Reagent, kit and device for detecting tumor micro-environment of colorectal cancer as well as application of reagent
A tumor microenvironment and detection reagent technology, which is applied in the field of colorectal cancer tumor microenvironment detection reagents
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0096] Four cases of stage II patients were selected: 2 cases of rectal adenocarcinoma, 1 case of colonic mucinous adenocarcinoma, and 1 case of colonic adenocarcinoma with mucinous adenocarcinoma.
[0097] Table 4:
[0098] Numbering tumor site Clinical stage T stage Follow-up time (year) whether to die 1 rectum II 4 6.7 no 2 high rectum II 3 4.0 no 3 Sigmoid colon II 4 1.7 no 4 ascending colon II 4 1.2 yes
[0099] Multiplex immunohistochemical analysis of immune cells and immune checkpoint molecular detection was performed on the paraffin sections of the tumor tissues of the above four cases. 2 slices per patient, a total of 2 staining panels, and a total of 10 molecules were labeled. The staining order of each molecule in 10 staining molecules and 2 panels is: Panel1: CD45RO, PD-L1, CD8, CD3, PD1; Panel2: FoxP3, CD163, CD68, CD4, PDL1, CD57.
[0100] Perform multiple immunohistochemical analysis of i...
Embodiment 2
[0133] DNA samples from 120 stage II CRC cases were used to construct a genome-wide sequencing library, and high-throughput sequencing was performed to detect whether there was a mutation in the POLE gene. The test results were as follows: 20 cases of POLE gene mutation samples among 120 samples, and 20 SNP site mutations were involved in total, and 100 cases of POLE gene wild type samples.
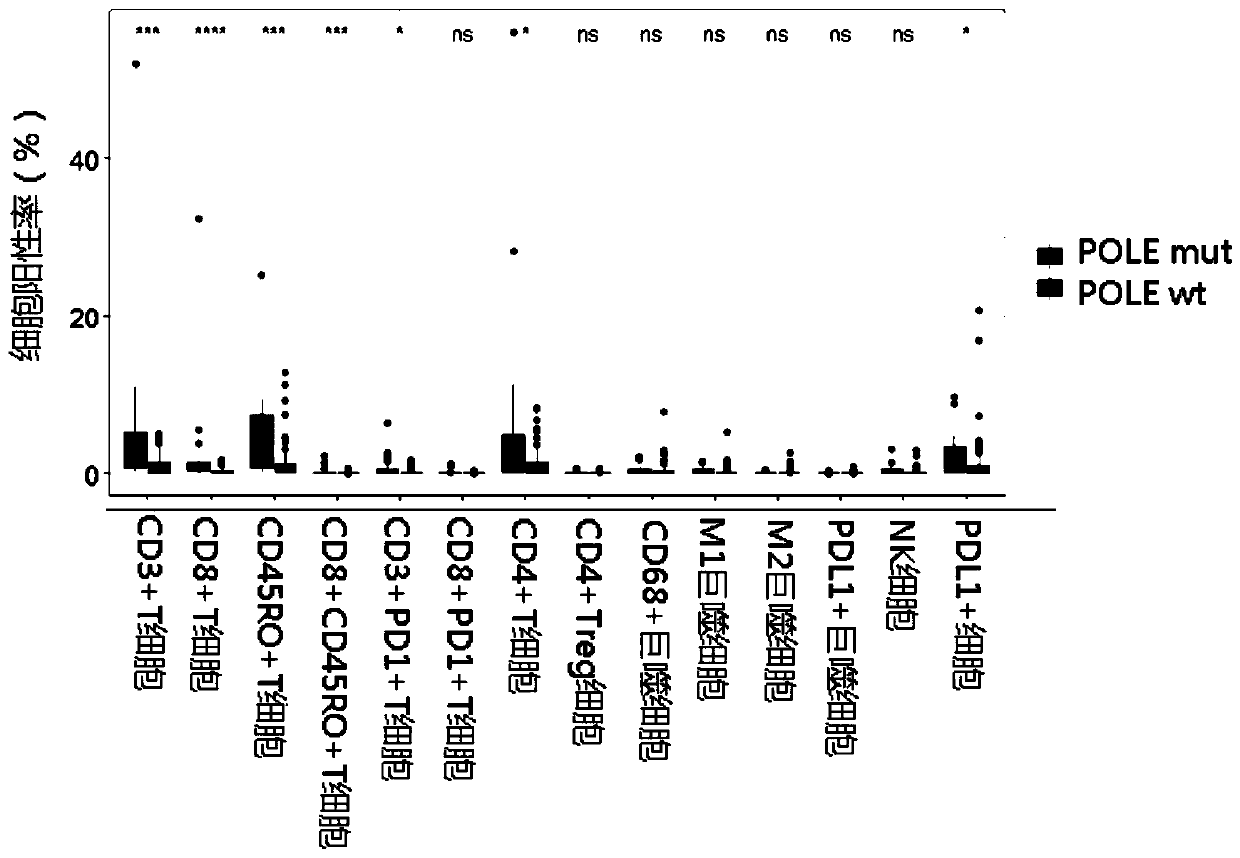
[0134] The POLE gene wild-type samples and POLE gene mutant samples were divided into two groups, and the expression of each molecular marker was detected by the same multiple immunohistochemical method as in Example 1, and the corresponding immune responses of the POLE gene mutant and wild-type samples were detected. The positive rate expression of microenvironmental marker cells. See the test results figure 1 , figure 1 The percentage of positive cells for the different genotypes of POLE and expression of each molecular marker or bimolecular marker is shown.
Embodiment 3
[0136] The same multiple immunohistochemical detection method as in Example 1 was used to detect the positive rate of cells of each molecular marker in the tumor epithelium (CT) in 120 cases of stage II CRC. The test results are shown in Table 2 and Table 3.
[0137] From the above description, it can be seen that the above-mentioned embodiments of the present invention have achieved the following technical effects: the use of the detection reagent of the POLE gene provided by the application and the molecular markers in any of the above-mentioned combinations and the combination thereof are effective against colorectal cancer. When testing, the tumor microenvironment of the corresponding patient can be detected more accurately, so that the survival and prognosis of the sample to be tested can be guided and predicted more effectively.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com