Method for detecting lytic polysaccharide monooxygenase enzyme activity and application thereof
A monooxygenase enzyme activity, polysaccharide monooxygenase technology, applied in the field of biology, can solve the problems of unstable ascorbate, unsuitable for non-purified samples, etc., and achieve short detection time, high sensitivity and low background. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] Experimental parameters for the determination of the activity of soluble polysaccharide monooxygenase:
[0025] (1) In a 200 μL reaction system, prepare the following enzyme activity reaction system:
[0026] 100mMPIPES buffer 50μL
[0027] Active substrate (10-acetyl-3,7-dihydroxyphenoxazine) 10μM
[0028] Coenzyme (horseradish catalase) 30U / ml
[0029] Carrier Disintegration Solution / Crude Enzyme Solution 100μL
[0030] Deionized water to 200μL
[0031] The carrier breaking solution / crude enzyme solution is derived from recombinant Escherichia coli BL21Gold(DE3)-pET28a capable of cloning and expressing soluble polysaccharide monooxygenase.
[0032] (2) Detection conditions: excitation wavelength 560nm, emission wavelength 590nm, detection temperature 30°C.
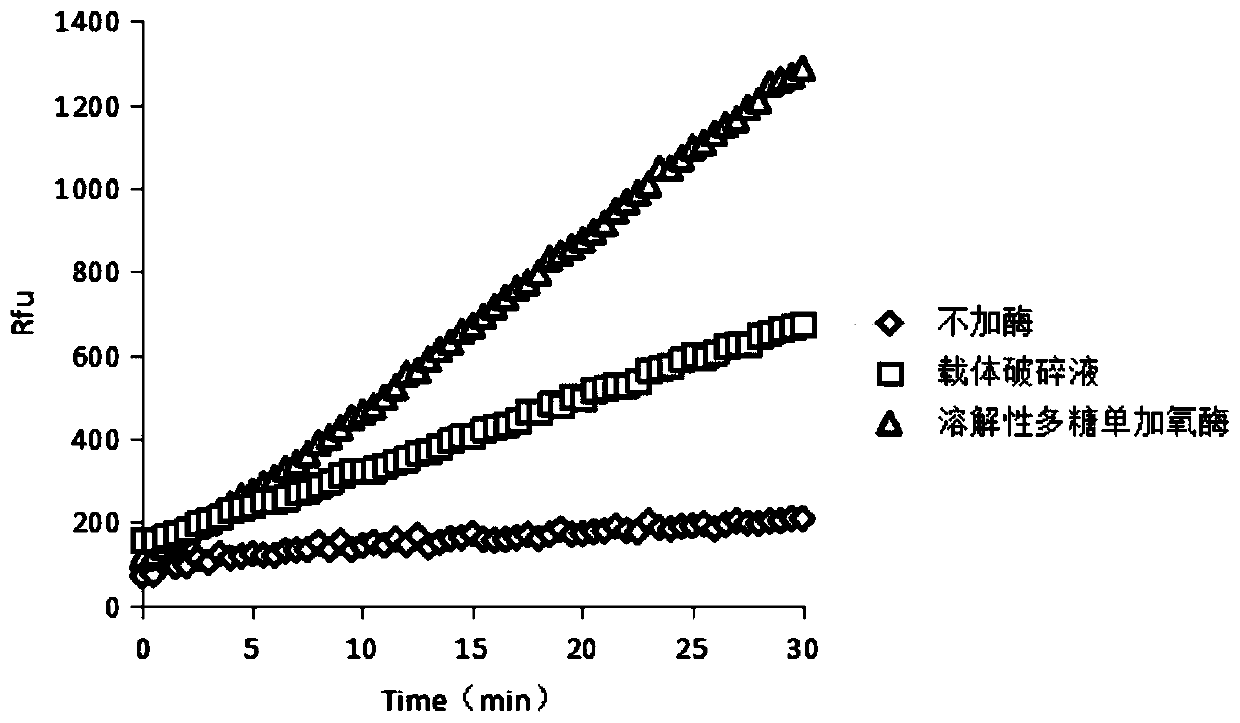
[0033] From figure 1 It can be seen from the curve that when no enzyme is added, the emission peak does not change, indicating that there is no intermolecular interaction between the systems. When the empty...
