Method for identifying and detecting 5-hydroxymethyl cytosine and 5-formyl cytosine in DNA
A technology of hydroxymethylcytosine and formylcytosine, which is applied in the field of identification and detection of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine and 5-formylcytosine in genomic DNA, can solve the problem of cumbersome steps, expensive equipment, and damage to biological tissues environment and other problems, to achieve the effect of simple steps and high sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
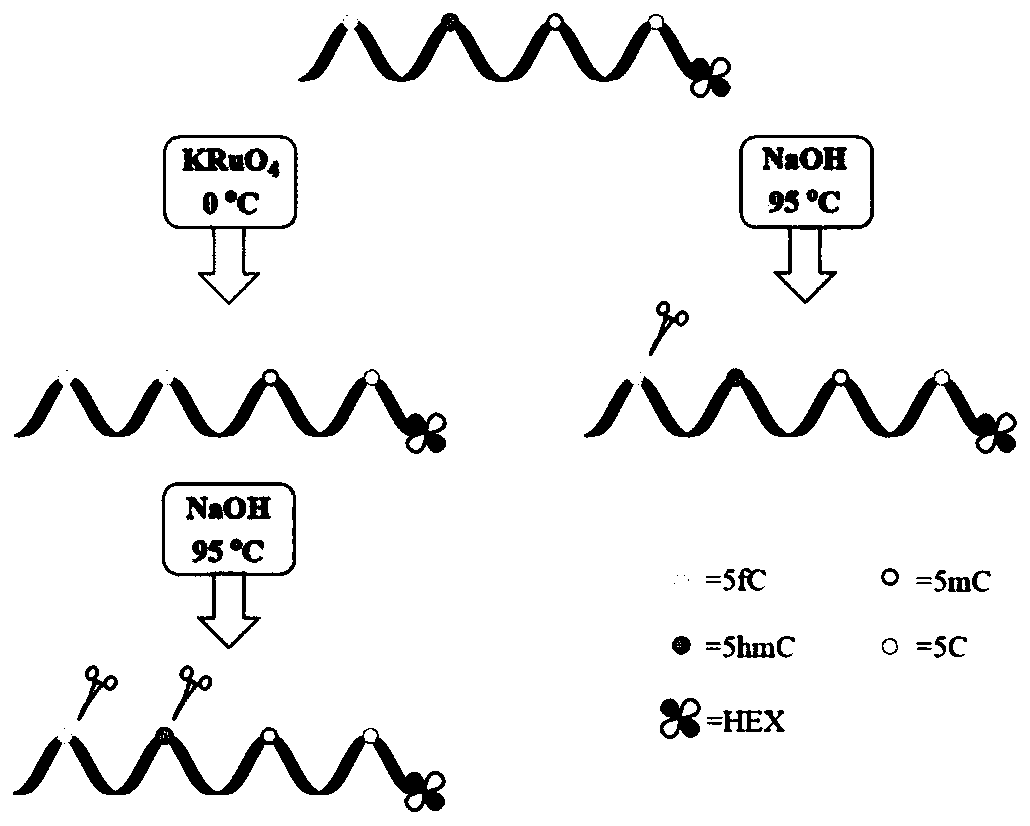
[0044] This example is the detection of sequences containing cytosine, 5-methylcytosine and 5-hydroxymethylcytosine at different positions.
[0045] 1. The oligonucleotide HEX-31mer-hmC17 (X=5hmC) whose sequence is 5'-TAATTGCGGTCAATTG(X)GGATCATGCGTATA-3' is used as a template for detection, and cytosine or 5-methylcytosine exists at the X site Other DNA sequences of pyrimidines (HEX-31mer-C17, X=C; HEX-31mer-mC17, X=5mC) were used as controls.
[0046] 2. Label the 5' end of the DNA sequence with 5'-hexachlorofluorescein-CE phosphoramidite (HEX). Add 200 nM of DNA to a solution containing 50 mM NaOH and 60 μM KRuO 4 The mixed solution was reacted in an ice-water bath for 60 min, the oxidized DNA sequence was purified by a small rapid spin nucleotide purification column, and the obtained DNA sequence was placed in 300 mM NaOH aqueous solution at 95 ° C for 15 min. After cooling to 4°C, a deionized formamide solution with a mass fraction of 80% was added to terminate the react...
