Method for identifying specific sequence fragments of key enzyme genes in specific plant species
A technology of key enzyme genes and sequence fragments, applied in the field of bioinformatics analysis, can solve problems such as long time and difficult cloning
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0103] Example 1 Identification of the Specific Sequence Fragment of Pinoresinol-lariciresinol Reductase (PLR) in Woad
[0104] 1. Obtaining homologous sequences
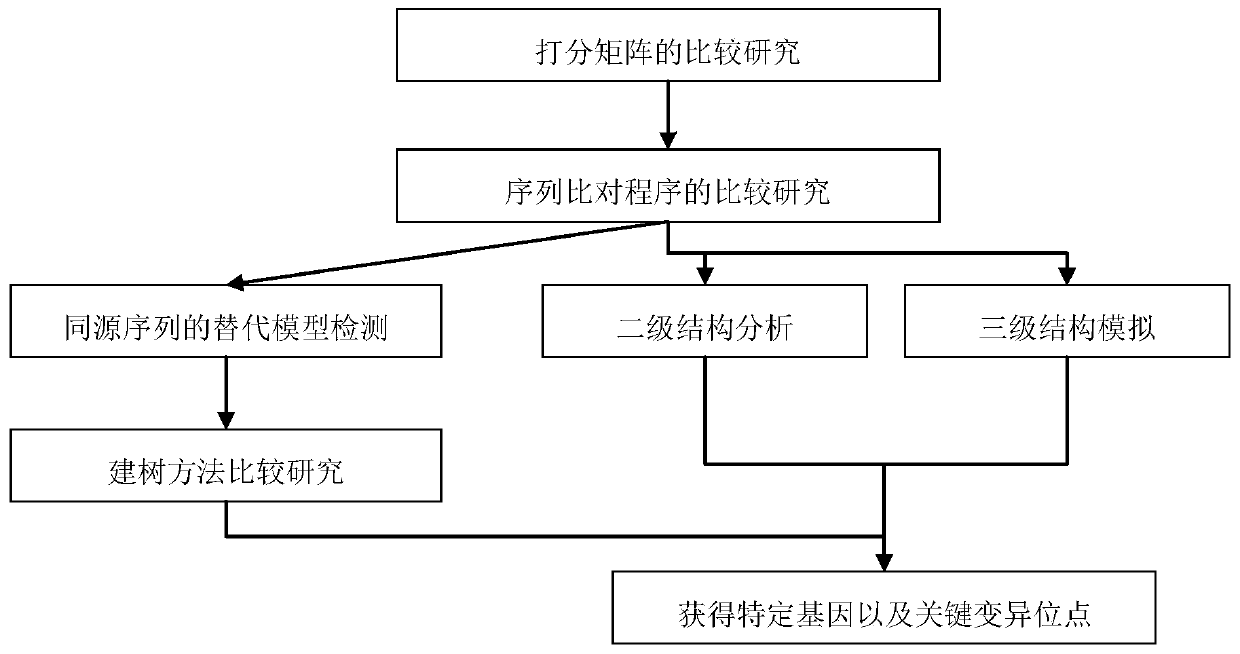
[0105] In order to systematically ascertain the distribution of larch-resinol reductase genes in plant groups, systematically classify them, and explore the phylogenetic relationship of PLR genes in different plant groups, it is necessary to search as many groups as possible to obtain a comprehensive molecular data.
