Salmonella phage LPST144 and antibacterial application of lyase of salmonella phage LPST144
A technology of LPST144 and bacteriophage lyase, applied in the field of Salmonella bacteriophage, can solve problems such as inability to effectively lyse bacteria, and achieve the effect of preventing pollution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
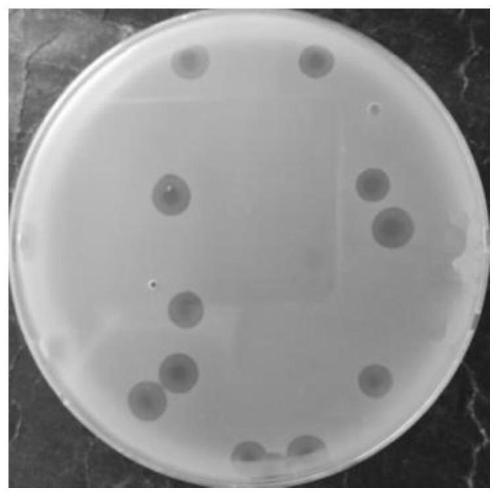
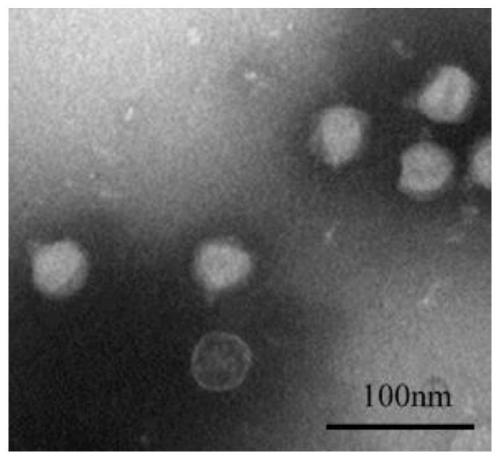
[0030] Example 1 Phage isolation and purification and morphological analysis
[0031] Samples taken from nature and Salmonella typhimurium ATCC 13311 cultured to logarithmic phase were cultured in liquid overnight for 12 h to 18 h, filtered through a 0.22 μm microporous membrane, and the filtrate was repeated according to the above method to obtain a phage stock solution. The purified phage adopts the double-layer plate method, and purifies continuously for 5-10 times until the size and transparency of the plaques appearing on the double-layer plate are consistent, that is, the purified phage ( figure 1 ). The phages were negatively stained with phosphotungstic acid, and then placed under a transmission electron microscope to observe the phage morphology. The specific operation steps were as follows: the copper mesh was immersed in the phage solution for 10 min, and then the excess liquid was absorbed with filter paper, and then the copper mesh was placed in phosphotungstic ac...
Embodiment 2
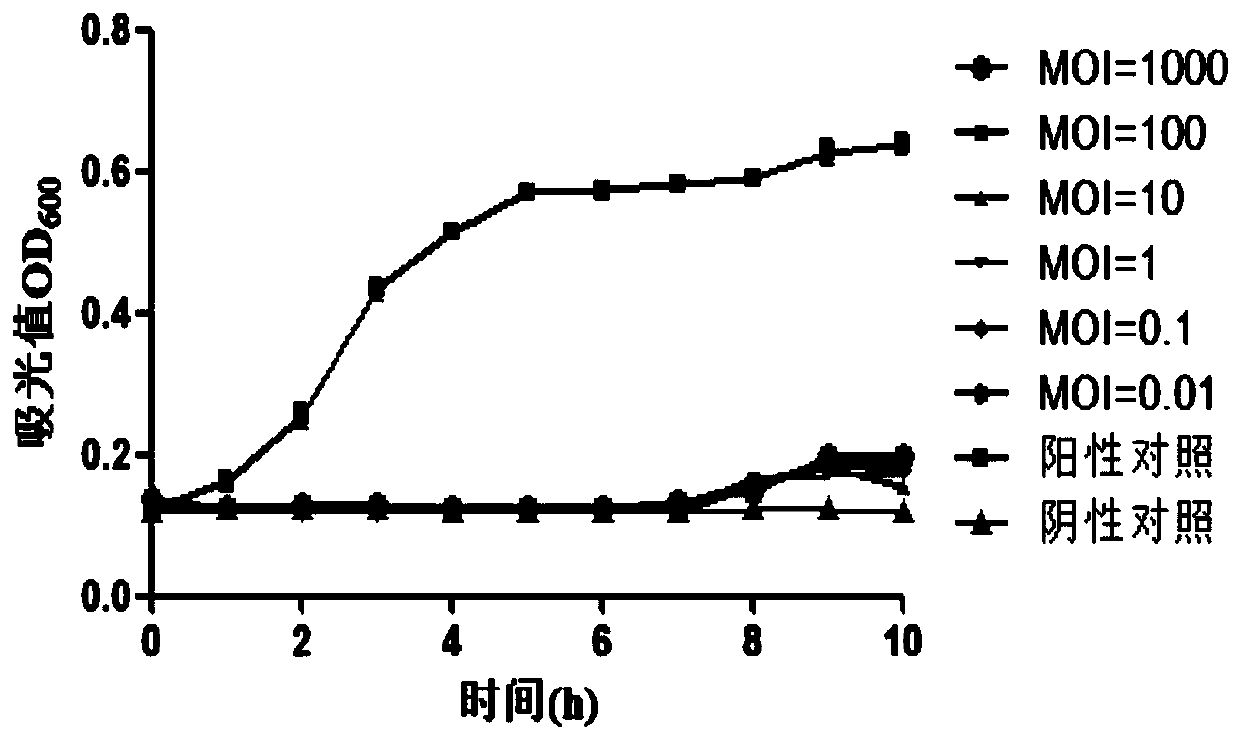
[0033] Example 2 Phage lysis curve
[0034] Set the multiplicity of infection MOI=1000, 100, 10, 1, 0.1, 0.01, 0.01, add 100 μL of each to the 96-well plate, and add 100 μL of 10 7 CFU / mL of the host bacteria Salmonella. Separate negative control by adding 200μL TSB medium; positive control adding 100μL10 7 CFU / mL of the host bacteria Salmonella broth and 100 μL TSB medium. The absorbance at 600 nm was measured every 1 h for a total of 10 h.
[0035] see the results image 3 As shown, the growth trend of the positive control group in the phage lysis curve was consistent with the normal growth trend of Salmonella. The phage showed certain lytic activity when infecting Salmonella at different MOIs. The bacteriophage has the strongest ability to lyse the host bacteria. The optical density of bacteria in the experimental group added with bacteriophage remained at the initial value and did not increase, which could completely inhibit the growth of bacteria. Completely killed...
Embodiment 3
[0036] Example 3 Salmonella phage LPST144 host lineage analysis results
[0037] The phage host profile was determined by the spotting method. Take 100 μL of the bacterial liquid to be tested that has been cultured to the logarithmic phase, add it to the warm semi-solid medium, and pour it into the pre-prepared LB plate after mixing. 9 Phage of PFU / mL was added dropwise to the surface of the upper plate, dried and then placed in an incubator at 37°C for 4 h to 6 h to observe the lysis (Table 1): Phage LPST144 can lyse 4 strains of different serotypes, among which the host bacteria Salmonella typhimurium (ATCC13311) has a significant lysis effect and can form transparent and clear plaques, but cannot lyse Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Listeria, Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The above results indicate that the phage LPST144 has a narrow host spectrum and strong specificity.
[0038] Table 1 The results of host profile analysis of bacteriophage ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com