Aluminum-graphite-carbide composite
A carbide and composite technology, applied in the field of composites, can solve the problems of not easy high thermal conductivity composites, etc., and achieve the effect of improving fragility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
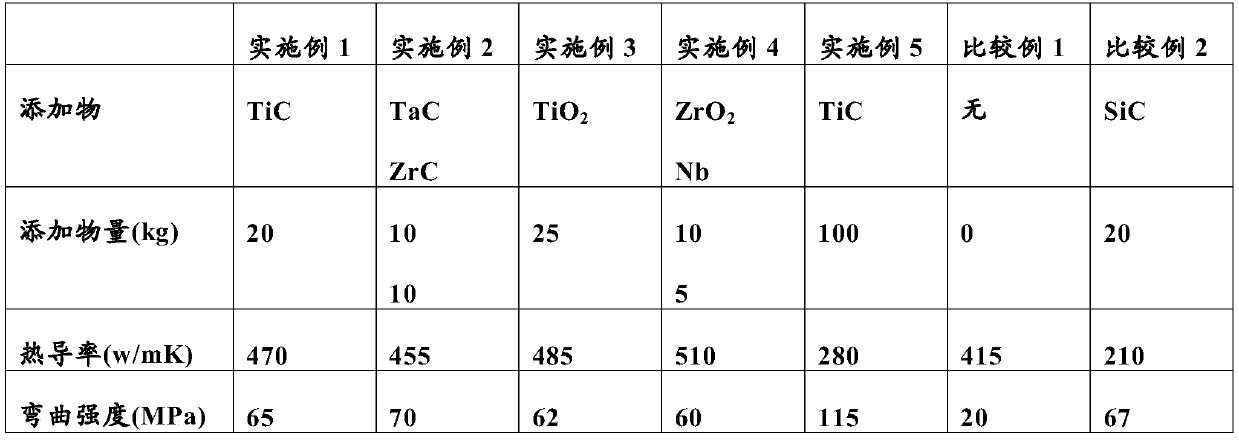
[0059] Add 20 kg of titanium carbide powder with an average particle size of 1.5 μm and 10 μm of 99% powder into 100 kg of 1 mm undersize of petroleum-based needle coke, put it into a mixer kept at 130 ° C, and slowly add asphalt to obtain Pasty substance.
[0060] The obtained paste-like substance was put into a container maintained at 130° C., and extruded with a die having a square shape of 150 mm in length and 200 mm in width.
[0061] The extrudate was calcined at 1300°C for 12 hours in a non-oxidizing atmosphere, put the calcined product into a pitch tank at 200°C, covered and sealed, and applied a pressure of 0.5 MPa to carry out pitch impregnation.
[0062] After repeating the aforementioned pitch impregnation and subsequent firing at 1300°C three more times, a sample of the obtained carbon-titanium carbide molded body was cut out, and the proportion of voids was measured, and it was 19.4%.
[0063] The formed body of carbon-titanium carbide obtained above was fired a...
Embodiment 2
[0066] Using 10 kg of tantalum carbide and 10 kg of zirconium carbide instead of the titanium carbide of Example 1, a sample piece of the same size was produced from the composite in the same manner.
Embodiment 3
[0068] A composite was produced in the same manner as in Example 1 except that 25 kg of titanium oxide was added instead of the titanium carbide. Small pieces were cut out of it, finely pulverized with a mortar, and analyzed by X-ray diffraction. As a result, only graphite and titanium carbide were detected. A sample piece of the same size was also fabricated from this composite.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| voidage | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com