A tail-anchored α-helix antimicrobial peptide gw4a and preparation method and application thereof
An antibacterial peptide and α-helix technology, applied in the field of α-helix antibacterial peptide GW4A and its preparation, can solve the problems of inactivated clinical application, poor stability, unsatisfactory antibacterial activity, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0017] Design of Antimicrobial Peptides
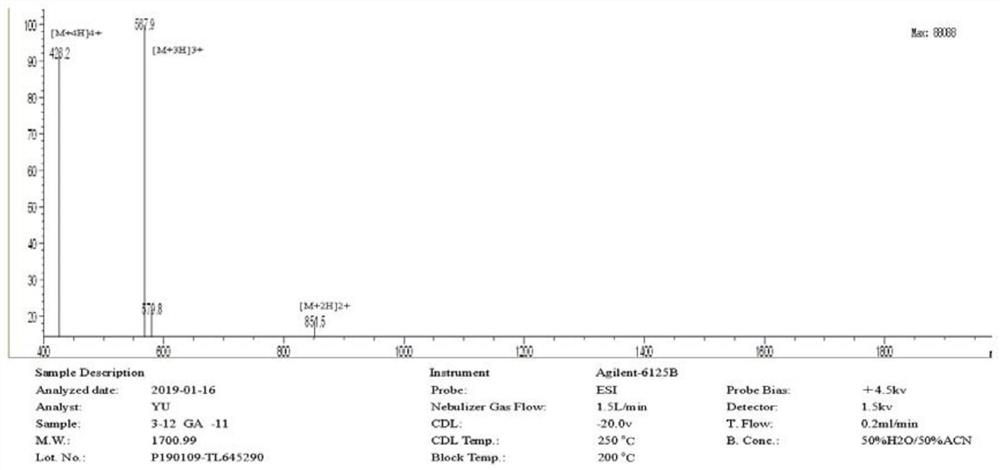
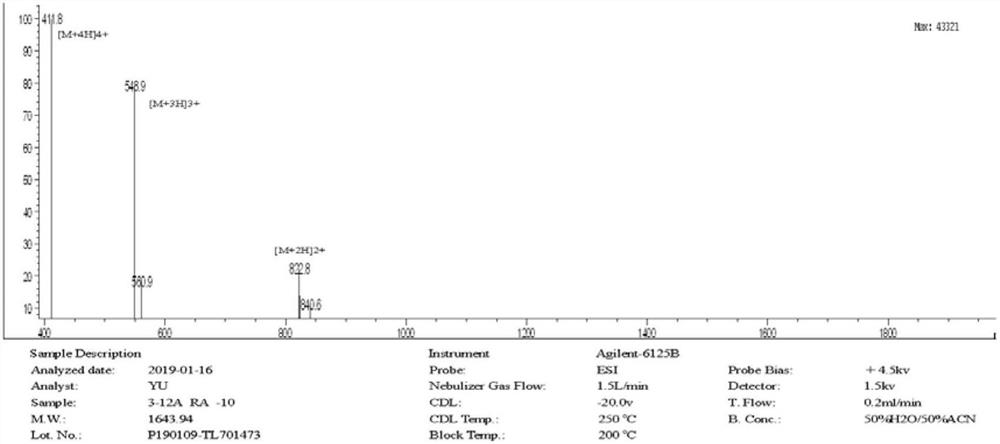
[0018] Taking W4 as the active center, the sequence of peptide W4 is: RWRWWWRWR, anchored with different hydrophobic amino acids (Ala, Trp, Val, Ile, Phe, Leu) at its tail, and designing a cap structure with glycine at the N-terminus. A series of antimicrobial peptides; when glycine is added to the N-terminal and alanine is anchored at the tail, it is named GW4A. The amino acid sequences of GW4A and W4A are shown in Table 1 when only glycine is anchored at the tail end.
