A microbial sensor for detecting biomarkers, a detection method, a culture and detection chip, and a detection system
A microbial sensor and biomarker technology, applied in the field of biomedical detection, can solve the problems of poor antibody stability, high cost, and difficult modification, and achieve the effect of low cost and simple structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
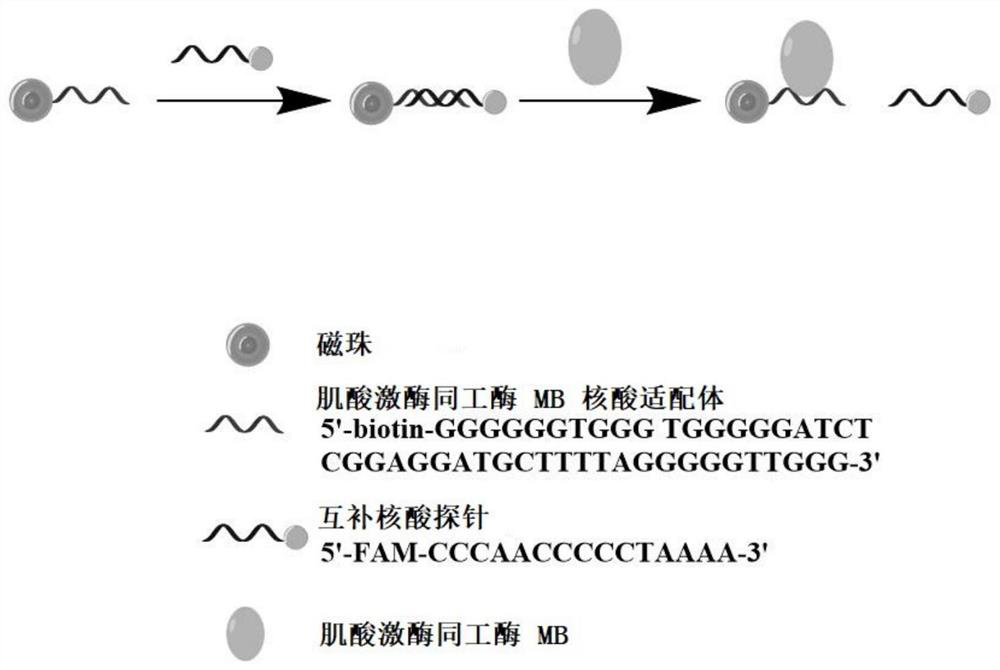
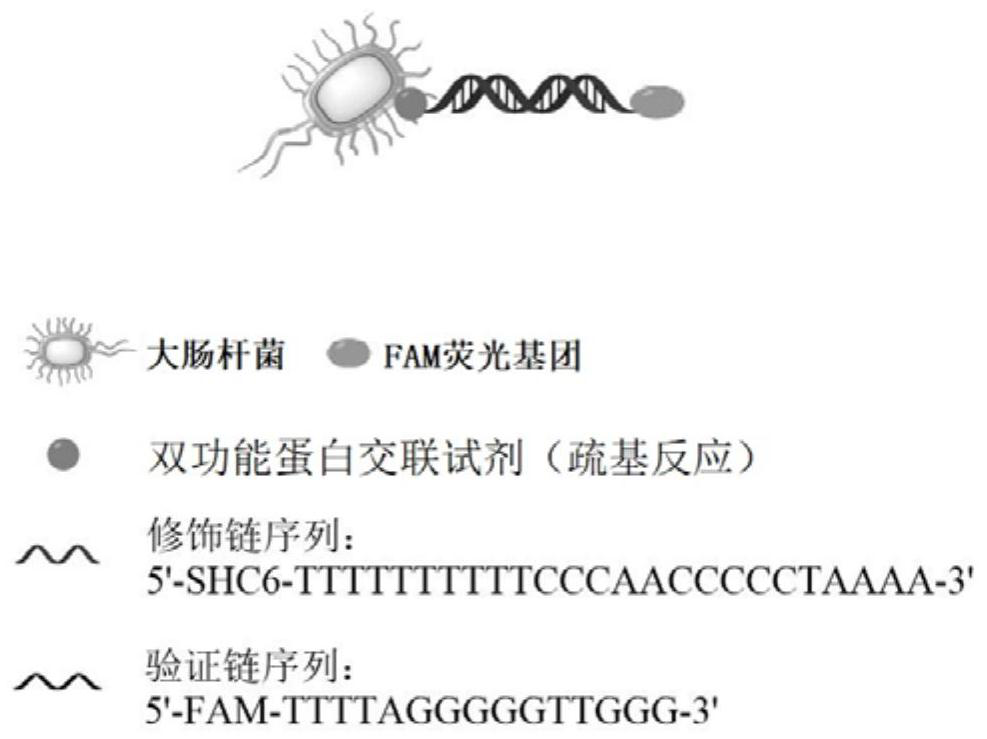
[0040]The invention provides a microbial sensor for detecting biomarkers, which is composed of component A and component B. Component A is a conjugate of magnetic beads and nucleic acid aptamers, and the nucleic acid aptamers can be combined with target biomarkers Specific binding; Component B is a genetically engineered bacterial solution that transforms fluorescent proteins and expresses resistance, and uses SMPB as a cross-linking agent to modify nucleic acid probes on genetically engineered strains. The nucleic acid sequence of the nucleic acid probe is complementary to the nucleic acid aptamer, preferably, the entire nucleic acid sequence of the nucleic acid probe is complementary to the partial sequence of the nucleic acid aptamer. The target biomarker competes with the nucleic acid probe to bind to the binding site of the nucleic acid aptamer, and the nucleic acid probe falls off from the nucleic acid aptamer. By detecting the fluorescence intensity of the fluorescent pr...
