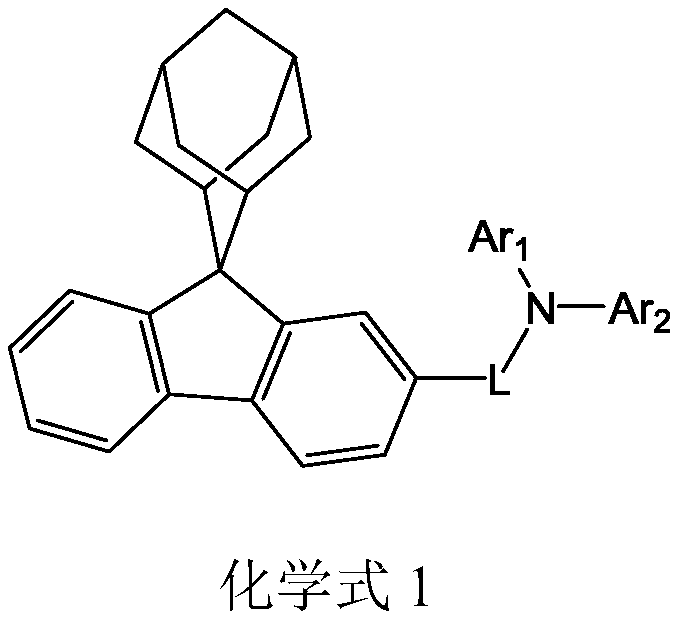
Organic electroluminescent material and organic electroluminescent device containing material
An electroluminescent material and electroluminescent device technology, which is applied in the directions of luminescent materials, electro-solid devices, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of excessive stacking, decreased device life, etc., to reduce device driving voltage, improve device efficiency and Life, increase in glass transition temperature and effect of vapor deposition temperature
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0095] Embodiment 1: blue organic electroluminescent device
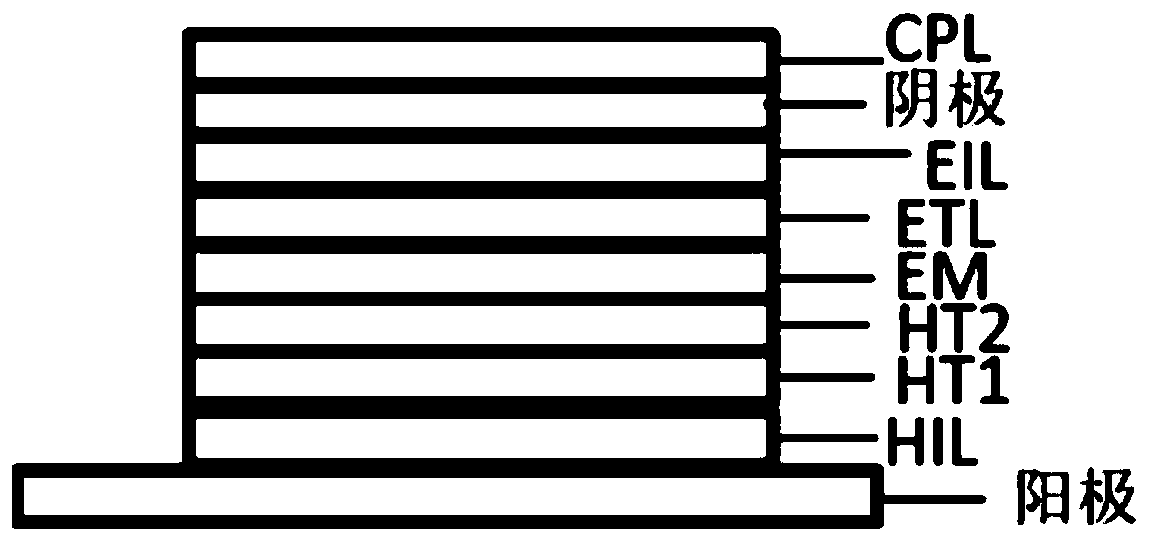
[0096] The anode was prepared by the following process: the thickness was The ITO substrate (manufactured by Corning) was cut into a size of 40mm×40mm×0.7mm, and it was prepared into an experimental substrate with cathode, anode and insulating layer patterns by photolithography process, and the surface was treated by ultraviolet ozone and O2:N2 plasma , to increase the work function of the anode (experimental substrate) and remove scum.
