Method for treating ischemic tissue
An ischemic, tissue technology, applied in gene therapy, chemical instruments and methods, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problems of high surgical risk, high recurrence rate of vascular occlusion, and high transplant failure rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0086] Impaired blood flow to extremities and soft tissues, usually through large vascular (arterial) and microvascular (capillary) processes, is a major common cause in patients with PAD and CLI. Restoring adequate blood flow to ischemic tissue allows for a successful repair response. Therapeutic angiogenesis refers to the use of drugs, genes, cells, or mechanical devices to induce blood vessel formation in ischemic tissue. The main benefits are inducing the growth of new blood vessels and promoting collateral vessel formation to increase blood flow to ischemic tissues. Angiogenesis may ultimately reduce the risk of adverse cardiovascular events, relieve ischemic pain, heal ulcers, prevent major amputations, and improve quality of life and prolong survival in patients with CLI, especially those who are not eligible for surgery.
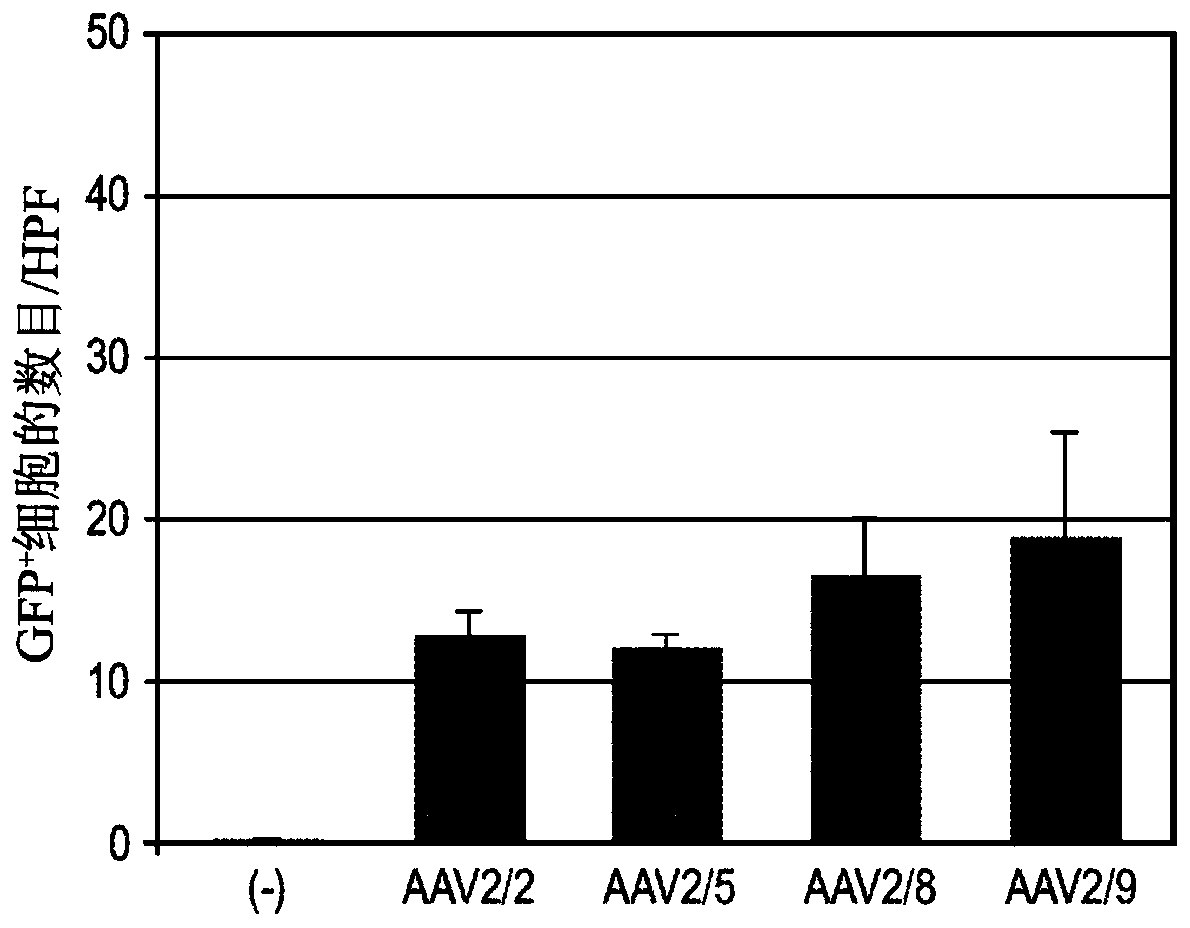
[0087] Adhesion molecules on the cell surface mediate cell-cell interactions and homing. Intercellular interactions mediated by adhesion receptor / ...
