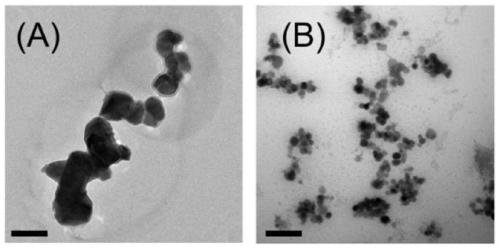
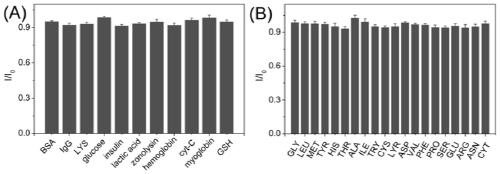
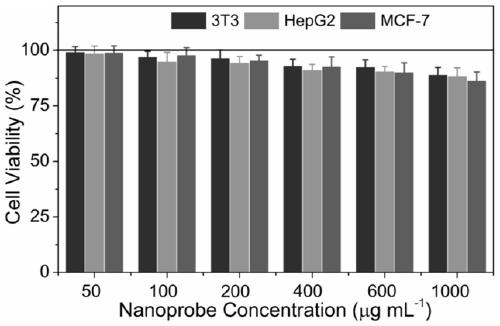
Intracellular fluorescence labeling method of food-derived probiotics and in-vivo application thereof
A labeling method and probiotic technology, applied in the research field of food-derived probiotics, can solve the problems of low sensitivity and short emission wavelength, and achieve the effects of simple steps, low cost, good stability and labeling reproducibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0055] A method for intracellular fluorescent labeling of food-derived probiotics
[0056] (1) Preparation of DNA-coated long-lasting fluorescent nanoprobes.
[0057] Mix 40mg DNA with 10mL PBS and gently stir, add 40mg EDC and 40mgNHS, stir well, react at room temperature for 30 minutes, weigh accurately, add 10mg long persistence nanoprobes (ZGGO PLNPs), react at room temperature for 30 minutes, and finally wash with PBS Wash and purify, and store away from light.
[0058] (2) Preparation of competent probiotic bacteria that are easy to ingest and accommodate foreign DNA.
[0059] Cultivate probiotics overnight at 37°C, transfer 25mL to 100mL MRS medium containing 1% glycine, culture to logarithmic phase (OD600=0.6), 4°C, use 3000g centrifugal force, centrifuge for 5min, collect the bacteria, and place on ice 10min, with 100mL pre-cooled 10mM MgCl 2 Wash once, then wash with pre-cooled 3.5mM MgCl 2 (Containing sucrose at a concentration of 925mM) solution was washed twic...
Embodiment 2
[0064] A method for intracellular fluorescent labeling of food-derived probiotics. The steps and method are basically the same as in Example 1, except that the probiotics are Bifidobacterium lactis V9, and correspondingly fluorescently labeled Bifidobacterium lactis V9 is obtained.
Embodiment 3
[0066] A method for intracellular fluorescent labeling of food-derived probiotics, the steps and method are basically the same as in Example 1, the difference is that the probiotics are Lactobacillus reuteri, and fluorescently labeled Lactobacillus reuteri is obtained accordingly.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com