Plasma molecular marker combination for predicting radiation damage
A technology for radiation damage and plasma, which is applied in the field of plasma molecular marker combinations for predicting radiation damage, and can solve problems such as large fluctuations and difficult radiation doses
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
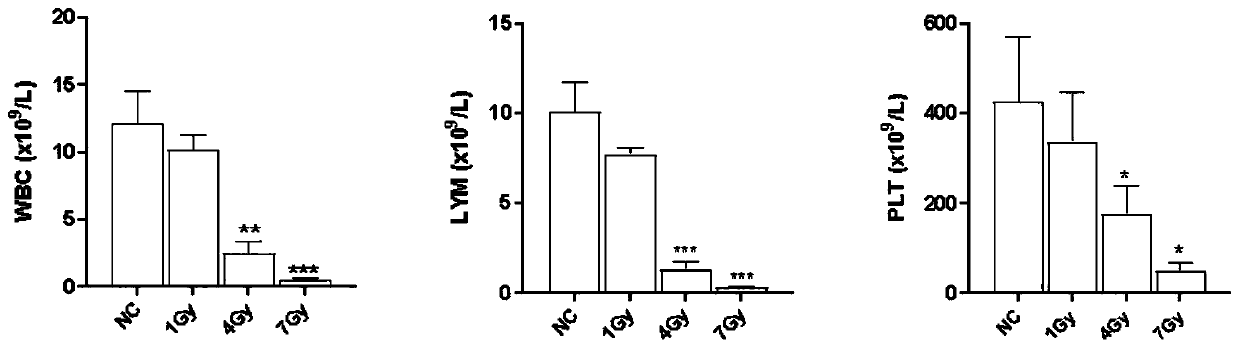
[0075] Example 1. With the increase of irradiation dose, the degree of injury of mice gradually increased
[0076] 6-8 weeks C57BL / 6 mice, a total of 40, were randomly divided into 4 groups, 10 mice in each group, and were subjected to 0, 1, 4, 7Gy 60 After Coγ-ray irradiation, blood was collected through the tail vein on the third day, and the number of white blood cells (WBC), lymphocytes (LYM) and platelets (PLT) in peripheral blood was analyzed with an automatic blood cell analyzer.
