Wide-energy-spectrum white-light neutron resonance photographic detector and detection method
A detector and neutron technology, applied in the field of wide-energy spectrum white light neutron resonance photographic detector and detection, can solve the problems of poor radiation resistance, difficult imaging to achieve ideal results, and no C element distribution image presented.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
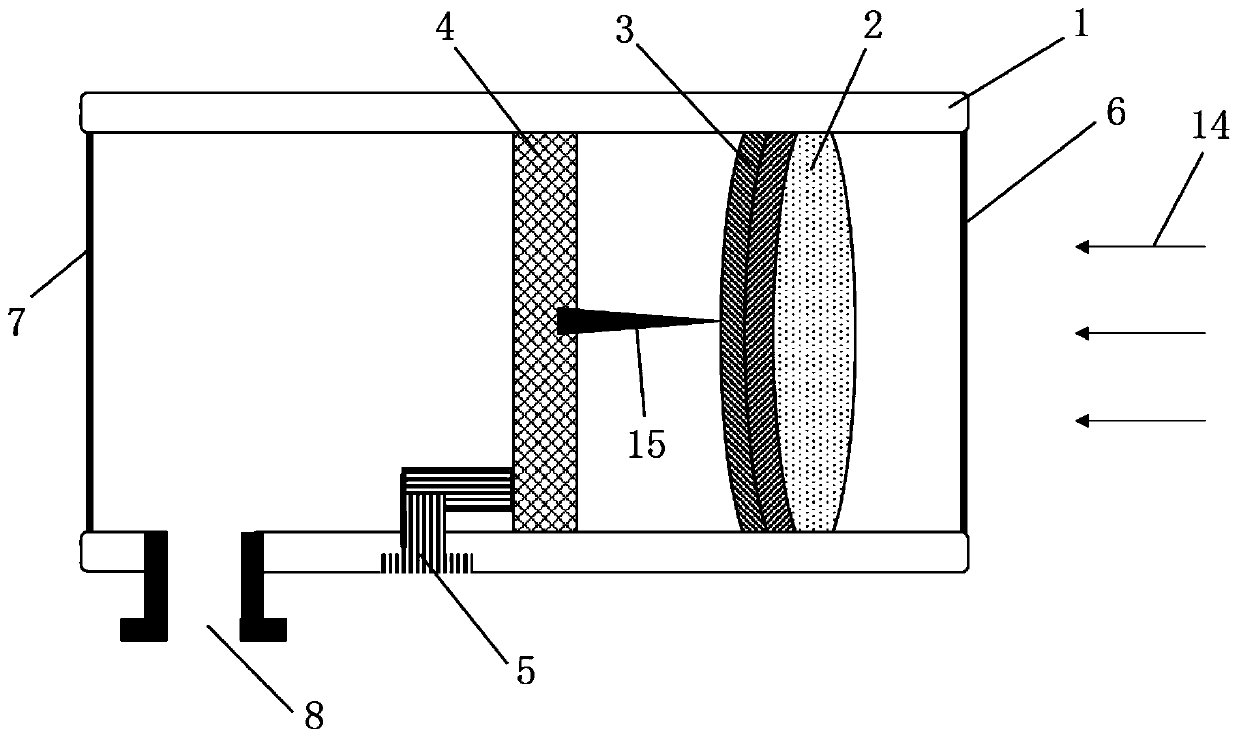
[0041] In this embodiment, a wide-energy-spectrum white-light neutron resonance photographic detector, such as figure 2 As shown, it includes detector body 1, neutron-sensitive MCP2, ordinary high-performance MCP3, position-sensitive anode strip array circuit board 4 and signal lead-out electrode 5. The interior of the detector body is a cavity structure, and the two ends of the detector body are respectively There are incident window 6 and rear window 7. Along the direction from the incident window to the rear window, neutron-sensitive MCP, ordinary high-performance MCP and position-sensitive anode strip array circuit board are sequentially arranged inside the detector body, and the side wall of the detector body near the rear window There is a vacuum port 8 on the top, and the signal lead-out electrode is connected to the position-sensitive anode strip array circuit board, and one end of the signal lead-out electrode is arranged on the side wall of the detector body. Wherei...
