A protease-producing polylactic acid-degrading bacterium and its application
A technology for producing protease and polylactic acid, which is applied in the direction of bacteria, hydrolase, and microorganism-based methods, can solve the problems of difficult degradation, limited types and quantities of microorganisms, and few PLA-degrading bacteria, so as to make up for the limited range of pH tolerance , good degradation effect, and strong adaptability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] The isolation of embodiment 1 bacterial strain
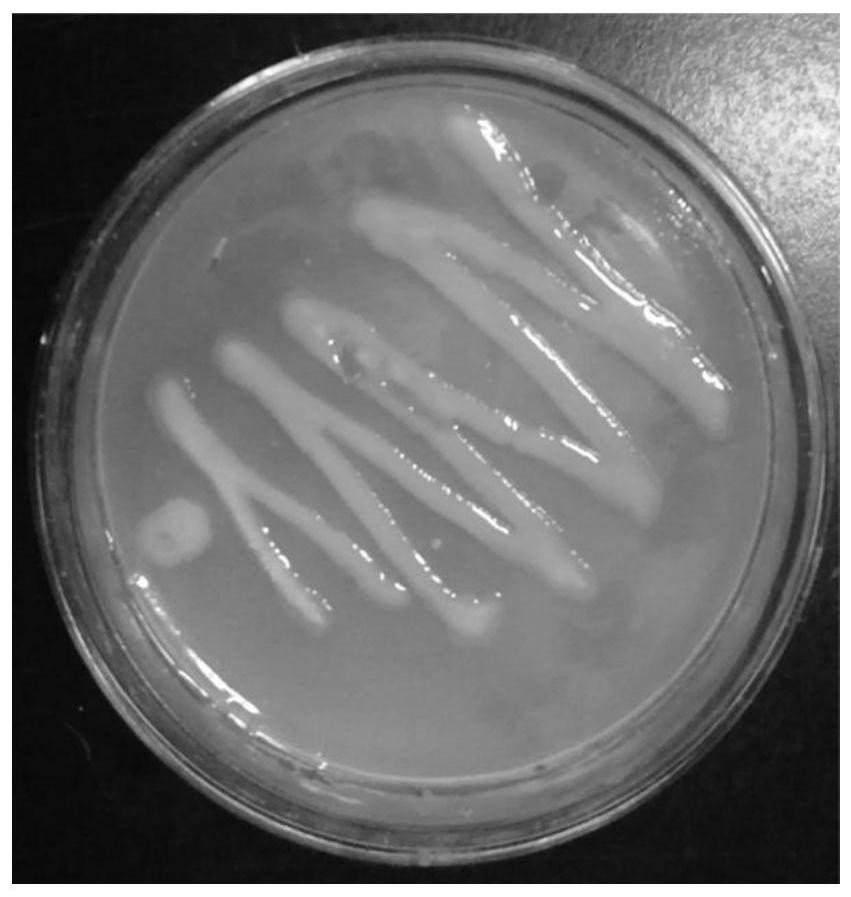
[0036] Collect the soil of a farmland with PLA / PBAT in Weifang, Shandong, weigh 10g of soil in a 150mL triangular flask of 90mL sterile water, and configure 10 -1 to 10 -6 The soil bacteria suspension with a series of concentration gradients was inoculated in the inorganic salt medium with PLA as the only carbon source. After culturing in a constant temperature incubator at 37°C for 3 days, the growth of microorganisms on the medium was observed, and a single colony was picked. Continuously inoculated several times in the inorganic salt medium with PLA as the only carbon source for isolation and purification until a strain of bacteria was isolated, and then observed its colony morphology, as shown in figure 1 As shown, the colony is milky white and round, with smooth and moist surface, flat edges and opaque.
Embodiment 2
[0037] The identification of embodiment 2 bacterial strains
[0038] 1. Physiological and biochemical experiments of strains
[0039] Pick a single colony of this strain on the inorganic salt medium with PLA as the only carbon source, and test the main physiological and biochemical experiments of this strain according to the "Common Bacterial System Identification Manual". The results are shown in Table 1 below. The characteristics are: V-P test and contact enzyme are positive; Gram staining test, M.R test, starch hydrolysis test and oil hydrolysis test are negative.
