Radiation sensitive gene marker and application thereof in identifying low LET ray radiation
A genetic marker and radiation-sensitive technology, applied in the field of radiation biological radiation type detection, can solve the problem of inability to completely block X-rays
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
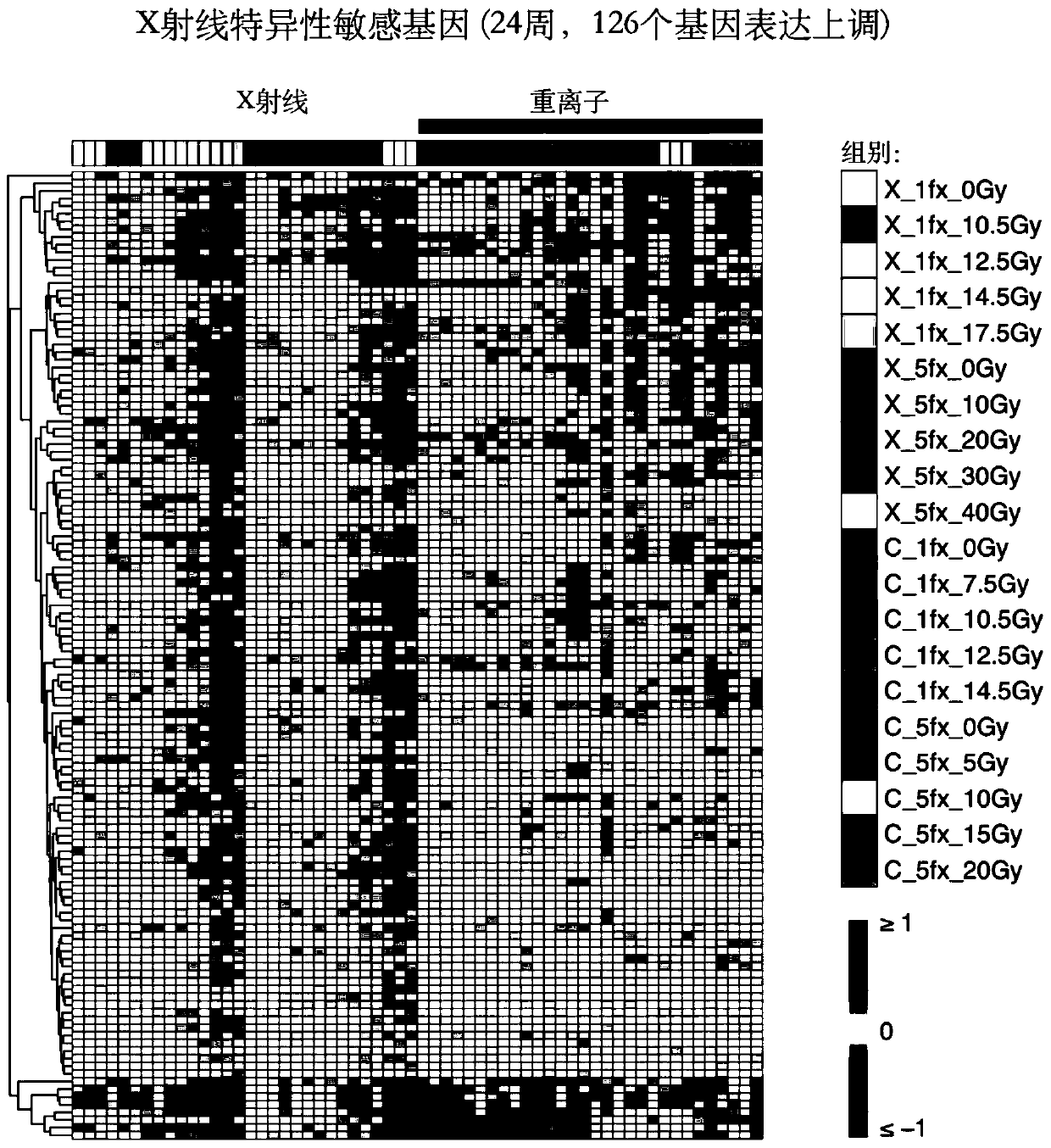
[0058] Example 1 Screening and Obtaining of Radiation Sensitive Gene Markers
[0059] 1. Animal experiment irradiation and grouping: 8-10 weeks old C57BL6 female mice, SPF rearing, and feeding conditions are: temperature (23±1)℃, relative humidity 55%±5%, pressure difference ≤10Pa, daily Light for 12h, and eat and drink freely.