Embodiment 2
[0035] Construction of the Standard Curve of Enzyme Concentration and Fluorescence Intensification Rate of Soluble Polysaccharide Monooxygenase
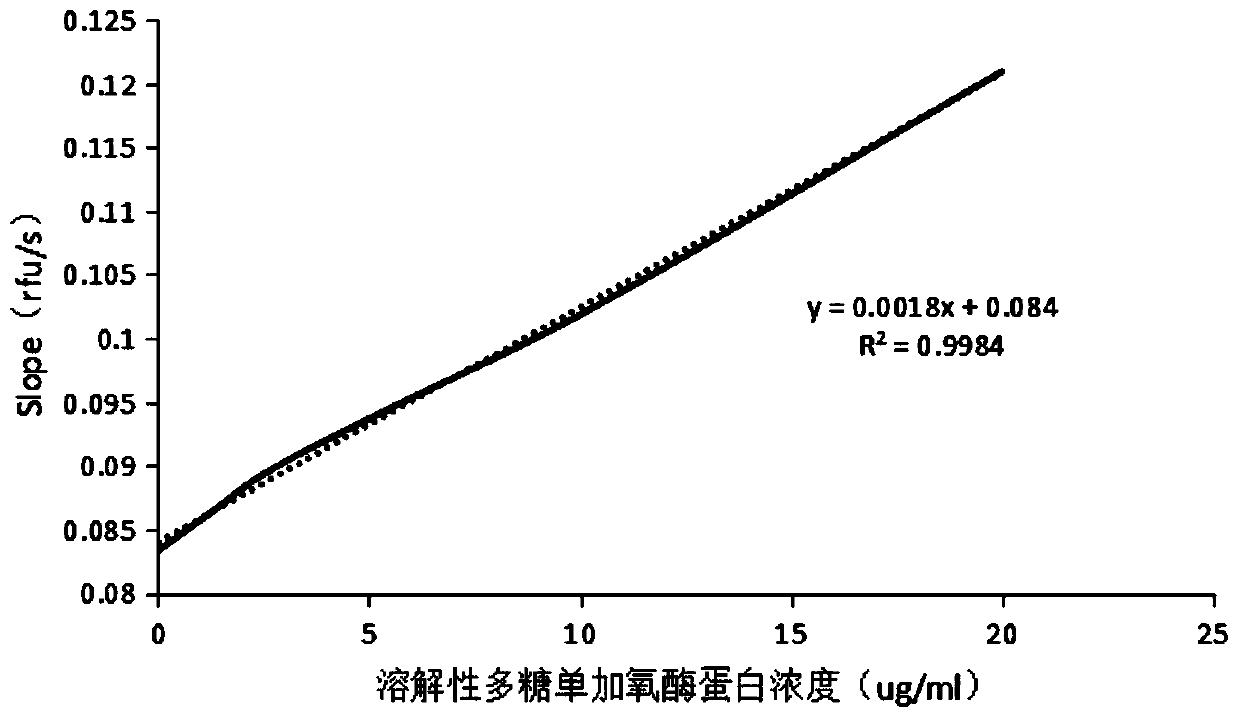
[0036] Add different volumes of soluble polysaccharide monooxygenase into 2mL centrifuge tubes, and dilute to 1000μL with ultrapure water. The final concentration of enzyme protein is: 0μg / mL, 1.25μg / mL, 2.5μg / mL, 5μg / mL, 10μg / mL, 20μg / mL, take 100ul into 96-well ELISA plate, add substrate 10-acetyl-3,7-dihydroxyphenoxazine (final concentration 10uM) and coenzyme horseradish catalase (final concentration 30U / ml), measure its fluorescence intensity at 30°C; take the concentration of soluble polysaccharide monooxygenase as the abscissa, and the rate of fluorescence enhancement as the ordinate to plot the activity of soluble polysaccharide monooxygenase standard curve (such as figure 2 shown).
