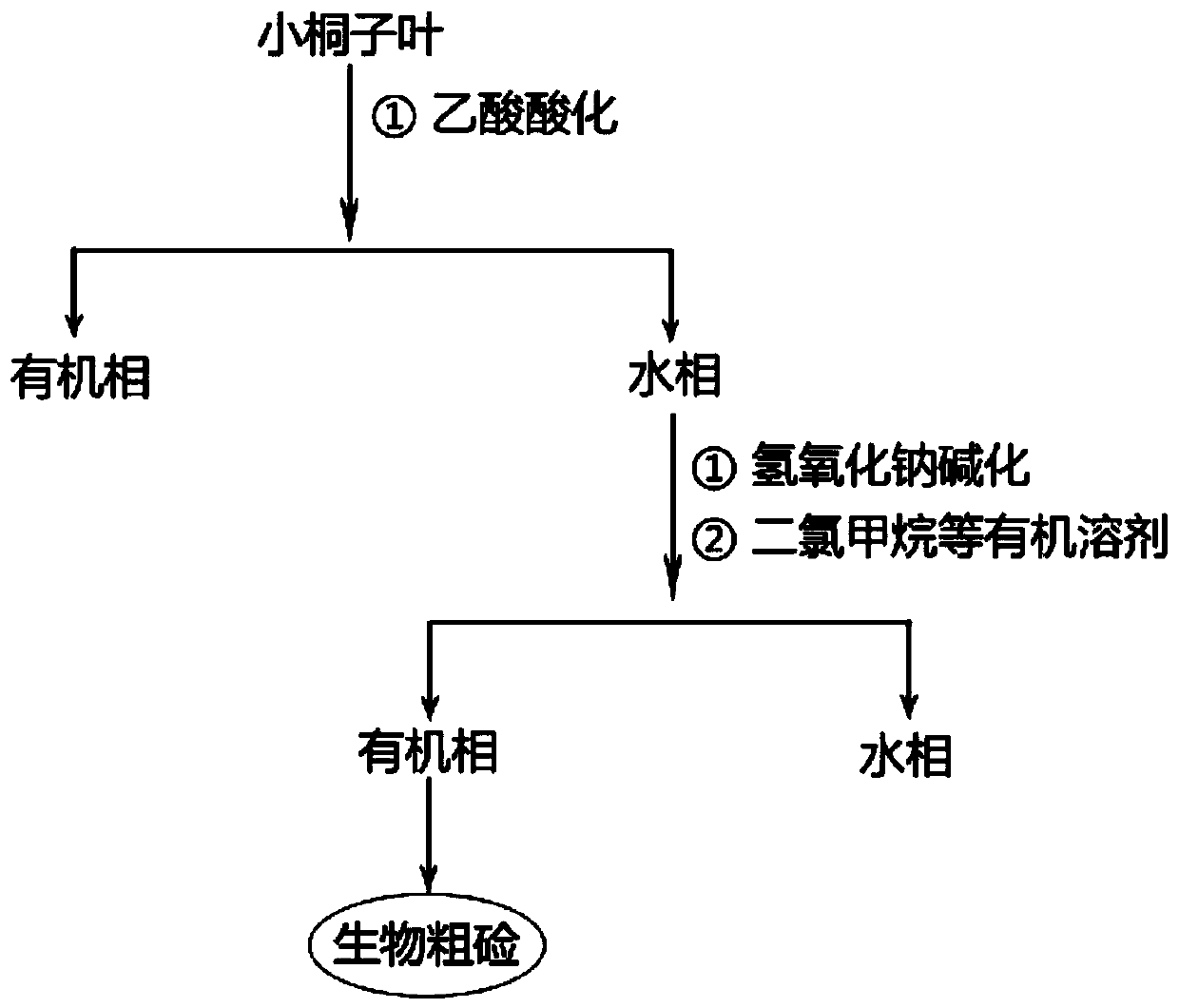
Extraction process of biological crude alkali from leaves of jatropha curcas
An extraction process and technology of jatropha leaves, applied in the field of biotechnology, can solve problems such as less research on jatropha bioalkaloids
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Such as figure 1 As shown, the jatropha leaves were air-dried naturally. Use a pulverizer to crush, sieve, size ≤ 5.0mm, and store at room temperature. Take 1.0 kg of Jatropha jatropha leaves, disperse them in 10 L of absolute ethanol, and process them ultrasonically while stirring. The ultrasonic power is 500 W, and the ultrasonic time is 20 minutes. Remove the residue by filtration, remove ethanol from the obtained yellow solution, add 1.0L of 10% acetic acid aqueous solution, soak for 0.5h, completely dissolve the acidified alkaloid in water, and filter with filter paper to obtain a yellow water phase. This process was repeated twice, and the yellow aqueous phases were combined and concentrated together.
[0028] Add 10% sodium hydroxide aqueous solution to the filtered aqueous phase to adjust the pH value to about 10. Put the combined 3.0L aqueous phase in a suction filter bottle containing filter cloth, vacuum pump suction to remove residue, the pressure of the ...
Embodiment 2
[0030] The jatropha leaves were dried for 18 hours at 60°C in a dryer. Use a pulverizer to crush, sieve, size ≤ 2.0mm, and store at room temperature. Take 1.0 kg of Jatropha Jatropha leaves, disperse them in 10L ethanol / water (95:5), and perform ultrasonic treatment while stirring. The ultrasonic power is 500W, and the ultrasonic time is 20min. Remove the residue by filtration, remove ethanol from the obtained yellow solution by rotary evaporation, add 950 mL of 10% acetic acid aqueous solution to completely dissolve the acidified alkaloid in water, and filter with filter paper to obtain a yellow aqueous solution. This process was repeated twice, and the yellow aqueous phases were combined and concentrated together.
[0031] Add 10% sodium hydroxide aqueous solution to the filtered aqueous phase to adjust the pH value to about 10. Put the combined 3.0L aqueous phase in a suction filter bottle containing filter cloth, vacuum pump to remove residue, the pressure of the vacuum ...
Embodiment 3
[0033] Jatropha leaves were dried for 12 hours at 70°C in a dryer. Use a pulverizer to crush, sieve, size ≤ 3.0mm, and store at room temperature. Take 2.0kg Jatropha leaves, disperse them in 20L ethanol / water (90:10), and ultrasonicate while stirring. The ultrasonic power is 300W, and the ultrasonic time is 30min. Remove the residue by filtration, remove ethanol from the obtained yellow solution by rotary evaporation, add 1.9 L of 8% acetic acid aqueous solution to completely dissolve the acidified alkaloid in water, and filter with filter paper to obtain a yellow aqueous solution. This process was repeated twice, and the yellow aqueous phases were combined and concentrated together.
[0034] Add 20% sodium hydroxide aqueous solution to the filtered aqueous phase to adjust the pH value to about 10. Put the combined 6.0L aqueous phase in a suction filter bottle containing filter cloth, vacuum pump to remove the residue, the pressure of the vacuum pump is 0.5MPa, and then extr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com