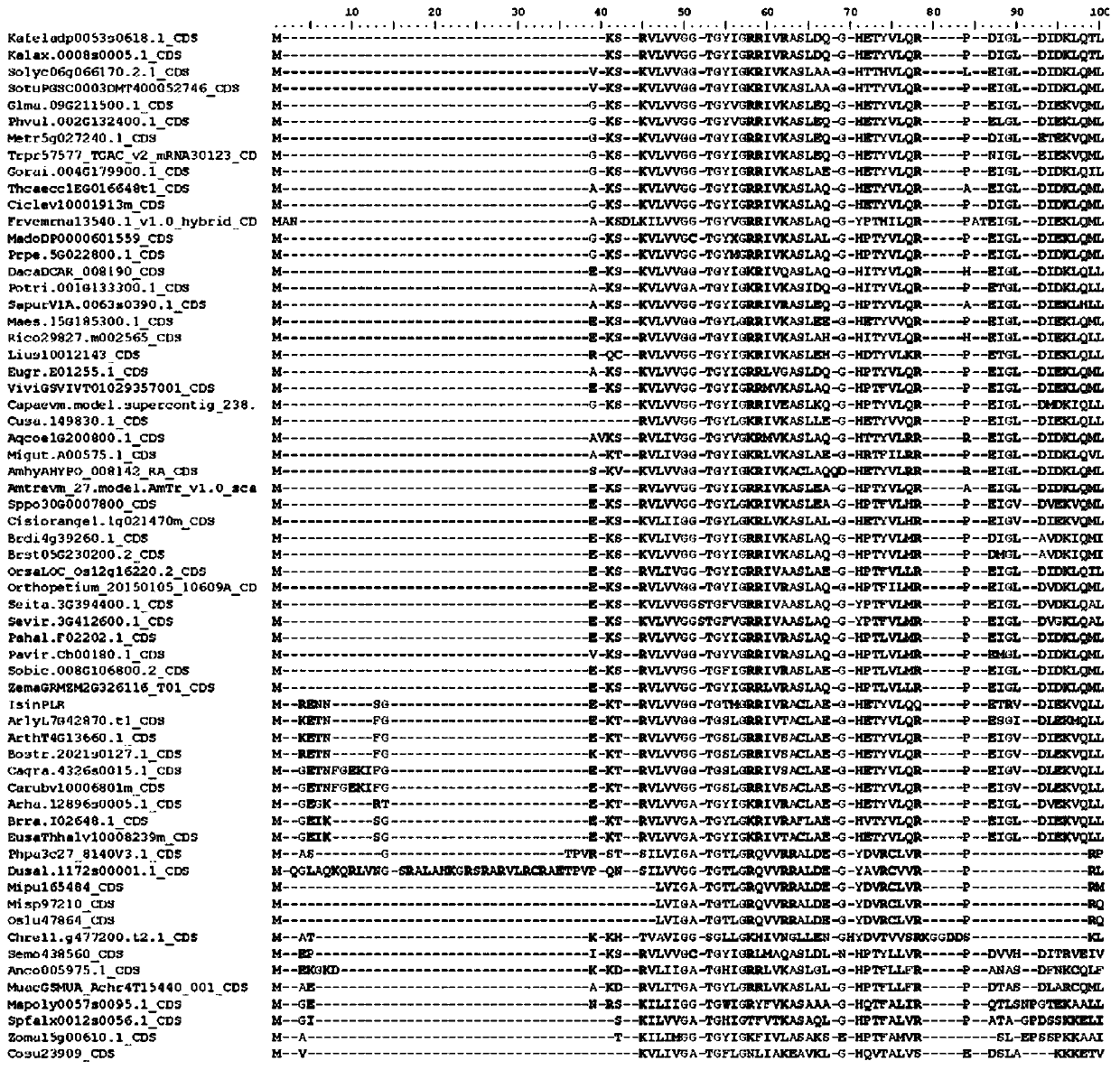
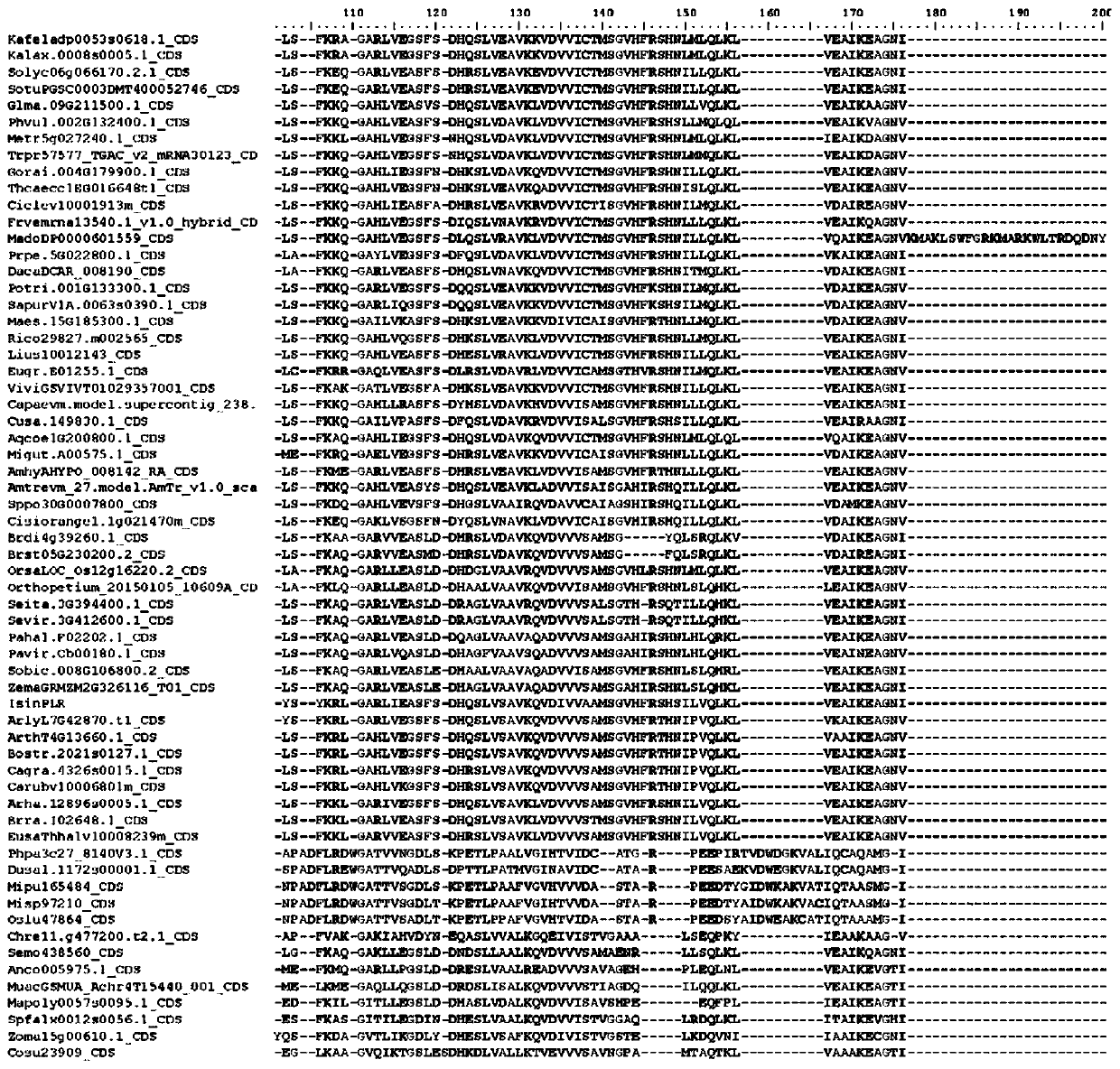
[0106] The flax PLR protein sequence with clear function and PLR gene family structure characteristics was selected as the query sequence (Transcript Name: Lus10012143; Transcript Name: Lus10010403; Transcript Name: Lus10012145; and Transcript Name: Lus10012147) to search for homologous sequences in the database, in 64 The homologous sequence of the PLR gene was obtained by BLAST (Basic Local Alignment Search Tool) in a plant with complete genome sequence information. The main parameters of BLAST...
Embodiment 2
[0149] Example 2 Characterization of the position of specific sequence fragments in the three-dimensional structure of proteins
[0150] In order to infer the distribution position of the specific conserved sequence in the protein structure and the distribution of possible functional sites, the PLR homologous sequence in Isatis indigo was selected and carried out by Swiss-Model (http: / / swissmodel.expasy.org / ) Three-dimensional structural simulation of proteins.
[0151] In order to ensure the accuracy of the simulation, based on the optimal comparison results, according to the global model quality estimation (Global Model Quality Estimation, GMQE) score and the qualitative model energy analysis (QualitativeModel Energy