[0037] figure 2 It shows that with the increase of the soluble polysaccharide monooxygenase enzyme concentration, the fluorescence enhanc...
Embodiment 3
[0039] Inhibitory effect of EDTA on soluble polysaccharide monooxygenase
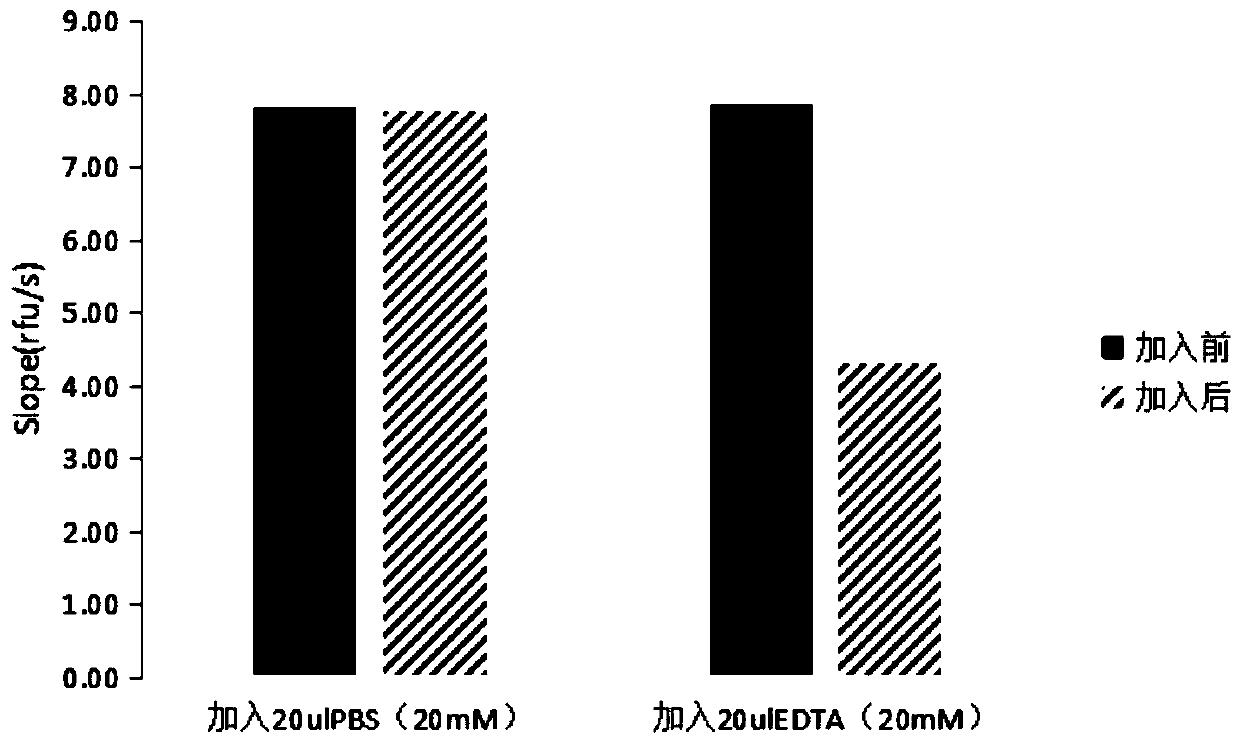
[0040] Take 2 parts of 100ul soluble polysaccharide monooxygenase and add coenzyme horseradish catalase (final concentration 30U / ml) and substrate 10-acetyl-3,7-dihydroxyphenoxazine (final concentration 10uM) In the reaction system of , marked as reaction 1 and reaction 2, the rate of fluorescence enhancement was measured. After 10 min, 20ulPBS (20mM) buffer was added to reaction 1, and 20ulEDTA (20mM) was added to reaction 2, and the fluorescence enhancement rate was measured.
[0041] From image 3 The change of fluorescence rate shows that PBS buffer has no effect on the reaction, and EDTA can inhibit the activity of soluble polysaccharide monooxygenase.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com