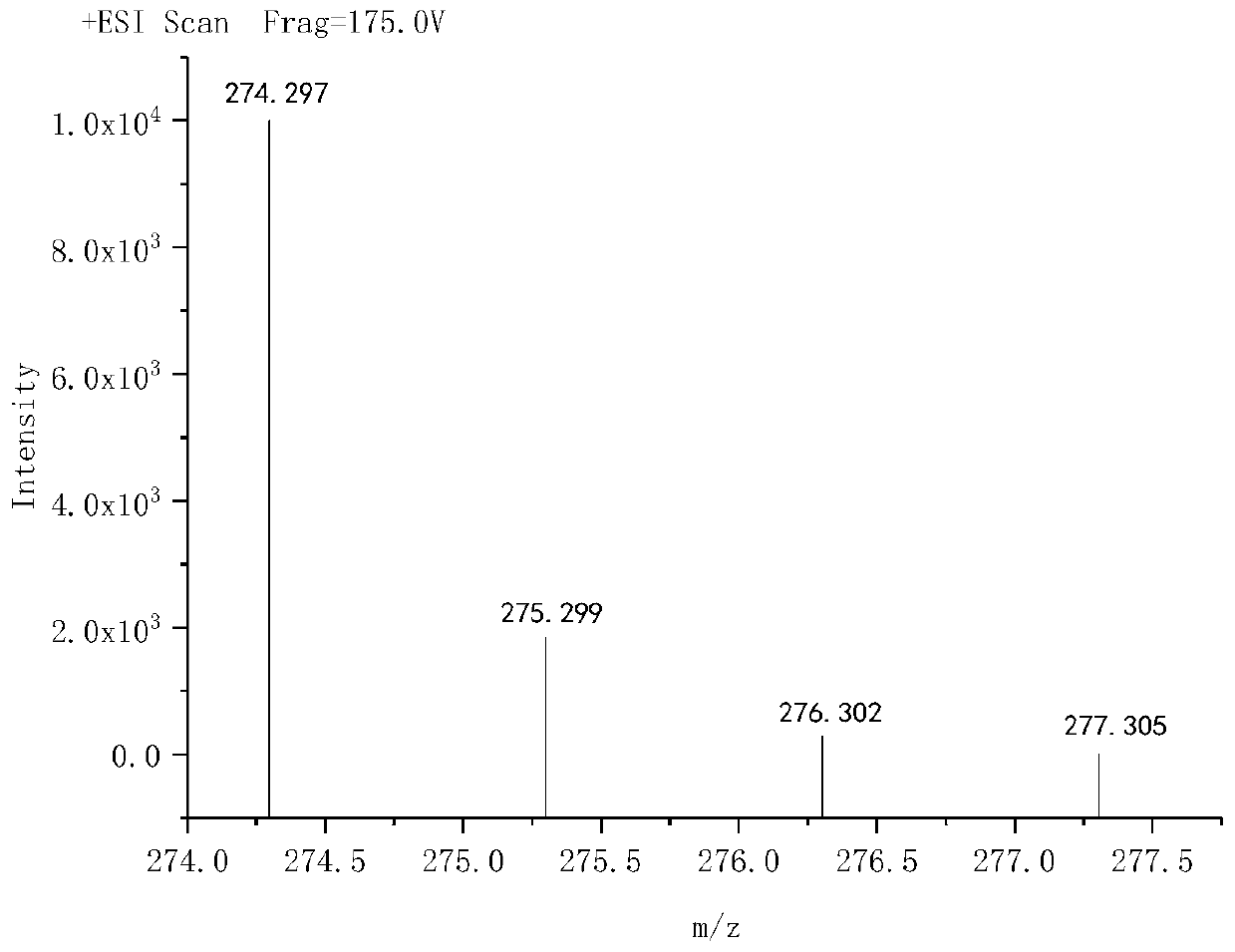
[0036] (1) Synthesis of G1 ultra-low molecular weight branched tertiary amine polyamine: Accurately weigh 0.1 mole of diethylenetriamine and 0.1 mole of dimethylallylamine and dissolve them in 80 mL of anhydrous methanol respectively, and diethylenetriamine Transfer the methanol solution of dimethyl allylamine to a round bottom flask, and slowly add the methanol solution of dimethylallylamine into the round bottom flask with a constant pressure separatory funnel at 25°C and stir. After the dropwise addition, heat up Heat to reflux for 8 hours at 95°C. After the reaction, use a rotary evaporator to evaporate the solvent at 105°C and an absolute vacuum of less than 3000Pa to obtain G1 ultra-low molecular weight branched tertiary amine polyamine. The molecular formula...
