Scutellaria baicalensis leaf extract, preparation method and application thereof
A technology of scutellaria baicalensis leaves and extracts, which is applied in the field of extraction of non-medicinal parts of Chinese herbal medicines, can solve the problems that the comprehensive development and utilization of scutellaria baicalensis leaves have not fully improved the economic value of scutellaria baicalensis leaves, and improve learning and memory ability and oxidative damage , the effect of increasing economic value
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] Example 1: The preparation method of Scutellaria baicalensis leaf extract: Scutellaria baicalensis leaf 400g, water temperature 89 ℃, add 15 times the quality of water for the first time and decoct for 1 hour, filter; add 10 times the quality of water for the second time and decoct for 1 hour, filter, The combined filtrates were concentrated, and then the concentrated solution was freeze-dried to obtain the crude extract of Scutellaria baicalensis leaves. The crude extract of Scutellaria baicalensis obtained above was separated by HPD100 macroporous adsorption resin, and water, 50% ethanol and 95% ethanol were used as elution solvents respectively, and eluted at a flow rate of 3 BV / h, and 3 BV were collected for each gradient. The 50% ethanol and 95% ethanol eluate were concentrated under reduced pressure and freeze-dried to obtain the extract of Scutellaria baicalensis leaves.
Embodiment 2
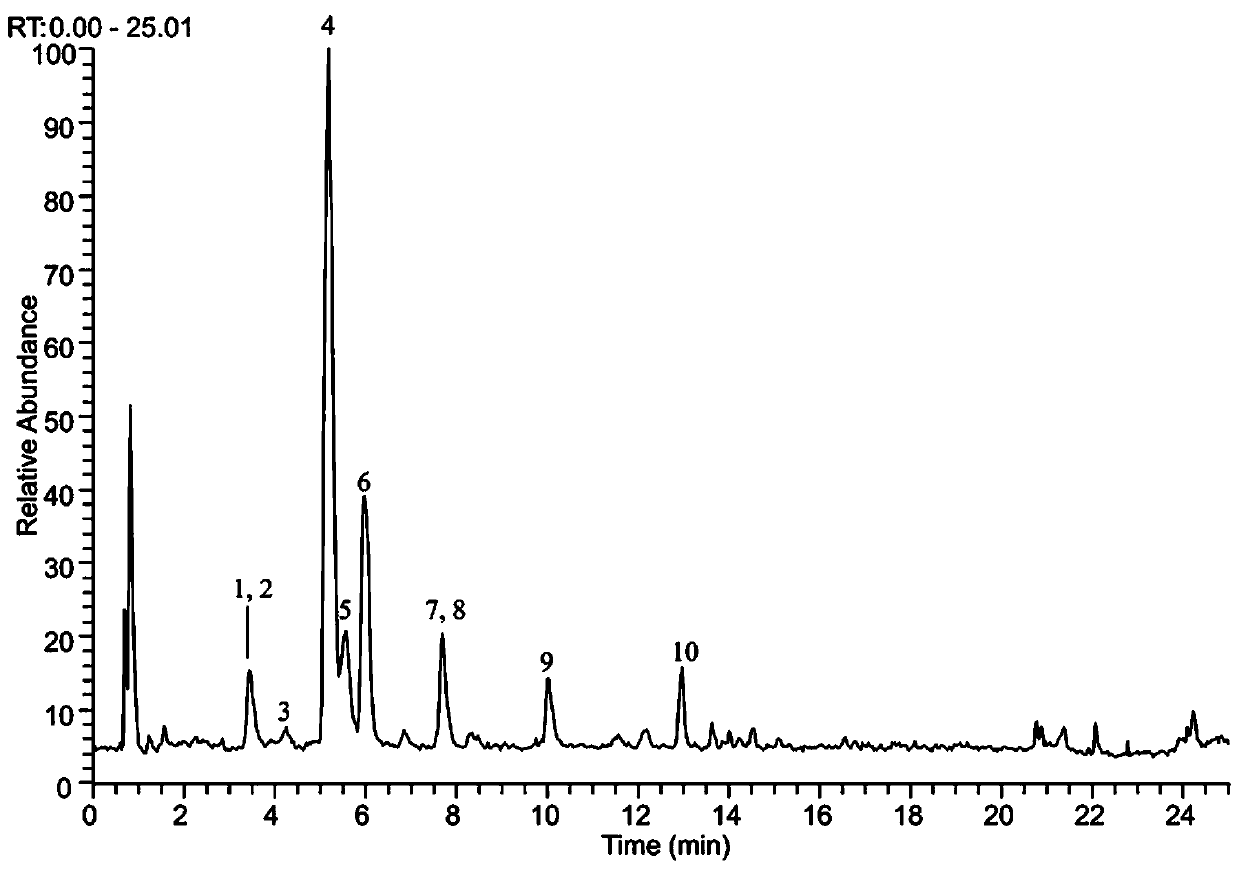
[0020] Example 2: Analysis of chemical components of Scutellaria baicalensis leaf extract: The main components of Scutellaria baicalensis leaf extract were identified by UHPLC-Q Exactive Orbitrap-MS analysis instrument and HSS T3 chromatographic column analysis. Through the comparison of reference substances and databases, combined with existing literature reports, a total of 10 main chemical components were identified. figure 1 .