[0060] 2. After induction of anesthesia by isoflurane before irradiation, transfer to a dedicated mouse chest irradiation device and fix it properly. X-ray and heavy ion (carbon-ions) rays are used to irradiate the whole lung field. X-ray is one of the representatives of low LET rays, which is irradiated after being accelerated by a medical linear accelerator (energy 6-10MV). As the main representative of high LET rays, heavy ion rays are carbon particle beams (energy 280MeV) that are accelerated by a cyclotron (20-30 meters in diameter) and then discharged, with extremely high energy and speed.
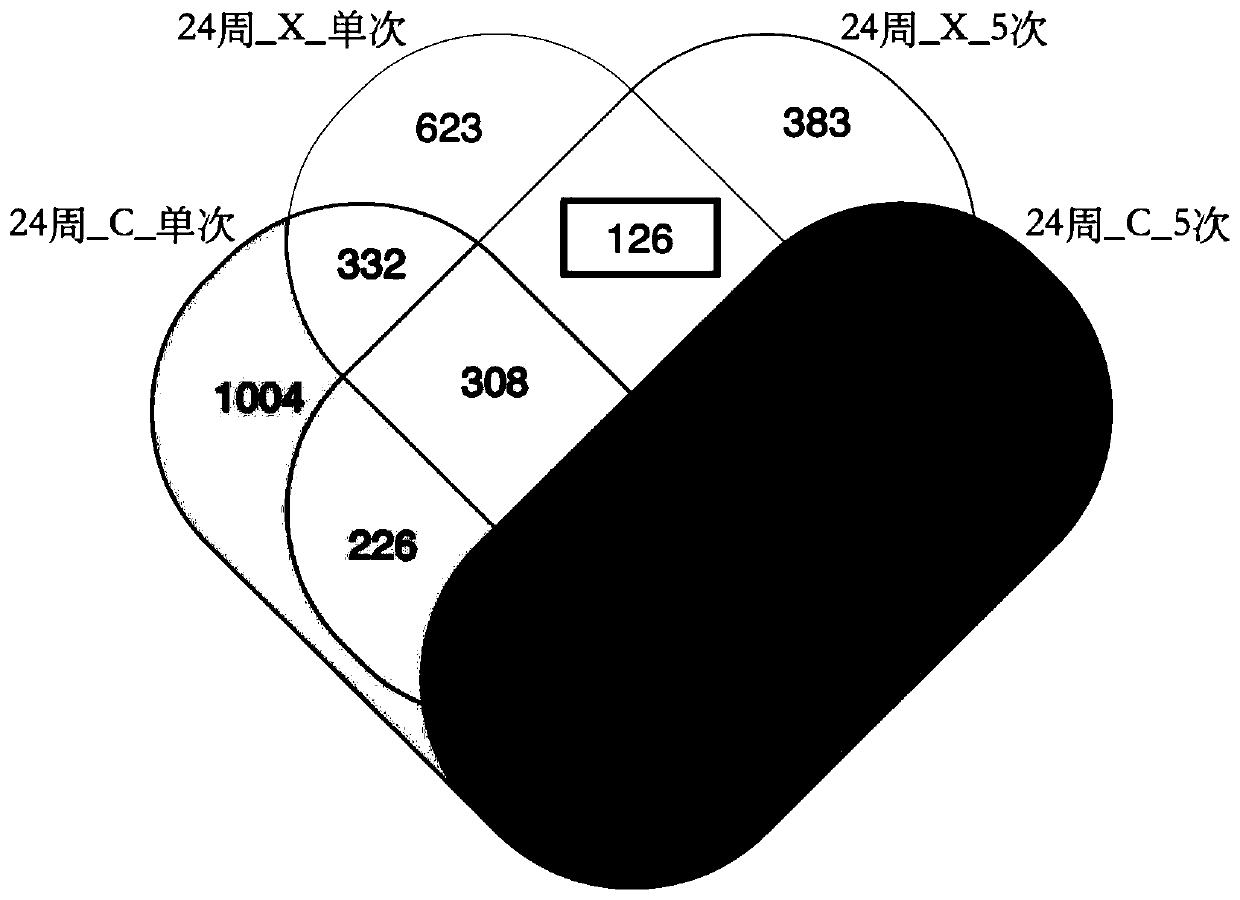
[0061] 3. Irradiation and grouping include X-ray gradient ...