Analysis, QMEAN) score (score The larger the value, the higher the reliability), select the most reliable homologous template, that is, the chain B, Pinoresinol-lariciresinol reductase, 1qyd.1.B) for homology modeling, see the table below 4.
[0152] Table...
Embodiment 3
[0156] Example 3 Application of the 3 sequences obtained in the present invention and their key sites as identification basis
[0157] The present invention has discovered 3 fragments and key sites thereof in Isatis indigo, namely:
[0158] SEQ ID NO: 1: MR E NNSGEK T RV, corresponding to motif 15;
[0159] SEQ ID NO: 2: LQ Q PETRVDIEKVQLLYSYKRLGARLIEAS, corresponding to motif 10;
[0160] SEQ ID NO: 3: DH EVGDDE, corresponding to motif 9.
[0161] The protein sequences of larch resin alcohol reductase from 4 different species were searched in NCBI (https: / / www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov / ) database, and compared with the sequence of Isatis indica. The different larch resin alcohol reductase protein sequences are poplar: Populus alba, TKS01263.1; japonicus: Lotus japonicus, BAF34846.1; strong spiny ball: Ferocactus pilosus, AYU58880.1; cactus: Echinocactus platyacanthus, AYU58879. 1). After comparison, it can be found that motif 15, motif 10 and motif 9 and their specific site...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com