Lipase mutant of marine streptomyces and application of lipase mutant
A technology of marine streptomyces and lipase, applied in the fields of genetic engineering and enzyme engineering, can solve problems such as difficulty in screening ideal strains, poor enzymatic properties, and small workload
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] Construction and expression of embodiment 1 marine Streptomyces lipase mutant
[0025] Structural analysis of MAS1 lipase (the amino acid sequence is SEQ ID NO: 1) found that, in addition to the catalytic triplet (S109-H232-D200), its catalytic pocket consists of T38, F39, G49, H108, T141, V202, V203, T237 Amino acid composition. In order to enhance the steric effect of the pocket on the TAG substrate and change the substrate selectivity of lipase, single mutants T38R / F, G40E / F, H108W, T141F / R, V202F, V203L / F, V233F / R, T237Y and double mutations H108W-T38R / F, H108W-G40F, H108W-T141F / R, H108W-V202L / F, H108WV233R / F, H108W-T237Y and other series of enzyme mutants. The genes of the above mutants were cloned into pET22b vector and transformed into BL21(DE3) for expression.
Embodiment 2
[0026] The screening of embodiment 2 marine Streptomyces lipase mutants
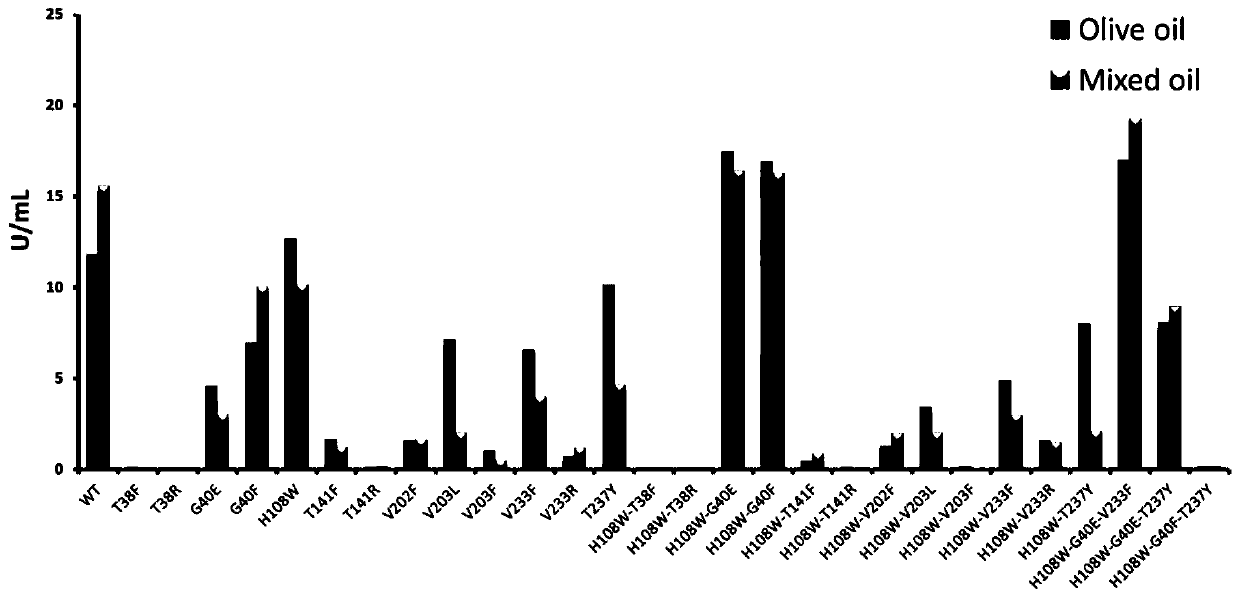
[0027] MAS1 lipase mutants were prepared using E. coli expression system, and emulsified olive oil (TAG: 98%, DAG: 2%) and Kao diglyceride (TAG: 65%, DAG: 32%, MAG: 2%) As a substrate, the difference in enzyme activity of the lysate was measured. The result is as figure 1 shown, from figure 1 It can be seen that the mutations at T38 and T141 lead to the loss of MAS1 lipase activity, and the mutations at V202 and V203 also greatly reduce the enzymatic hydrolysis activity. Only single mutations G40E / F, H108W, V233F, T237Y and double mutations H108W-G40E / F, H108W-V233F, H108W-T237Y had no obvious effect on the activity of the enzyme. Among them, the hydrolysis activity of G40F mutant to DAG substrate was higher than that of triglyceride substrate, suggesting that the mutation of G40F site may lead to the change of substrate selectivity of MAS1 lipase.
[0028] The amino acid sequence of the G40F single ...
Embodiment 3
[0030] Embodiment 3 Expression preparation of marine Streptomyces lipase mutant
[0031] (1) Construction of Pichia pastoris expression engineering bacteria: the MAS1-G40F gene was cloned into the Pichia pastoris expression vector pPICZαA vector, screened and sequenced to verify that the gene was correct. The pPICZαA-MAS1-G40F vector was linearized and electrotransformed into Pichia pastoris X-33 strain, and screened with bleomycin to obtain positive recombinant expression strains.
[0032] (2) Preparation of primary seed liquid: Inoculate the single colony obtained above into a sterilized Erlenmeyer flask containing 50mL of YPD liquid medium, and then place the Erlenmeyer flask at a temperature of 30°C and a rotating speed of 200rpm Vibrate in a shaking table for 18-24 hours to obtain the first-grade seed liquid;
[0033] (4) Preparation of the secondary seed liquid: Inject 5 mL of the primary seed liquid into 100 mL of sterilized fresh YPD liquid medium, and vibrate for 24 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com