Peelable porous antibacterial biological foam dressing and preparation method thereof
A bio-foam and peel-off technology, applied in local antibacterial agents, pharmaceutical formulations, drug combinations, etc., can solve the problems of reducing antibacterial and wound healing effects, secondary damage to healthy skin, unfavorable dressing replacement and peeling, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Example 1: Preparation of a porous antibacterial biofoam dressing lacking Pickering particles (comparative material: dressing #1)
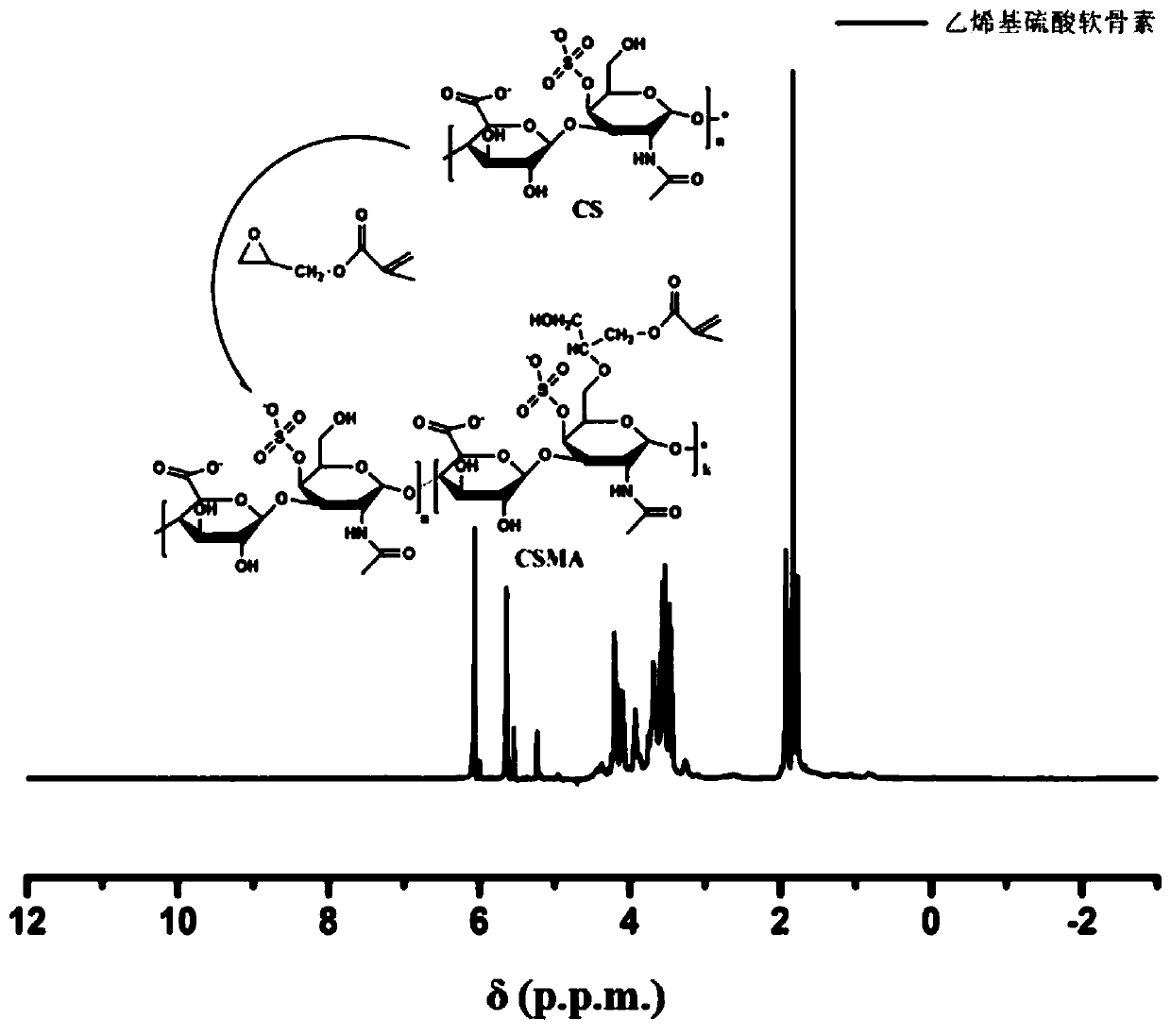
[0038] (1) Synthesis of methacrylic acid modified chondroitin sulfate (CSMA)
[0039] First, dissolve chondroitin sulfate sodium salt (CS, 5 g) in 100 mL phosphate buffered saline (PBS, pH=7.4), and then add 10 mL glycidyl methacrylate. The reaction solution was then vigorously stirred at room temperature for 15 days. The resulting product was extracted by precipitation with acetone. In order to remove residual glycidyl methacrylate, the white product was redissolved and extracted with chloroform. Finally, the aqueous phase was collected and concentrated, precipitated with acetone again, and the product was freeze-dried to obtain vinyl-modified chondroitin sulfate (CSMA), which was stored at -20°C for use.
[0040] (2) Preparation of graphene-supported zinc-doped copper oxide (Zn-CuO@GO) composite material
[0041] 0.15 g of copper acetate and 0...
Embodiment 2
[0044] Example 2: Preparation of a porous antibacterial bio-foam dressing lacking boric acid (comparative material: dressing #2)
[0045] (1) Synthesis of methacrylic acid modified chondroitin sulfate (CSMA)
[0046] First, dissolve chondroitin sulfate sodium salt (CS, 7 g) in 100 mL phosphate buffered saline (PBS, pH=7.4), and then add 10 mL glycidyl methacrylate. The reaction solution was then vigorously stirred at room temperature for 15 days. The resulting product was extracted by precipitation with acetone. In order to remove residual glycidyl methacrylate, the white product was redissolved and extracted with chloroform. Finally, the aqueous phase was collected and concentrated, precipitated with acetone again, and the product was freeze-dried to obtain vinyl-modified chondroitin sulfate (CSMA), which was stored at -20°C for use.
[0047] (2) Preparation of graphene-supported zinc-doped copper oxide (Zn-CuO@GO) composite material
[0048] 0.15 g of copper acetate and 0.055 g o...
Embodiment 3
[0051] Example 3: Preparation of porous antibacterial bio-foam dressing (bio-foam dressing #3)
[0052] (1) Synthesis of methacrylic acid modified chondroitin sulfate (CSMA)
[0053] First, dissolve chondroitin sulfate sodium salt (CS, 10 g) in 100 mL of phosphate buffered saline (PBS, pH=7.4), and then add 10 mL of glycidyl methacrylate. The reaction solution was then vigorously stirred at room temperature for 15 days. The resulting product was extracted by precipitation with acetone. In order to remove residual glycidyl methacrylate, the white product was redissolved and extracted with chloroform. Finally, the aqueous phase was collected and concentrated, precipitated with acetone again, and the product was freeze-dried to obtain methacrylic acid-modified chondroitin sulfate (CSMA), which was stored at -20°C for use.
[0054] (2) Preparation of graphene-supported zinc-doped copper oxide (Zn-CuO@GO) composite material
[0055] 0.15 g of copper acetate and 0.055 g of zinc acetate w...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com