[0021] Liquid phase conditions: mobile phase: A (acetonitrile), B (water, containing 0.1% formic acid); mobile phase gradient: 0 ~ 4 min, 15% ~20%A; 4 ~ 8 min, 20~23% A; 8 ~10min, 23~25%A; 10~14min, 25~50%A; 14~18min, 50~52%A; 18~20min, 52~90%A; 20~22min, 90%A ; 22 ~ 22.5min, 90 ~ 15% A; 22.5 ~ 25min, 15% A. Flow rate 0.30 ml / min, 2 μL injection volume, 40 °C column temperature, Waters ACQUITY UPLC HSS T3 column (2.1 × 100 m, 1.8 m).
[0022] Mass spectrometry conditions: Ionization mode using ESI electrospray negative ion detection, scan mode:...
Embodiment 3
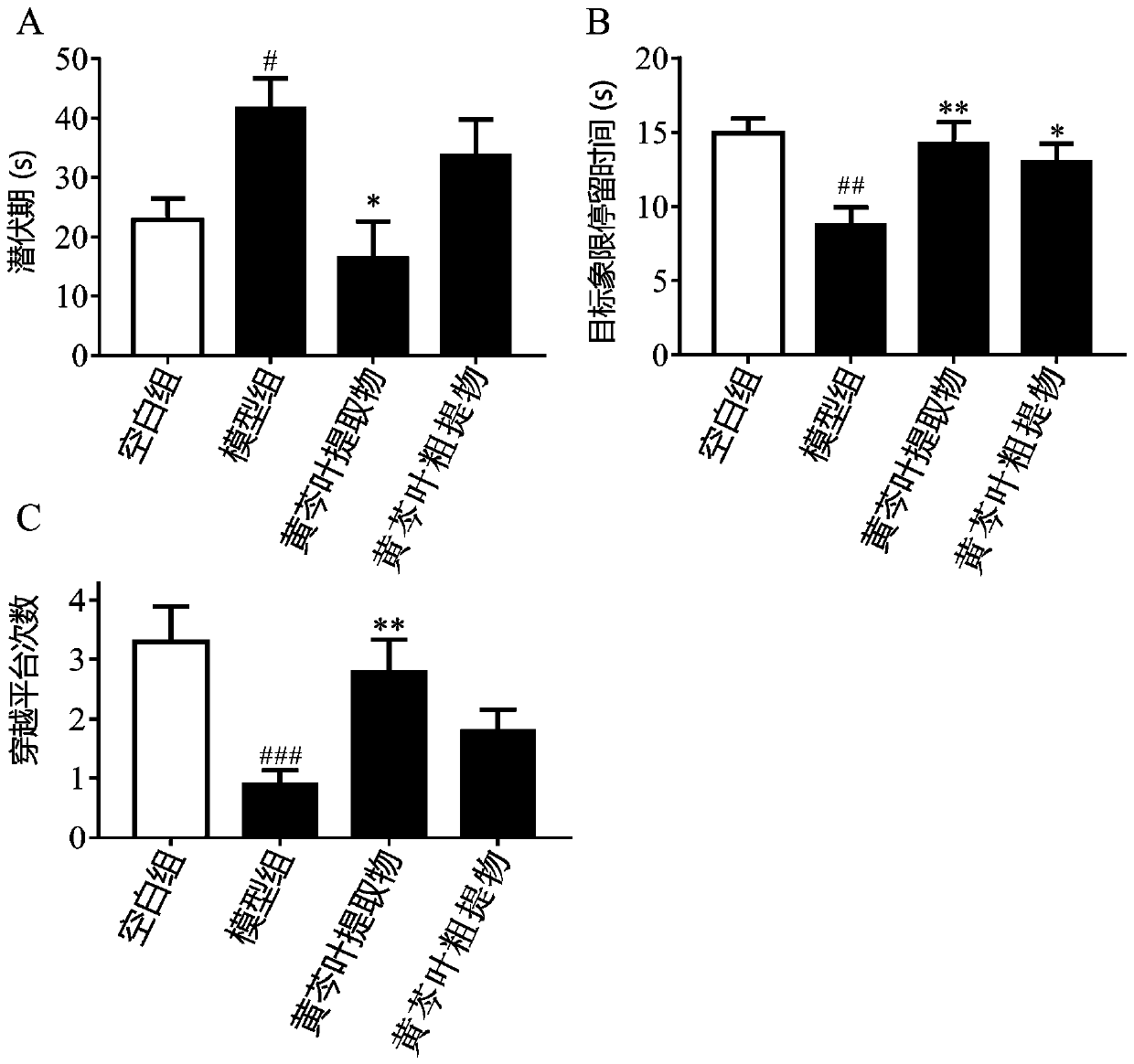
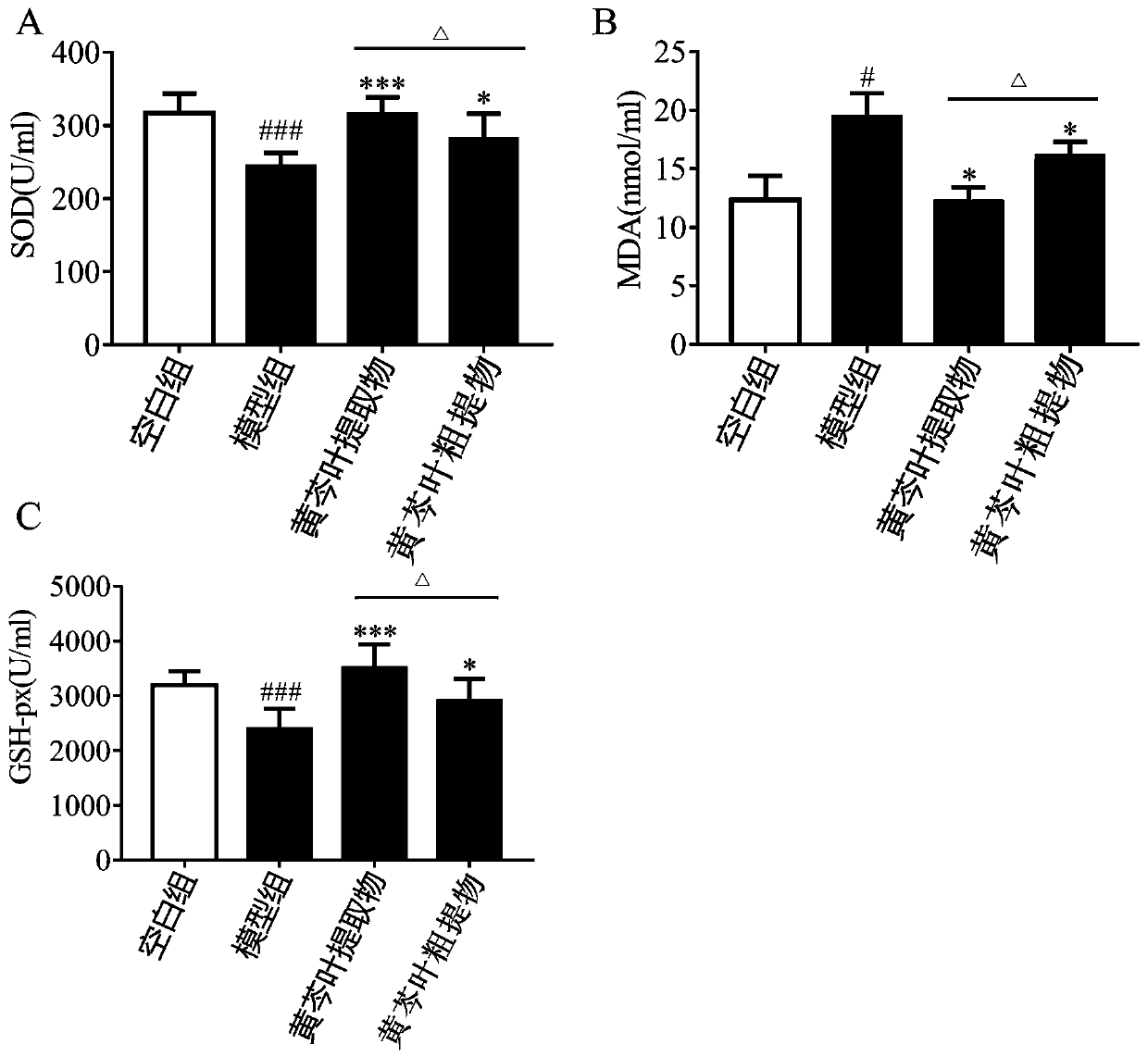
[0024] Example 3: Study on the effect of Scutellaria baicalensis leaf extract on aging rats
[0025] 1. 40 SPF-grade male SD rats were purchased from Beijing Weitong Lihua Co., Ltd., with a body weight of (180±20) g. The humidity in the animal laboratory is (50±10)%, the room temperature is (25±1)°C, and the light cycle is every 12 hours. Five mice are placed in each cage, and they can drink water and eat freely during the experiment.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com