Embodiment 2
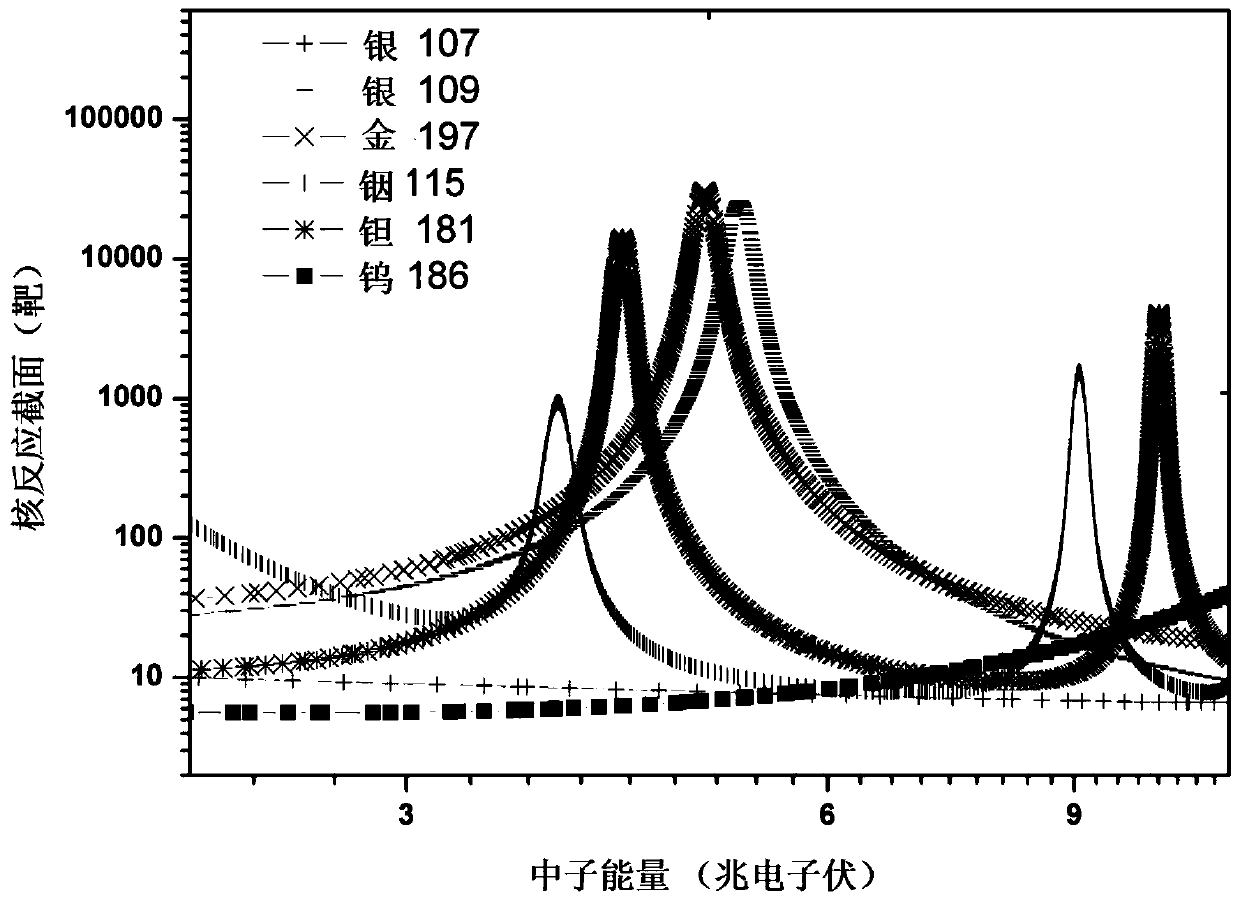
[0056] In this embodiment, a wide-energy-spectrum white-light neutron resonance photographic detector, such as Figure 5 As shown, compared with Embodiment 1, the difference lies in that the surface of the neutron-sensitive MCP close to the incident window is also covered with a plastic scintillation screen 16 . The neutron-sensitive MCP added with a plastic scintillation screen is used as a neutron conversion material to convert high-energy neutrons into fluorescence, and photons can also excite electrons in the neutron-sensitive MCP, which can obtain sufficient high-energy neutrons of MeV or higher The detection efficiency is high, thus covering the entire white light neutron resonance energy region (<20MeV), but adding a plastic scintillation screen will bring the problem of "the diffusion effect of scintillation light leads to a decrease in the position resolution ability".
