Application of retinoic acid receptor reactive protein 1 as a biomarker in chronic kidney disease
A technology for retinoic acid receptors and chronic kidney disease, applied in biological testing, biomaterial analysis, disease diagnosis, etc., can solve the problems of lack of sensitivity, specificity, and poor specificity in risk stratification, and achieve the purpose of guiding clinical treatment and judging prognosis , high specificity, good clinical treatment and prognosis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Upregulation of retinoic acid receptor reactive protein 1 in chronic kidney disease
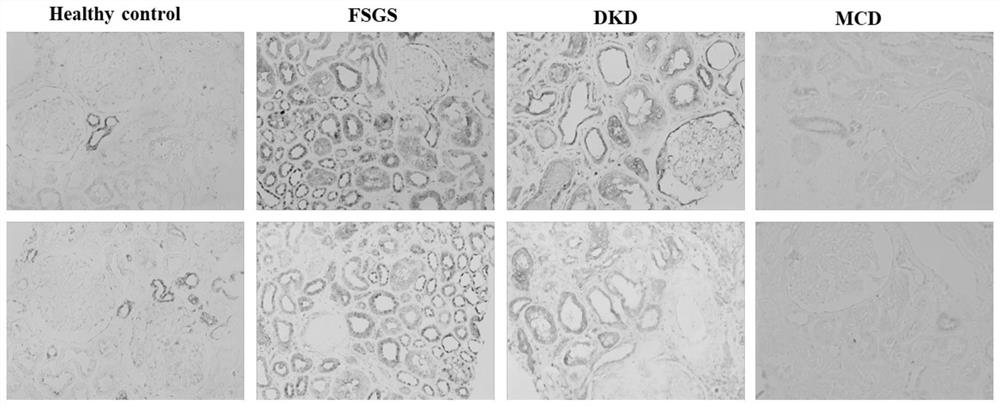
[0036] Immunohistochemical staining of kidney biopsy specimens in the early stage of CKD (chronic kidney disease),
[0037] Collect kidney biopsy specimens of different types of CKD early stage (GFR>60ml / min) (FSGS, DKD, MCD, etc.) with complete clinical data (including etiology, ACR, GFR, CRP, etc.), and use the relatively normal specimens around the nephrectomy tumor The tissue was used as a control, and the paraffin section was subjected to antigen retrieval according to the conventional method, followed by immunohistochemical staining, using the Santa Cruz TIG1 antibody (sc-98965, diluted 1:50) as the primary antibody, horseradish peroxidase-labeled goat antibody Rabbit secondary antibody was used to detect the expression level of RARRES1. The result is as figure 1 as shown, figure 1 It revealed that the expression of RARRES1 was significantly up-regulated in the FSGS group and ...
Embodiment 2
[0039] The transmembrane protein RARRES1 can be cleaved to have a soluble splice body
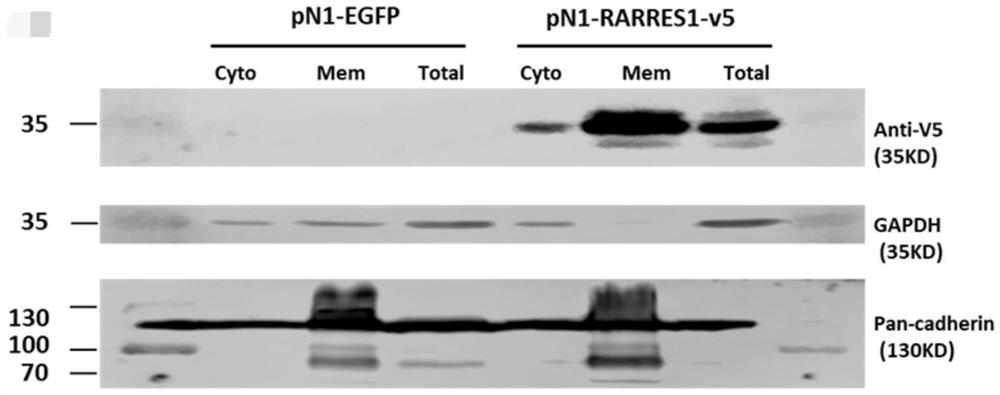
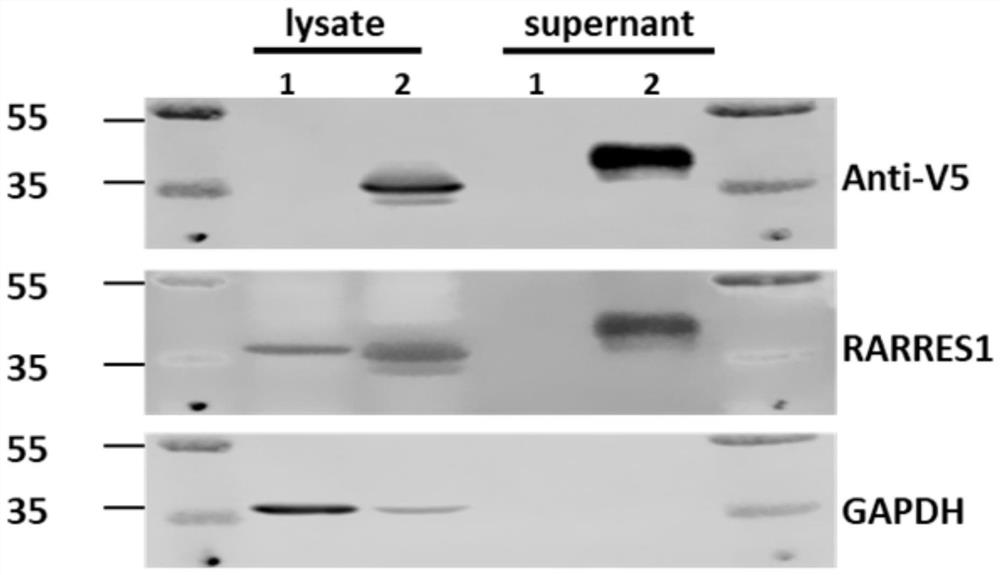