example 2
[0099] This example describes the delivery of novel stem cell therapies in the context of the method. In one aspect, administration is derived from BM-engineered tissue repair cells (TRCs) in which E-selectin is pre-installed on the cell surface. These engineered TRCs administered in ischemic limb tissues selectively adhere to activated endothelial cells (ECs) in ischemic tissue vessels expressing elevated counterparts that attract and interact with E-selectin. Ligand) and interact with ECs, especially cells on sprouting tips that reshuffle in sprouting angiogenesis, to promote neovascularization. Alternatively, ECs in wound vessels and tissue cells are primed with E-selectin by using viral vectors to create a supportive tissue microenvironment. E-selectin acts as a docking site for anchoring endogenous or exogenous TRCs expressing E-selectin ligands, thereby increasing the precise interaction / homing of TRCs to ischemic tissue.
[0100] Autologous tissue repair cells (TRC) p...
example 3
[0120] The lack of a reliable animal model of hindlimb gangrene limits molecular studies and preclinical management of critical limb ischemia. This example describes the development and use of a mouse model of hindlimb gangrene to assess the efficacy of gene therapy.
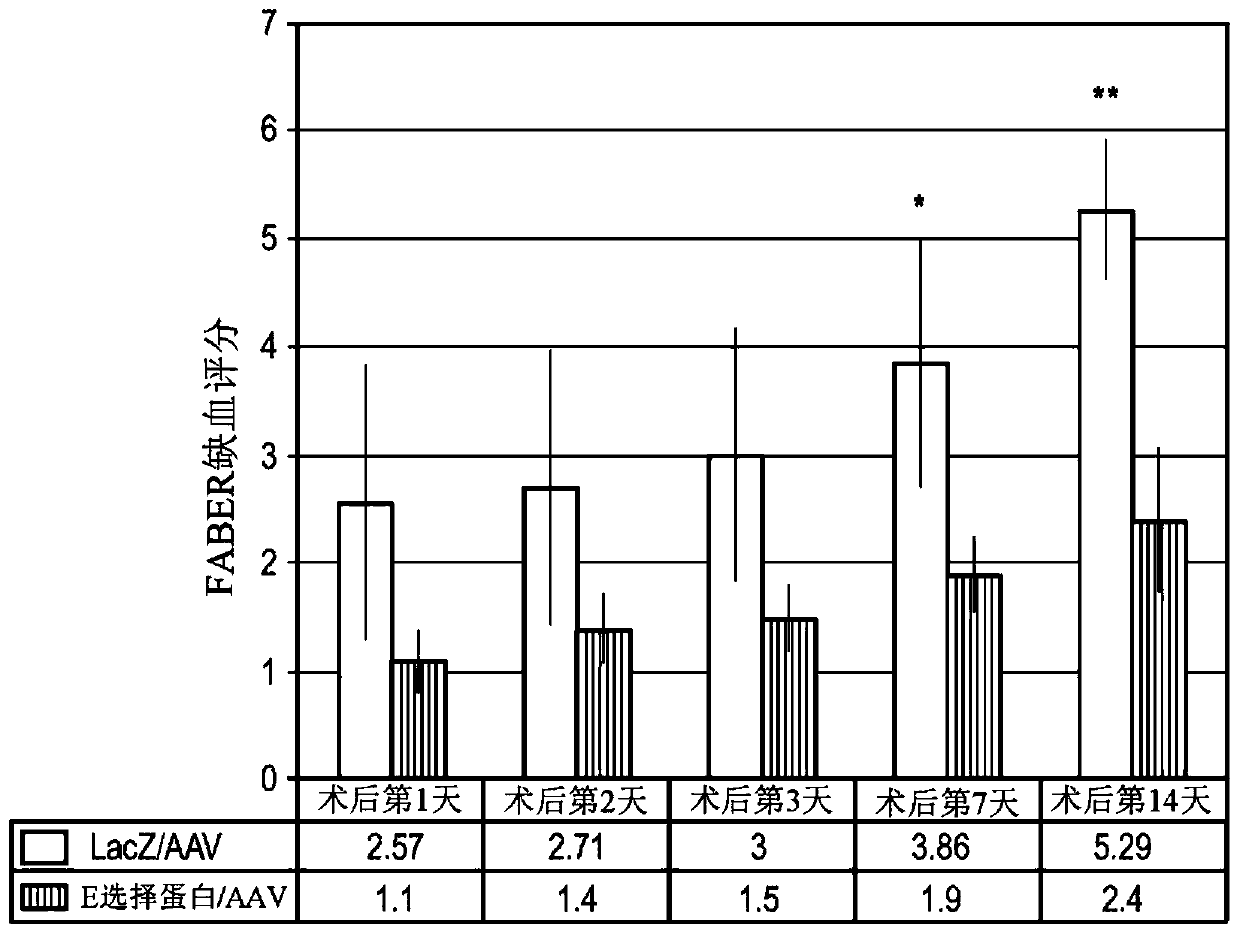
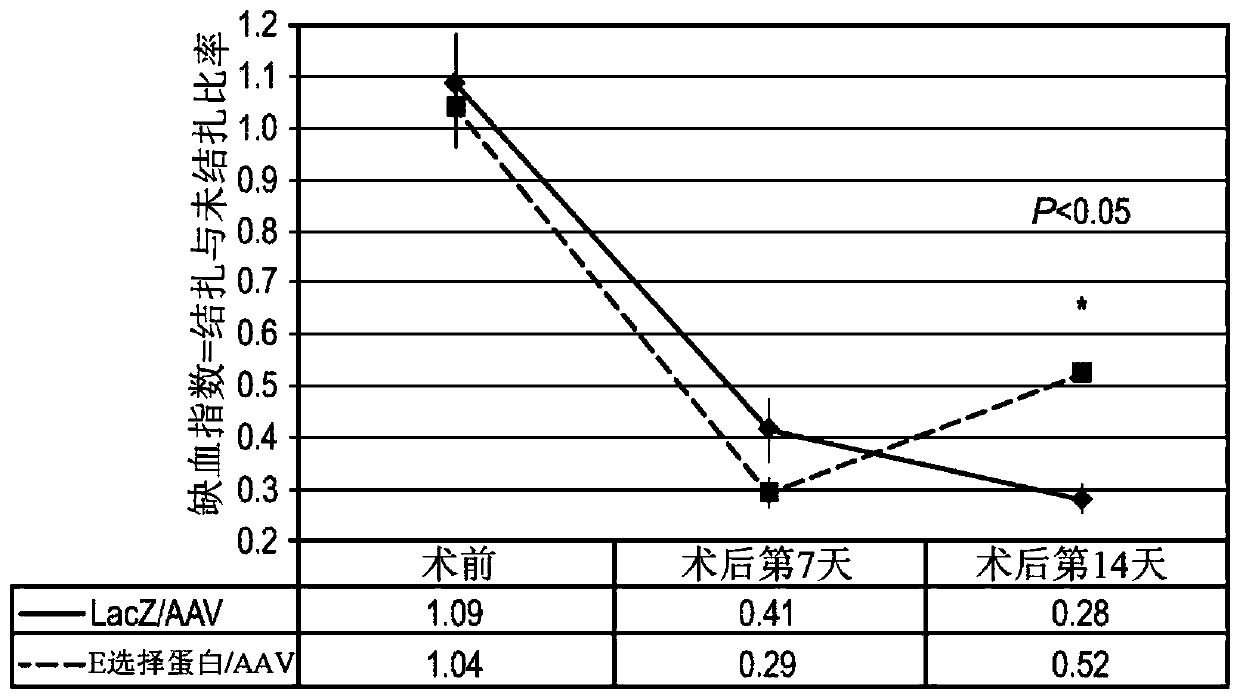
[0121] It was hypothesized that priming of ischemic hindlimb tissue with E-selectin / adeno-associated virus (AAV) would enhance therapeutic angiogenesis and attenuate gangrene.
[0122] Two methods of inducing hindlimb gangrene were tested. In the first approach, FVB mice underwent femoral artery ligation (FAL) to achieve critical limb ischemia. In the second approach, FVB mice were subjected to the FAL combination and administered NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME), a nitrogen oxide synthase inhibitor, which further decreased hindlimb perfusion. E-selectin / AAV (treatment) or LacZ / AAV (control) were intramuscularly administered to the hind limbs of gangrene-induced mice before FAL and L-NAME. Gangrene w...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com