Preparation and application of Raman enhancement substrates based on multi-layer composite structures
A multi-layer composite and Raman technology, applied in Raman scattering, measuring devices, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of slow growth rate, stability and uniformity of few-layer nanomaterials, poor uniformity and stability, etc. problems, to achieve the effect of simple and fast preparation method, excellent stability, and improved detection limit
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] A method for preparing a Raman-enhanced substrate based on a multilayer composite structure, comprising the steps of:
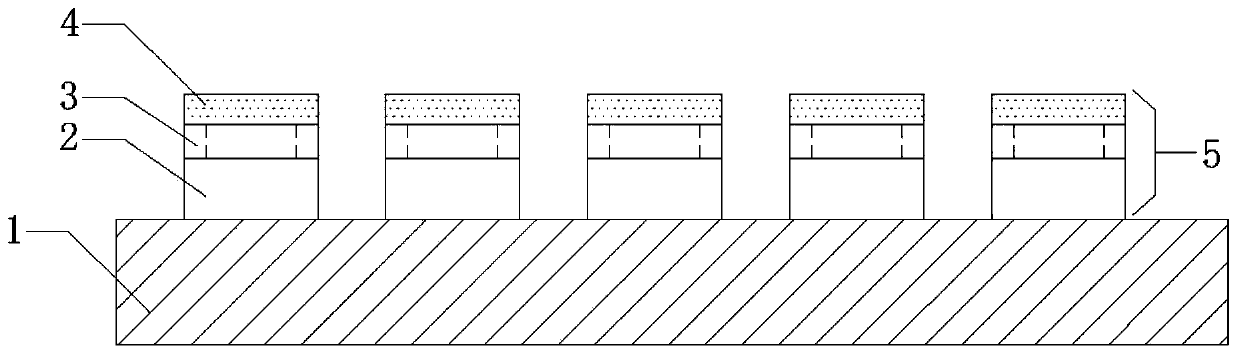
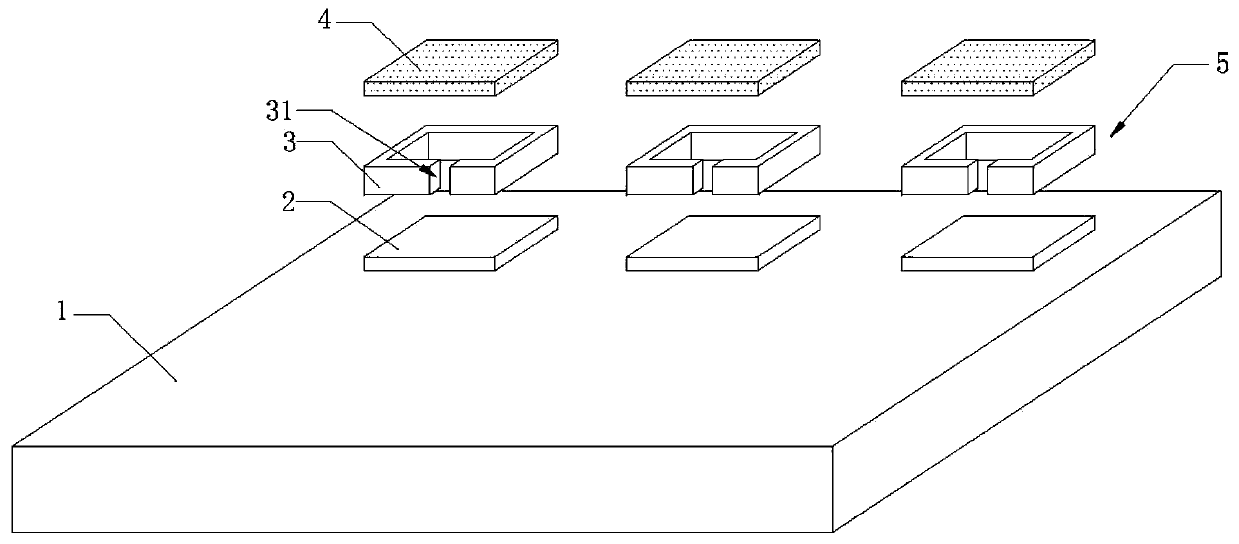
[0046] A. On the quartz substrate 1, place several 2 substrates 2, a spacer 3 is placed on the upper surface of each substrate 2, and a spacer 3 with a cross-sectional area of 1×1 cm is placed on the upper surface of each spacer 3 2 The molybdenum sheet 4 obtained several composite laminates 5;
[0047] B. Preparation of molybdenum oxide substrate: Put the quartz substrate 1 with several composite laminates 5 into the heating equipment that has been preheated at 600°C for heat treatment, and react at a temperature of 600°C for 5 minutes; take out the quartz substrate 1, cooling, removing the spacer 3, and making a molybdenum oxide substrate;
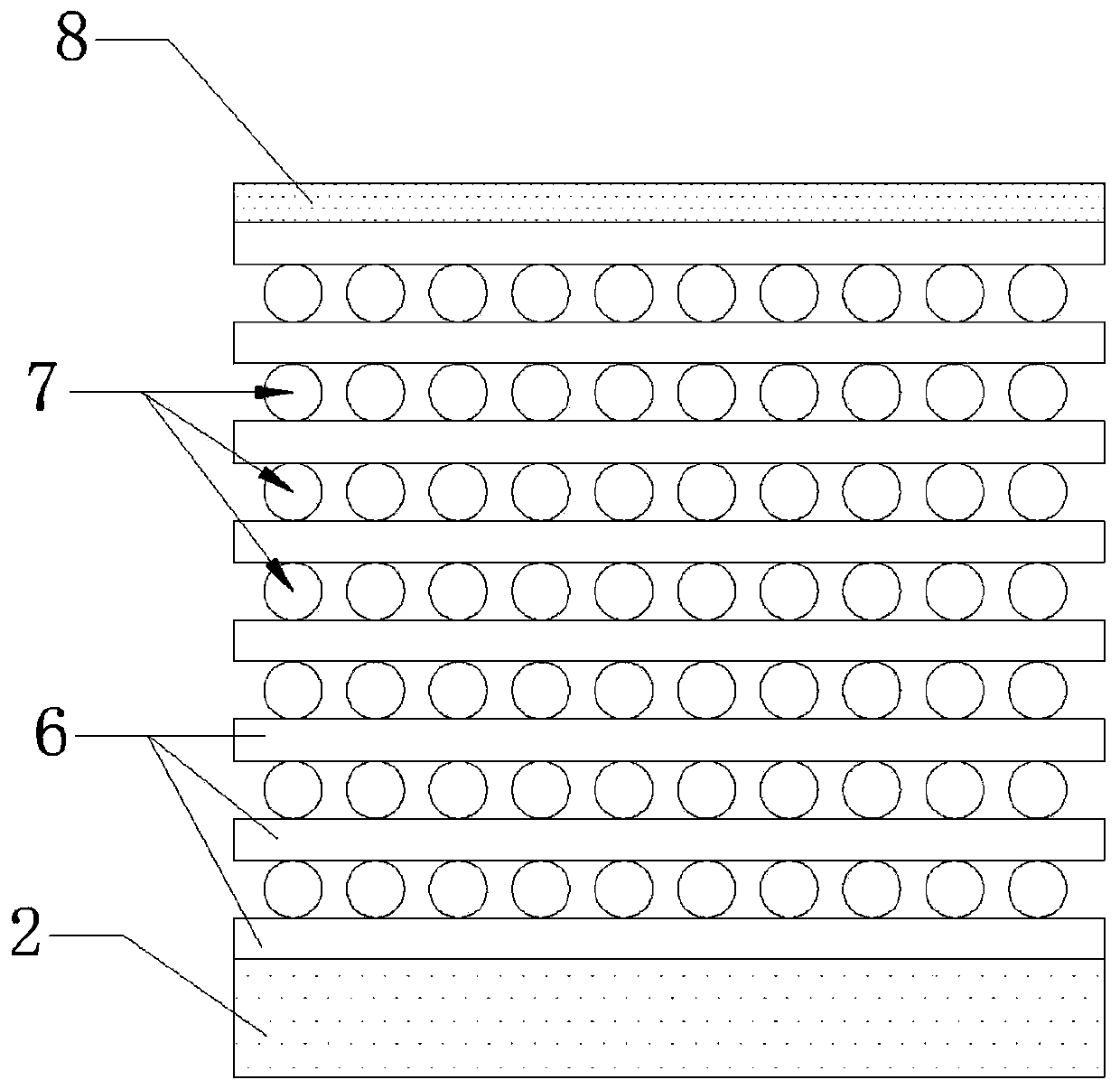
[0048] C. Deploy SnCl 2 Solution: prepare SnCl with a concentration of 10nmol / L in a glass container 2 solution, and then to the SnCl 2 Dilute hydrochloric acid was added dropwise to the solution to adjust...
Embodiment 2
[0056] A method for applying a Raman-enhanced substrate based on a multilayer composite structure, comprising the steps of:
[0057] Step (1): Take the R6G molecule, dissolve it in deionized water, and prepare a concentration of 4×10 -6 M's R6G molecular solution;
[0058] Step (2): Place the Raman-enhanced substrate based on the multilayer composite structure prepared in Example 2 on step (1) 4×10 -6 In the R6G molecular solution of M, place it for 20 minutes, then take it out, dry the surface, and obtain the sample to be tested;
[0059] Step (3): Using a micro-Raman spectrometer with an excitation light wavelength range of 514nm, a 50x eyepiece, an excitation light intensity of 0.625mW, and an integration time of 10s, measure the R6G molecule at 1100cm -1 -1700cm -1 The characteristic vibration; and with the same thickness (100nm) of pure molybdenum oxide for 4×10 -6 Raman enhancement effect of the R6G molecular solution of M.
Embodiment 3
[0063] A method for applying a Raman-enhanced substrate based on a multilayer composite structure, comprising the steps of:
[0064] Step (1): Take MB molecules, dissolve them in deionized water, and prepare the concentration to be 4×10 -3 M, 4×10 -4 M, 4×10 -5 M, 4×10 -6 M, 4×10 -7 M, 1×10 -7 M, 6×10 -8 M, 2×10 -8 MB molecular solution of M;
[0065] Step (2): The Raman-enhanced substrates based on the multi-layer composite structure prepared in Example 2 were respectively placed in step (1) with a concentration of 4×10 -3 M, 4×10 -4 M, 4×10 -5 M, 4×10 -6 M, 4×10 -7 M, 1×10 -7 M, 6×10 -8 M, 2×10 -8 In the MB molecular solution of M, place it for 20 minutes, then take it out, dry the surface, and obtain the sample to be tested;
[0066] Step (3): Using a micro-Raman spectrometer with an excitation light wavelength range of 633nm, a 50x eyepiece, an excitation light intensity of 0.945mW, and an integration time of 10s, measure the MB molecule at 1100cm -1 -1700c...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com