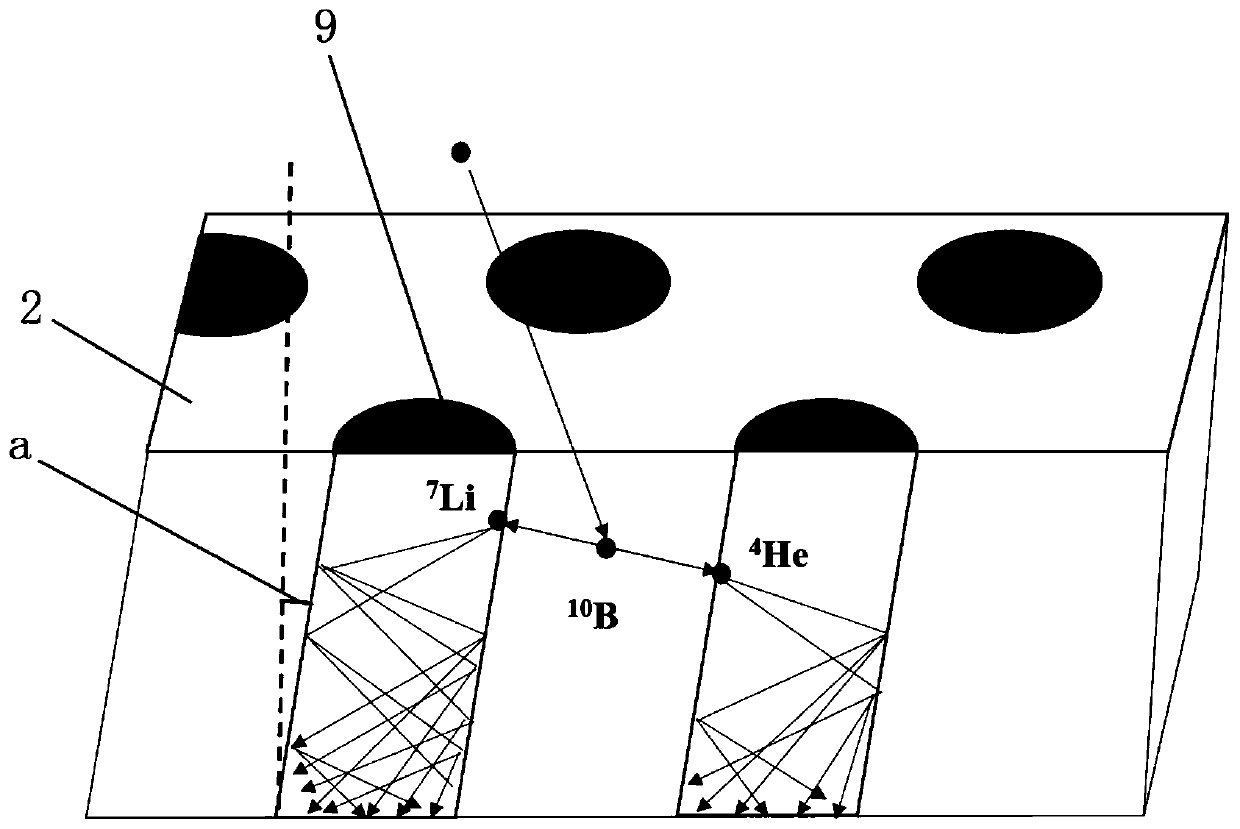
[0057] The principle is: 10 The cross-section of the capture reaction between B nuclides and neut...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com