Embodiment 2
[0089] This implementation provides the application of the radiation sensitive gene markers screened in Example 1 in identifying low LET radiation.
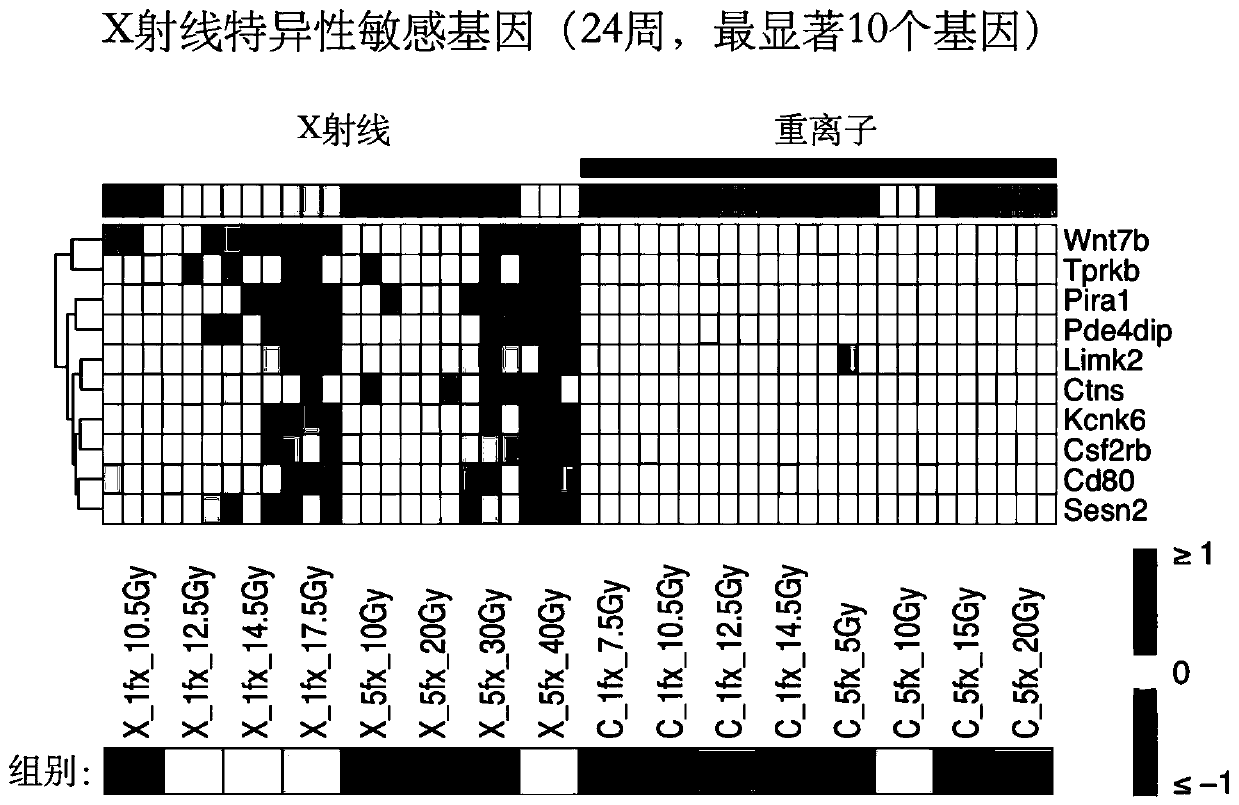
[0090] See Figure 4 , The expression multiples of 10 genes after gradient-dose X-rays and carbon ion beams were irradiated. There was almost no radiation response in the heavy ion beam irradiation group.
[0091] See Figure 5 , The difference in gene expression values of 10 genes under gradient dose X-ray and carbon ion radiation for 24 weeks, the difference was statistically significant (P <0.0001).
[0092] See Image 6 , Receiver operating characteristic curve (receiver operating characteristic curve, ROC) graph, 10 genes in the gradient dose X-ray, carbon ion radiation after the average gene expression of the X-ray identification ability. The area under the curve (AUC) is equal to 0.984, the 95% confidence interval (Confidence interval, CI) is 0.952–1.000, and when the average expression of the above 10 genes is equal to 1.033,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com