[0077] The result is as figure 1 shown. The results showed that after different doses of γ-ray irradiation, the number of WBC, LYM and PLT in the peripheral blood images gradually decreased with the increase of the irradiation dose, indicating that with the increase of the irradiation dose, the degree of injury of the mice was gradually aggravated.
Embodiment 2
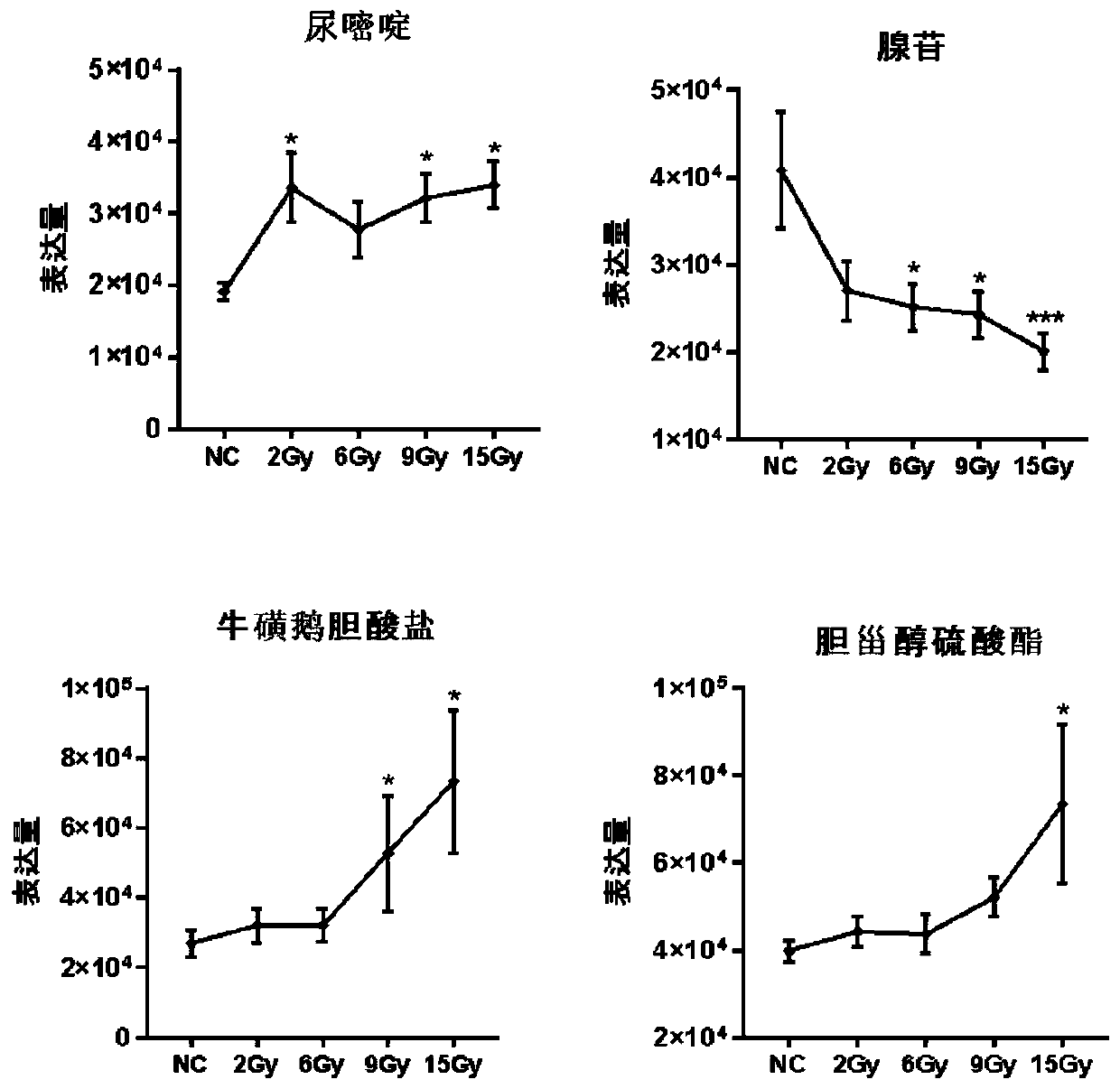
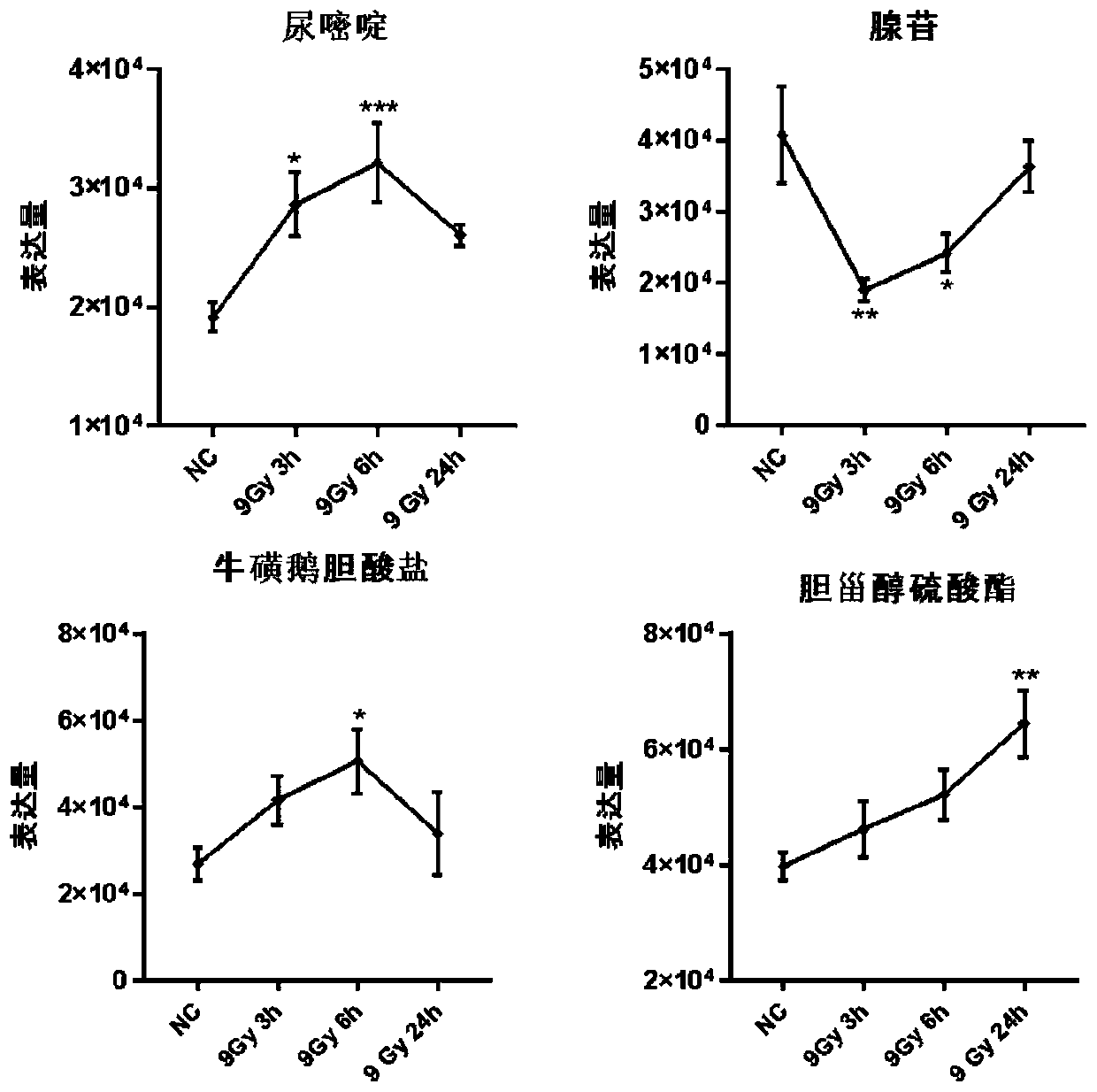
[0078] Example 2. Preparation of samples for detection of plasma markers after irradiation in mice
[0079] 6-8 weeks C57BL / 6 mice, a total of 80, were randomly divided into 8 groups, 10 mice in each group, and 5 groups were treated with 0, 2, 6, 9, 15Gy 60 Coγ-rays were irradiated, and blood was collected 6 hours after irradiation; the other three groups received 9Gy 60 Coγ-rays were irradiated, and blood was collected 3, 6, and 24 hours after irradiation.
[0080] After the mice were anesthetized, blood was collected from the heart, anticoagulated with heparin, centrifuged at 3000rpm, plasma was extracted, stored and transported at -80°C.
Embodiment 3
[0081] Embodiment 3, mass spectrometry sample processing and analysis
[0082] Take out the samples stored in Example 2 at -80°C, slowly dissolve at 4°C, take 100 μl of samples from each group, add 400 μl of pre-cooled methanol-acetonitrile solution (1:1, v / v), vortex for 60 seconds, and place at -20°C Precipitate protein for 1h, centrifuge at 14000rcf, 4°C for 20min, and take the supernatant to freeze-dry. The samples were separated by Agilent 1290 Infinity LC ultra-high performance liquid chromatography system (UHPLC) HILIC column, and detected by electrospray ionization (ESI) positive ion and negative ion modes respectively. The samples were separated by UHPLC and analyzed by mass spectrometry with Triple TOF 5600 mass spectrometer (AB SCIEX).
[0083] The specific experimental conditions are:
[0084] Chromatographic conditions: the samples were separated by Agilent 1290 Infinity LC ultra-high performance liquid chromatography system (UHPLC) HILIC column. The column tem...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com