Embodiment 2
[0044] For different target biomarkers, the present invention optimizes the length of the complementary nucleic acid probe, the temperature of the reaction, and the experimental conditions for the binding of the nucleic acid aptamer to the complementary nucleic acid probe, and the incubation temperature of the CK-MB competition reaction is 37°C ; The number of washes after the coupling of the nucleic acid aptamer and the complementary probe is 5 times; the coupling time of the nucleic acid aptamer and the complementary probe is 1 h; the competition incubation of the protein biomarker CK-MB and the nucleic acid aptamer The time is 1h. Under these optimal conditions, the competitive binding reaction of target biomarkers with nucleic acid aptamers and complementary nucleic acid probes is achieved.
[0045] The invention provides a microbial sensor for detecting biomarkers, which is composed of component A and component B. Component A is a conjugate of magnetic beads and nucleic a...
Embodiment 3
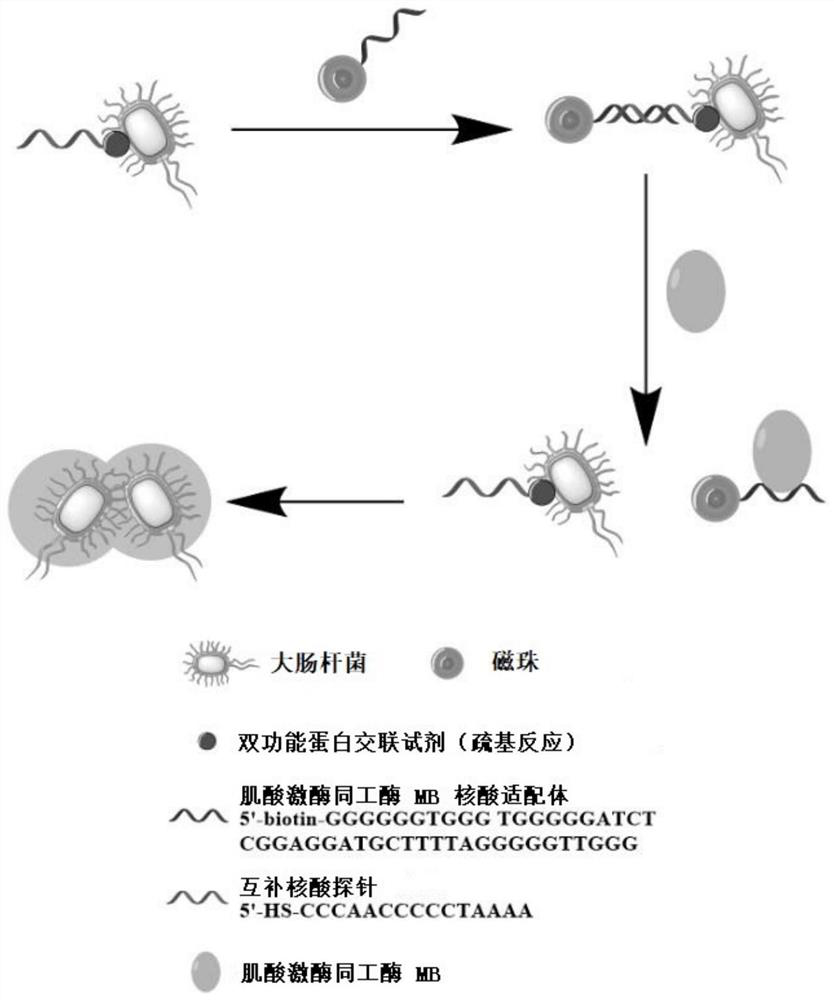
[0048] Such as image 3 As shown, the present invention provides a method for microbial sensor detection of biomarkers, comprising the following steps:
[0049] Step 0: Mix the magnetic beads with an equal volume of nucleic acid aptamer solution, and after incubation, discard the supernatant after magnetic separation to obtain Component A;
[0050] The fluorescent protein and the resistant plasmid are introduced into the competent engineering strain, the culture strain is picked up to expand the monoclonal colony, and the nucleic acid probe is modified on the surface of the genetically engineered bacteria to prepare component B.
[0051] Step 1: Add component B to component A for incubation, magnetically separate, and collect magnetic beads;
[0052] After the magnetic beads are bound to the nucleic acid aptamer, wash them several times. After the end, add the genetically engineered bacteria solution that has been modified with the nucleic acid aptamer complementary nucleic a...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Radius | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com