Embodiment 2
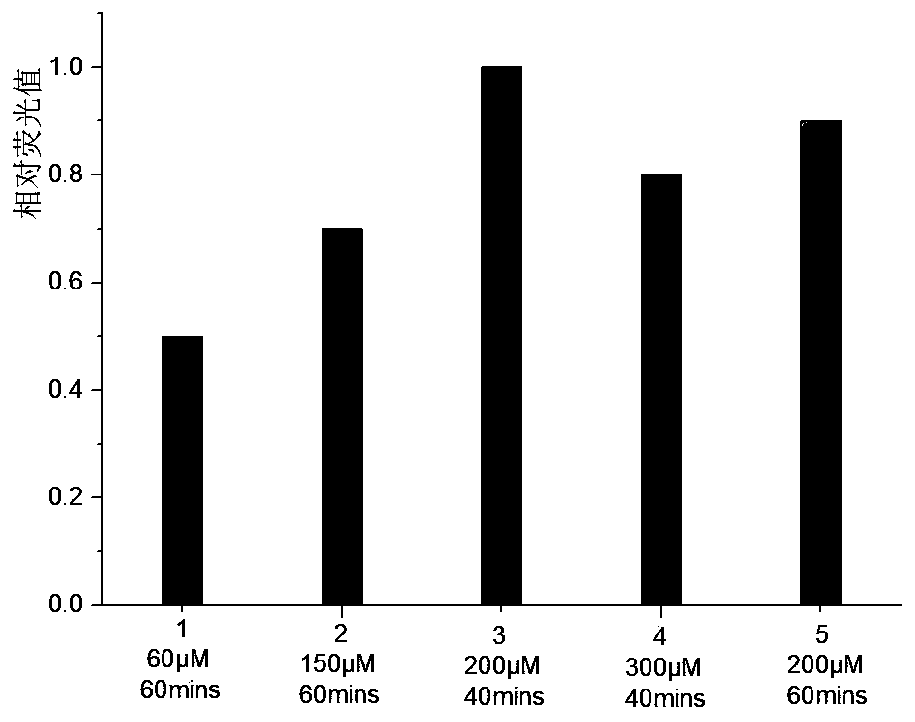
[0049] Exploring the Oxidation Reaction KRuO 4 The effect of concentration and treatment time on the cleavage efficiency of sequences containing 5-hydroxymethylcytosine sites (HEX-31mer-hmC17 containing a single 5-hydroxymethylcytosine site). Oxidation reaction in the presence of 50mM NaOH and different concentrations of KRuO 4 The mixed solution was carried out in an ice-water bath. Handle different times. The product DNA was purified by filtration through a semi-permeable membrane, and 3M NaOH stock solution was added to ensure the final alkali concentration was 300mM, and incubated at 95°C for 15min.
[0050] Results: When the oxidation reaction was carried out at 200 μM KRuO 4 Carry out 40min in middle and then carry out thermo-alkali reaction, cracking efficiency is the highest ( image 3 ). Higher concentration of KRuO 4 or longer reaction times will result in fewer cleavage products.
Embodiment 3
[0052] This embodiment is used for the detection of sequences with multiple 5-hydroxymethylcytosine sites.
[0053] 1. The oligonucleotide HEX-31mer-hmC17 (X=C, Y=5hmC, Z=C), HEX- 31mer-hmC17-hmC26 (X=C, Y=5hmC, Z=5hmC) and HEX-31mer-hmC7-hmC17-hmC26 (X=5hmC, Y=5hmC, Z=5hmC) were used as templates.
[0054] 2. Mark the 5' ends of the three DNA sequences with HEX, and use the method in step 2 of Example 1 to process the DNA sequences.
[0055] Results: It was observed that HEX-31mer-hmC17 containing only one 5-hydroxymethylcytosine site had only one cleavage fragment ( Figure 4 band 2), and the correct length after cleavage of HEX-31mer-hmC17-hmC26 containing two 5-hydroxymethylcytosine sites can be observed in the results of denaturing polyacrylamide gel analysis ( Figure 4 Strip 4). Not approved by KRuO 4 Oxidized DNA remained intact under the same alkaline conditions and no cleavage was observed in denaturing polyacrylamide gel analysis ( Figure 4 Strips 1, 3 and 5)....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com