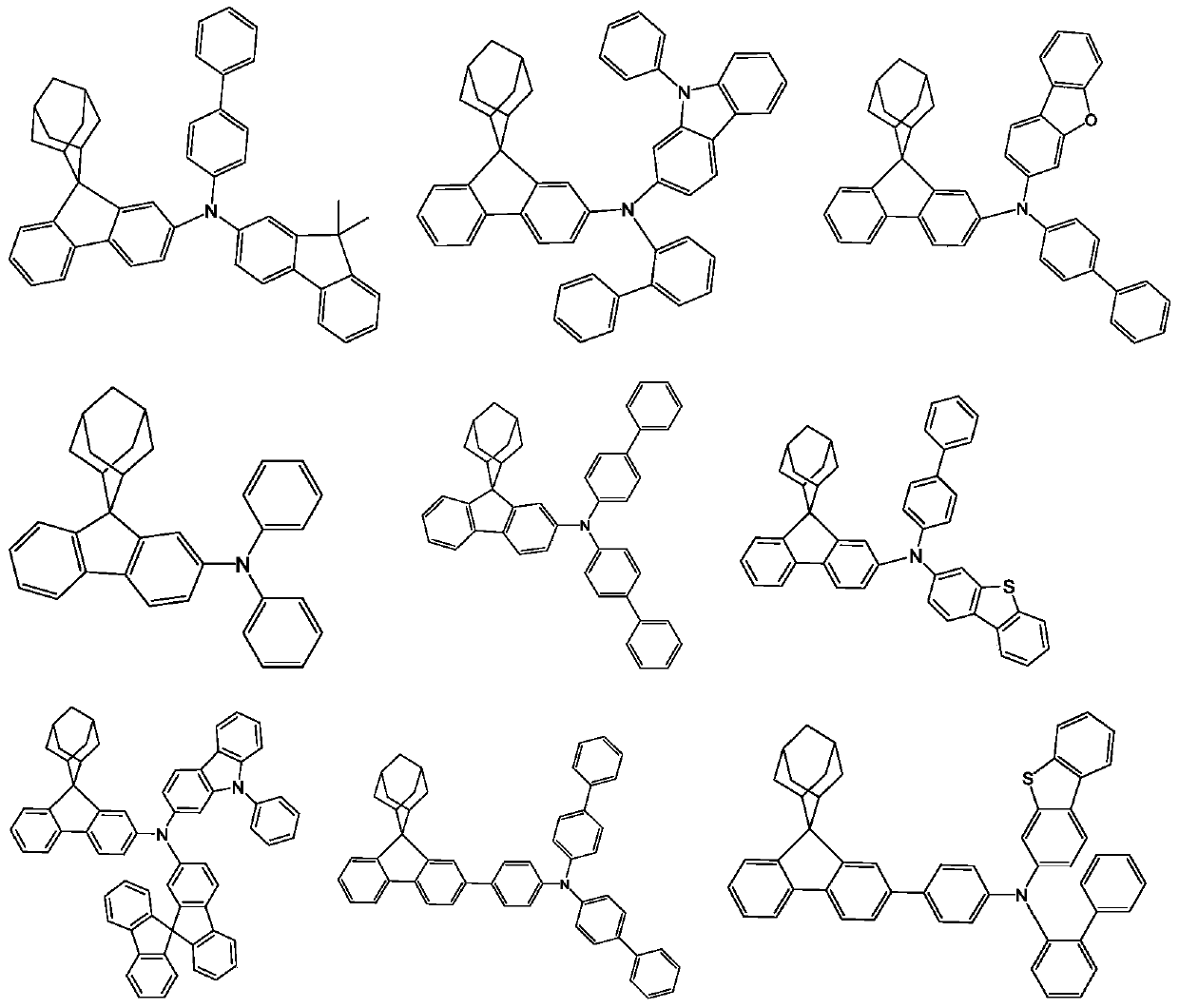
[0097] Vacuum evaporated m-MTDATA on the experimental substrate (anode) to form a thickness of The hole injection layer (HIL), and compound 1 is vacuum evaporated on the hole injection layer to form a thickness of The first hole transport layer (HT1).
[0098] Evaporate TCTA on the first hole transport layer to form a thickness of The second hole transport layer (HT2).
[0099] Using α,β-AND as the main body and doping 4,4'-(3,8-diphenylpyrene-1,6-diylbis(N,N-diphenylanili...
Embodiment 2-5
[0103] An organic electroluminescent device was fabricated by the same method as in Example 1 except that the compounds shown in Table 1 were each used when forming the first hole transport layer (HT1).
[0104] That is, Example 2 uses Compound 2 to make an organic electroluminescent device, Example 3 uses Compound 3 to make an organic electroluminescent device, Example 4 uses Compound 4 to make an organic electroluminescent device, and Example 5 uses Compound 5 to make an organic electroluminescent device. Light-emitting device, the device performance is shown in Table 1.
Embodiment 6
[0116] Embodiment 6: red organic electroluminescent device
[0117] The anode was prepared by the following process: the thickness was The ITO substrate (manufactured by Corning) was cut into a size of 40mm × 40mm × 0.7mm, and it was prepared into an experimental substrate with cathode, anode and insulating layer patterns by using a photolithography process, using ultraviolet ozone and O 2 :N 2 Plasma surface treatment was performed to increase the work function of the anode (experimental substrate) and to remove scum.
[0118] Vacuum vapor-deposit m-MTDATA on the experimental substrate (anode) to form a thickness of The hole injection layer (HIL), and NPB is evaporated on the hole injection layer to form a thickness of The first hole transport layer (HT1).
[0119] Compound 6 is vacuum evaporated on the first hole transport layer to form a thickness of The second hole transport layer (HT2).
[0120] Evaporate 4,4'-N,N'-dicarbazole-biphenyl (referred to as "CBP") as ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com