[0040] It is generally accepted that RARRES1 is a type I transmembrane protein. In this example, the human RARRES1 subtype eukaryotic expression plasmid (pN1-RARRES1-v5) was transfected into 293T cells, and the cell membrane proteins were extracted using the instructions of the Biovision Cell Membrane Protein Extraction Kit (Catalog #K268), and loaded separately 30 μl of cytoplasmic protein, total cell membrane protein, and total cell protein were subjected to western-blot, and V5 antibody was used to detect RARRES1, and Pan-cadherin was used to detect known membrane proteins. The results suggested that membrane proteins were rich in RARRES1, which was consistent with the prediction of transmembrane proteins ( like figure 2 shown). At the same time, 24 hours after plasmid transfection, serum-free medium was used, cell culture supernatant was collected, and 30ug of cell total protein and ...
Embodiment 3
[0042] The human RARRES1 genome sequence was amplified from the SPORT 6 plasmid by PCR method, and a Xbal I restriction site was added at the C-terminus while carrying the V5 tag. The PCR product was then ligated into pGEMTasy vector (Promega A1360). At the same time, the human RARRES1 gene fragment was cloned into the pTRETight vector (Clontech: CAT NO.631059) with EcoR I and NheI restriction sites to make it contain AFEI restriction sites. Subsequently, the human RARRES1-V5 fragment was cloned into the above-mentioned vector digested with AFEI and NotI double enzymes, and the pTRE-hRARRES1-v5 vector was constructed. After the pTRE-hRARRES1-v5 vector was digested with EcoRI and NotI, it was inserted into the vector of pN1-EGFP digested by the same double digestion, and pN1-RARRES1-v5 was constructed ( Figure 5 ).
[0043] The human RARRES1 genome sequence was amplified from the SPORT 6 plasmid by PCR, StuI and XbaI restriction sites were designed at both ends, and connecte...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com