[0019] Table 1 Amino acid sequences of GW4A and W4A
[0020] peptide amino acid sequence Molecular weight (Dalton) wxya Gly Arg Trp Arg Trp Trp Trp Arg Trp Arg Ala-NH2 1700.99 W4A Arg Trp Arg Trp Trp Trp Arg Trp Arg Ala-NH2 1643.94
[0021] The charge numbers of GW4A and W4A are +5, respectively, and the average hydrophobicity values are 0.684 and 0.752, respectively. The carboxyl termini of both peptides, GW4A and W4A, were amid...
Embodiment 2
[0023] Synthesis of Two Antimicrobial Peptides GW4A and W4A by Solid Phase Chemical Synthesis
[0024] 1. The preparation of antimicrobial peptides is carried out one by one from the C-terminal to the N-terminal, and is completed by a peptide synthesizer. First, Fmoc-X (X is the first amino acid at the C-terminal of each antimicrobial peptide) is inserted into Wang resin, and then the Fmoc group is removed to obtain X-Wang resin; then Fmoc-Y-Trt-OH (9 -Fmoxy-trimethyl-Y, Y is the second amino acid at the C-terminus of each antimicrobial peptide); according to this procedure, it is synthesized from the C-terminus to the N-terminus until the synthesis is completed, and the side of the Fmoc group is removed Resin for chain protection.
[0025] 2. Add a cleavage reagent to the peptide resin obtained above, react for 2 hours at 20°C in the dark, filter; wash the precipitate with TFA (trifluoroacetic acid), mix the washing liquid with the above filtrate, concentrate with a rotary e...
Embodiment 3
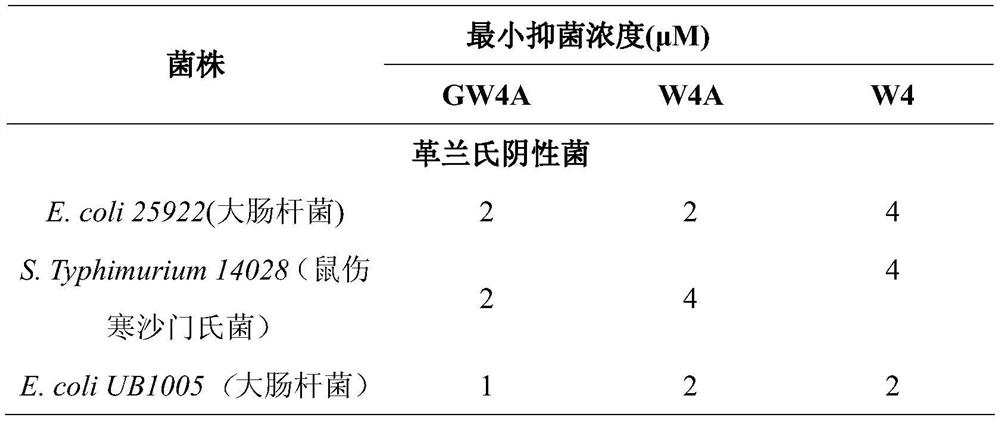
[0028] Embodiment 3: Determination of biological activity of antimicrobial peptides
[0029] 1. Determination of antibacterial activity: Prepare the peptide as a storage solution for use. The minimum inhibitory concentrations of several antimicrobial peptides were determined by the broth microdilution method. Using 0.01% acetic acid (containing 0.2% BSA) as the diluent, a series of gradient antimicrobial peptide solutions were sequentially prepared using the double dilution method. Take 100 μL of the above solution and place it in a 96-well cell culture plate, then add an equal volume of the bacteria solution to be tested (~10 5 individual / mL) in each well. Positive controls (containing bacterial fluid but not antimicrobial peptides) and negative controls (neither bacterial fluid nor peptides) were set up. Incubate at a constant temperature of 37°C for 20 hours, and the minimum inhibitory concentration is the one where no turbidity is seen at the bottom of the well with the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com