Method for detecting aquatic product pathogenic microorganisms based on random amplifying and labelling and in-situ synthesized microfluid chip
A pathogenic microorganism, microfluidic chip technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial determination/inspection, resistance to vector-borne diseases, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0049] Embodiment 1, using the random amplification labeling method and in-situ synthesis of microfluidic chips, using "cultured large yellow croaker" 1# as the sample to be tested, detecting the pathogenic microorganisms carried by it, and performing the following steps in sequence:
[0050] 1) Design of chip probes for detection of aquatic pathogenic microorganisms:
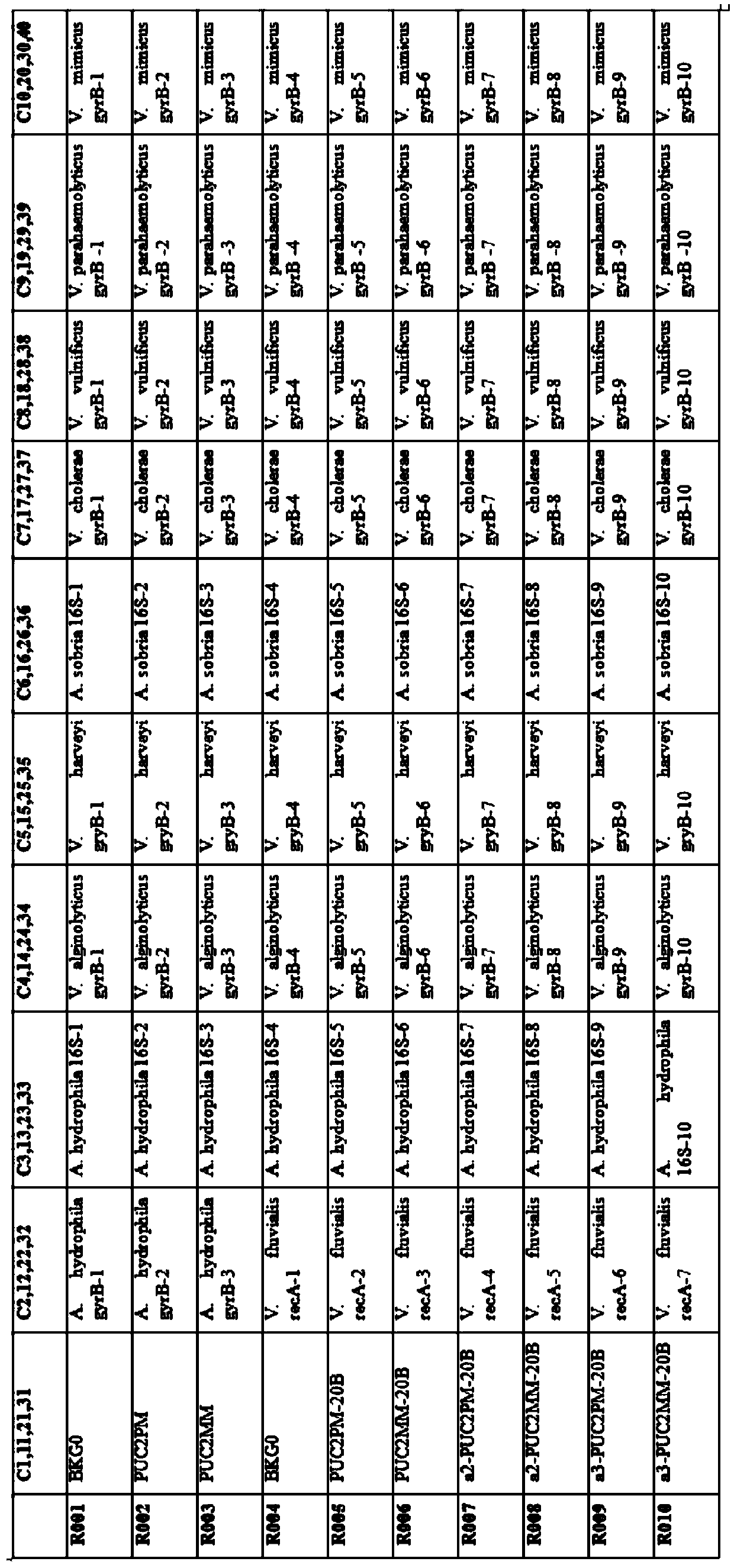
[0051] 895 oligonucleotide probes (including 42 quality control probes, ie, including 42 positive / negative control probes) as described in Table 1 were designed; each probe was repeated 4 times.
[0052] 2), preparation of oligonucleotide chip
[0053] Prepare oligonucleotide chips:
[0054] Chemically modified oligonucleotide probe sequences are sequentially synthesized on the aldehyde-modified glass slide, and the arrangement of the probes on the chip is as follows: figure 1 Shown (arranged randomly).
[0055] Perform fluorescence analysis on the synthesized chip on a chip scanner to detect the fluorescenc...
Embodiment 2
[0076] Embodiment 2, using the above-mentioned random amplification labeling method and in-situ synthesis of microfluidic chips, with "cultured Penaeus vannamei" 2# as the sample to be tested, the pathogenic microorganisms carried by it are detected, and the following steps are carried out in sequence:
[0077] Replace the "cultured large yellow croaker" 1# sample in Example 1 with the 0.2g shrimp meat sample, and all the other are equal to Example 1.
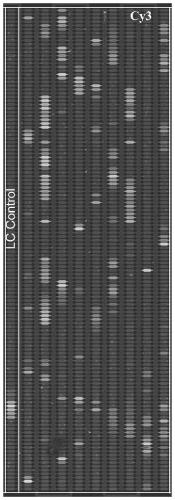
[0078] The end result is as image 3 As shown, Vibrio alginolyticus, Aeromonas hydrophila, Aeromonas temperatus, white spot disease virus and infectious subcutaneous and hematopoietic tissue necrosis virus were detected in "Cultured Penaeus vannamei" 2#; The gyr B, rec A and dna J genes of Vibrio algae were detected, and the number of detected probes accounted for 47.36% (9), 50% (10) and 30% of the probes designed for these genes, respectively. % (6 entries). The 16S rRNA and gyr B genes of Aeromonas hydrophila were detected...
Embodiment 3
[0081] Embodiment 3, using the above-mentioned random amplification labeling method and in-situ synthesis of microfluidic chips, the pathogenic microorganisms carried by the cultured fish samples purchased randomly on the market are detected, and the following steps are carried out in sequence:
[0082] Take 0.2g sample and extract the total DNA / RNA using a commercial DNA / RNA extraction kit. The gene fragments of pathogenic microorganisms were labeled with Cy3 by random amplification labeling method, and the pathogenic microorganisms carried by them were detected after hybridization with microfluidic chips. Use chip analysis software to obtain the fluorescence signal intensity and standard error of each probe. When the hybridization results of chip quality control probes and positive / negative control probes are correct, we believe that the hybridization process is correct and the chip results are credible. For each detected gene, when the signal intensity of more than 3 probes...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com