[0040] Table 1 Physiological and biochemical experiment results
[0041]
[0042] 2. Identification of the 16S rRNA gene sequence of the strain
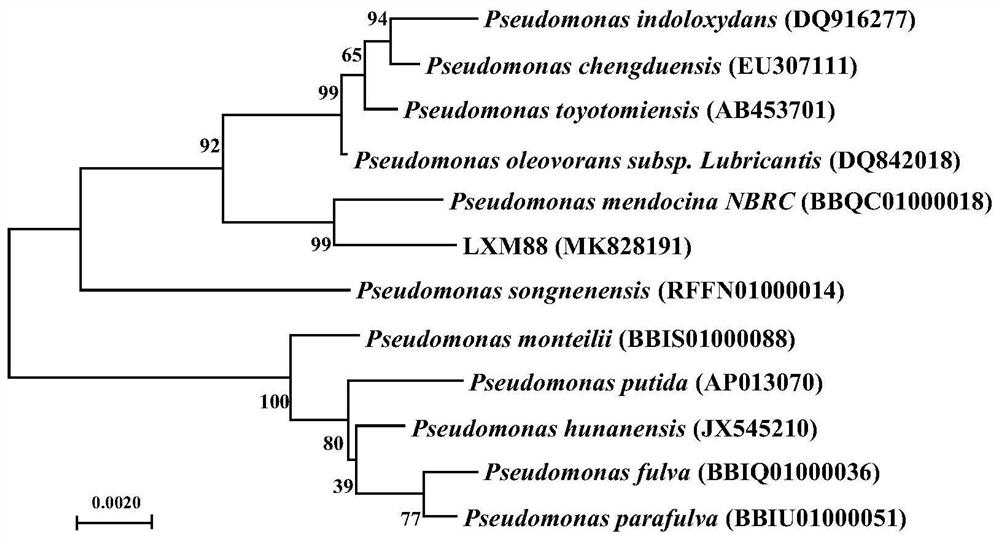
[0043]The strain was cultured on LB medium for 3 days at 37°C on a shaker with a rotation speed of 130r / min, the DNA of the strain was extracted by boiling water, and the bacterial general primer 27F (AGAGTTTGATCCTGGCTCAG) and 1492R (AAGGAGGTGATCCAAGCC) were used ...
Embodiment 3
[0045] Embodiment 3 bacterial strain produces protease ability identification
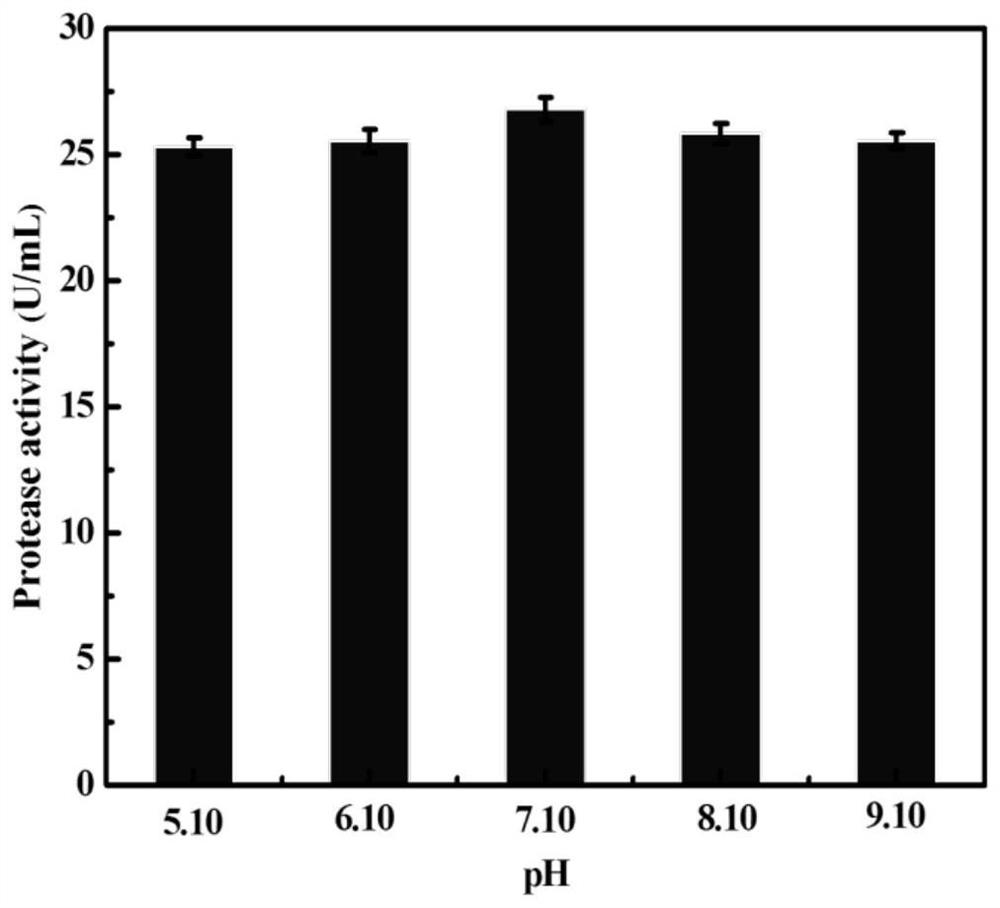
[0046] Inoculate this bacterium on skimmed milk powder culture medium, culture at 37°C for 3 days, observe the obvious transparent hydrolysis circle under the colony, it can be seen that this bacterium can produce protease.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com