Embodiment 2
[0047] Using diethylenetriamine and dimethylallylamine as raw materials, a one-pot method is used to prepare ultra-low molecular weight branched tertiary amine polyamines. The specific steps are as follows
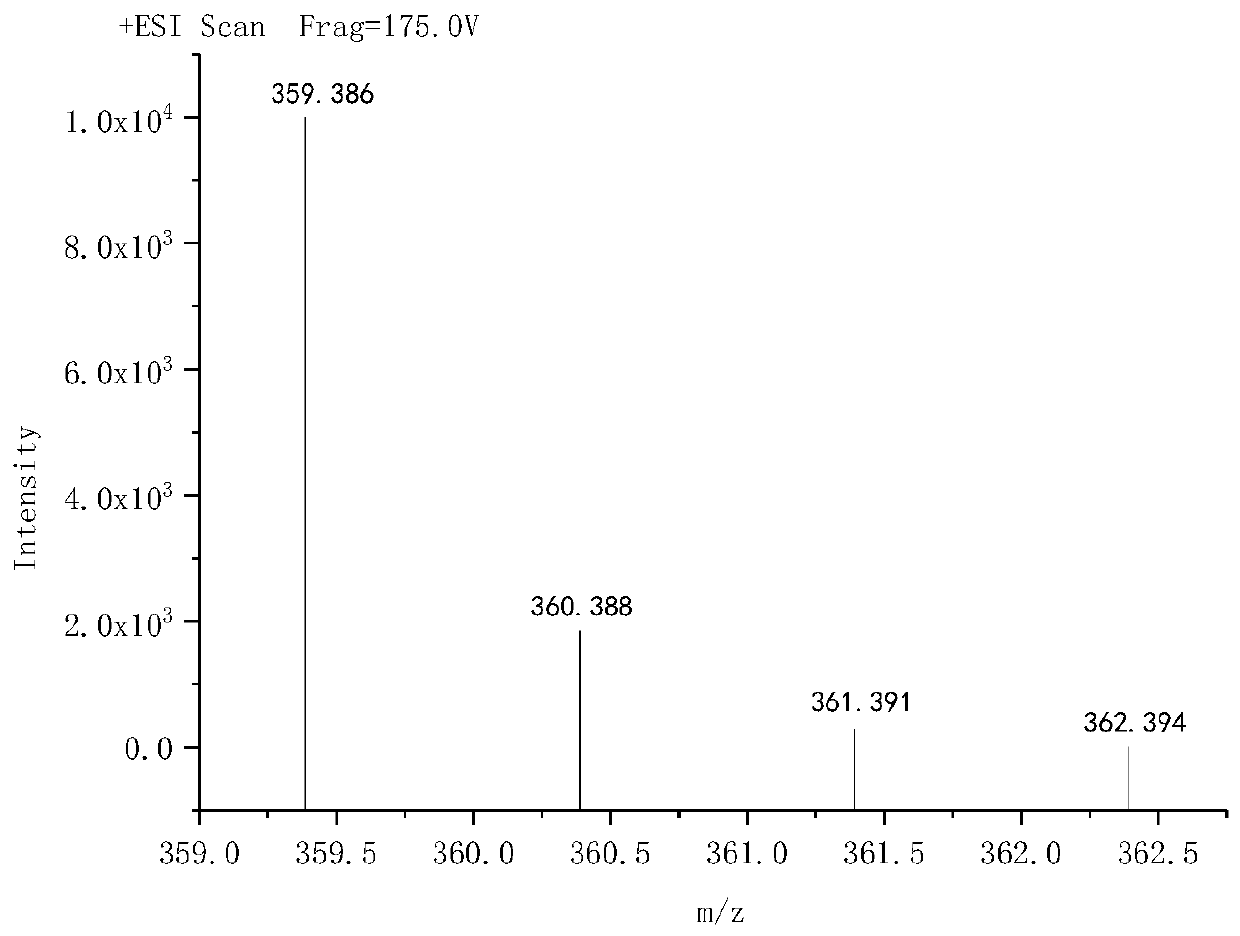
[0048] Accurately weigh diethylenetriamine and dimethylallyl with a molar ratio of 1:5 and dissolve them in 100mL of anhydrous methanol, and the diethylenetriamine is 0.1 mole, and the dimethyl The methanol solution of allylamine was added dropwise to the methanol solution of diethylenetriamine. After the dropwise addition, the temperature was raised to 100°C, and the reaction was heated under reflux for 12 hours. Distill under reduced pressure and evaporate the solvent to obtain G5 ultra-low molecular weight branched tertiary amine polyamine. Molecular formula of G5 ultra-low molecular weight branched tertiary amine polyamine: Molecular formula of G5 ultra-low molecular weight branched tertiary amine polyamine: C 29 h 68 N 8 , exact molecular weight: 528.557, molar mas...
Embodiment 3
[0051] Using ethylenediamine and dimethylallylamine as raw materials, the ultra-low molecular weight branched tertiary amine polyamine is prepared by a step-by-step synthesis method, and the specific steps are as follows:
[0052] (1) Synthesis of G1 ultra-low molecular weight branched tertiary amine polyamine: Take 0.1 mole of ethylenediamine and 0.1 mole of dimethylallylamine and dissolve them in 80 mL of anhydrous methanol respectively, transfer the methanol solution of ethylenediamine to Add the methanol solution of dimethylallylamine to the round bottom flask at 25°C using a constant pressure separatory funnel slowly into the round bottom flask and stir. After the dropwise addition, heat up to 95°C. Heat to reflux for 8 hours. After the reaction is completed, use a rotary evaporator to evaporate the solvent at 105° C. and an absolute vacuum of less than 3000 Pa to obtain G1 ultra-low molecular weight branched tertiary amine polyamine. The molecular formula of G1 ultra-low...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com