Carbon nanodot with thermal activation near-infrared up-conversion luminescence characteristic as well as preparation method and application of same
A technology of carbon nano-dots and luminescent properties, applied in the field of carbon nano-materials, can solve problems such as the scarcity of carbon nano-dots, the limitation of carbon nano-dots, and the lack of energy band regulation methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0048] The invention provides a method for preparing the above-mentioned near-infrared up-conversion luminescent carbon nano-dots, comprising the following steps:
[0049] (1) Dissolve red light-emitting carbon nanodots in a polar aprotic solvent for stripping, and obtain near-infrared up-conversion luminescent carbon nanodots after purification
[0050] (2) Mixing the up-conversion luminescent carbon nanodots with the raw materials containing electron-withdrawing groups, the raw materials containing electron-withdrawing groups are compounds containing electron-withdrawing groups or polymers containing electron-withdrawing groups to realize near-infrared Up-conversion and down-conversion luminescence.
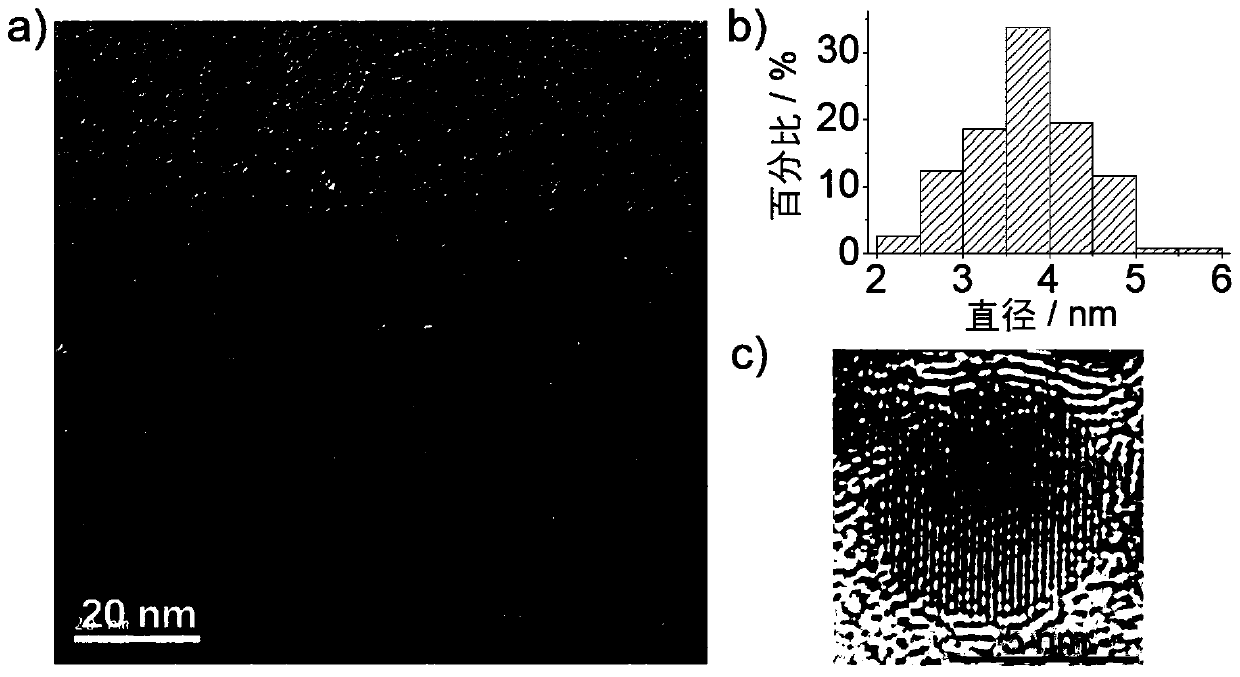
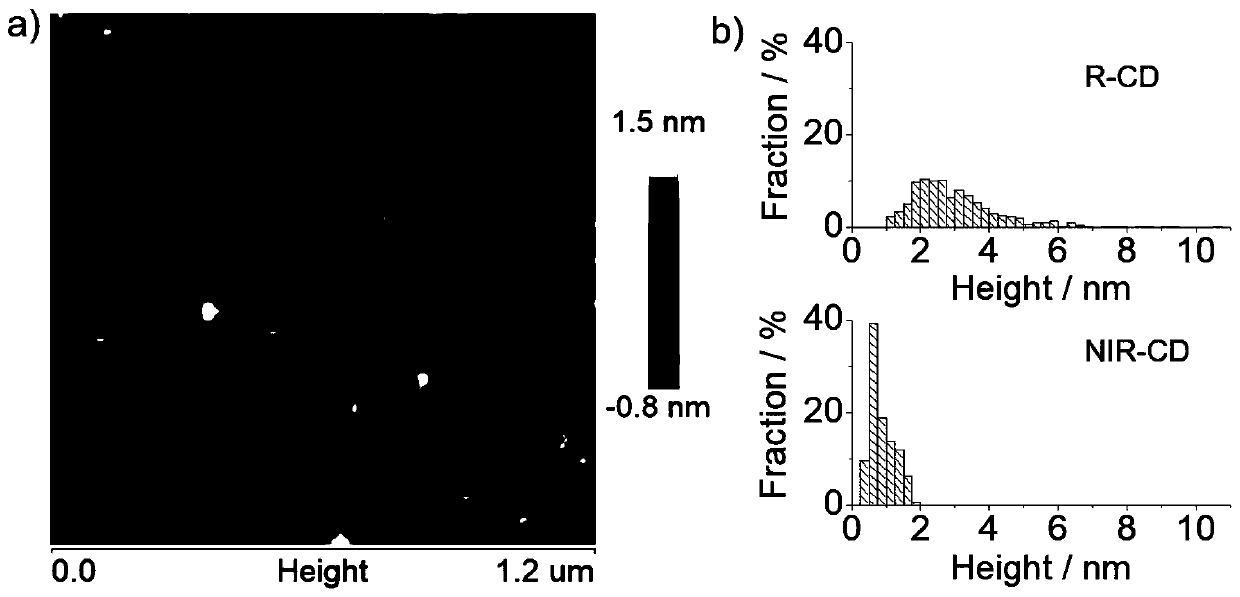
[0051] In the present invention, the size distribution of the up-conversion luminescent carbon nano-dots is 2-6 nm, and the height distribution is 0.4-2.0 nm, which are formed by stacking 1-3 layers of graphene-like sheets;
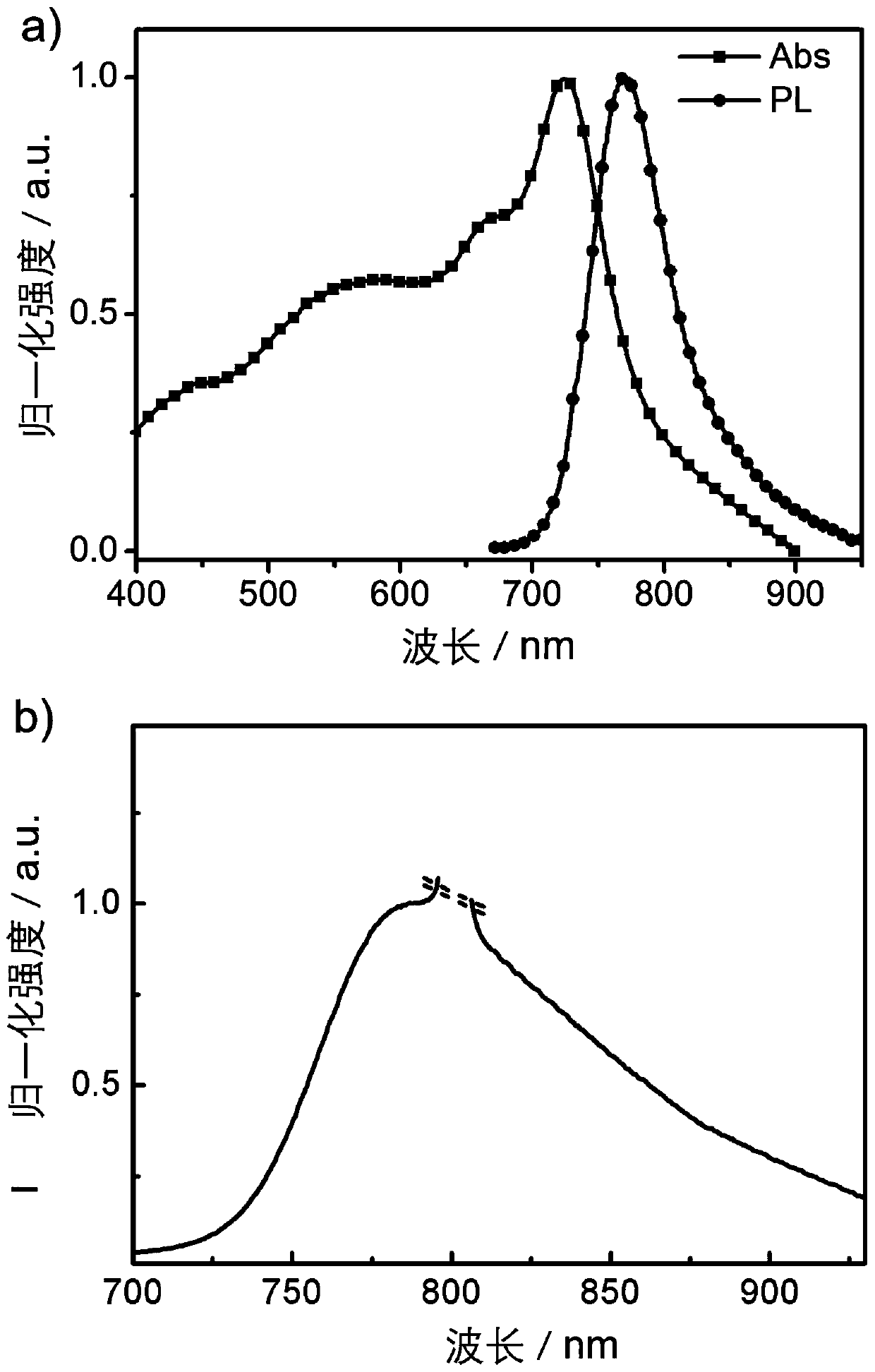
[0052] In the present invention, the main absorptio...
Embodiment 1
[0060] Near-infrared up-conversion luminescent carbon nano-dots are prepared by exfoliating red light-emitting carbon nano-dots in DMF with microwave heating.
[0061] The preparation method of the above-mentioned near-infrared up-conversion luminescent carbon nano-dots:
[0062] Dissolve 5 mg of red-emitting carbon nanodots (CD) in 100 mL of DMF, react in a microwave reactor at 100°C for 70 min, and remove the DMF by rotary evaporation to obtain a black solid, which is washed twice with ethanol to obtain a black powder, which is a near-infrared upper Converting Luminescent Carbon Nanodots (NIR-CD).
[0063] combine Figure 1~5 Illustrative Example 1:
[0064] Carry out transmission electron microscope (TEM) and atomic force microscope (AFM) characterization to the near-infrared up-conversion luminescent carbon nano-dot of embodiment 1, the result is as follows Figure 1-2 As shown, the TEM picture shows that the size distribution of carbon nanodots is 2-6nm, and the carbon...
Embodiment 2
[0069] Near-infrared up-conversion luminescent carbon nano-dots are prepared by ultrasonically preparing red light-emitting carbon nano-dots in DMSO.
[0070] The preparation method of the above-mentioned near-infrared up-conversion luminescent carbon nano-dots:
[0071] Dissolve 5 mg of red-emitting carbon nanodots in 100 mL of DMSO, sonicate in an ultrasonic cell disruptor (500 W) for 15 minutes, freeze-dry to remove DMSO to obtain a black solid, and wash the solid with ethanol twice to obtain a black powder, which is near-infrared upconversion luminescence carbon nanodots.
[0072] combine Image 6 Illustrative embodiment 2:
[0073] The DMSO solution of the near-infrared up-conversion luminescence carbon nano-dot of embodiment 2 is carried out fluorescence emission spectrum analysis, the result is as follows Image 6 As shown, the up-conversion luminescence peak is 784nm.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com