NGS-based automated sequencing analysis method and device for minimal residual disease
A small residue, sequencing analysis technology, applied in sequence analysis, genomics, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of potential harm to the human body, lack of a mature analysis process, and inability to detect cell subclones
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0107] Embodiment 1 analysis method construction
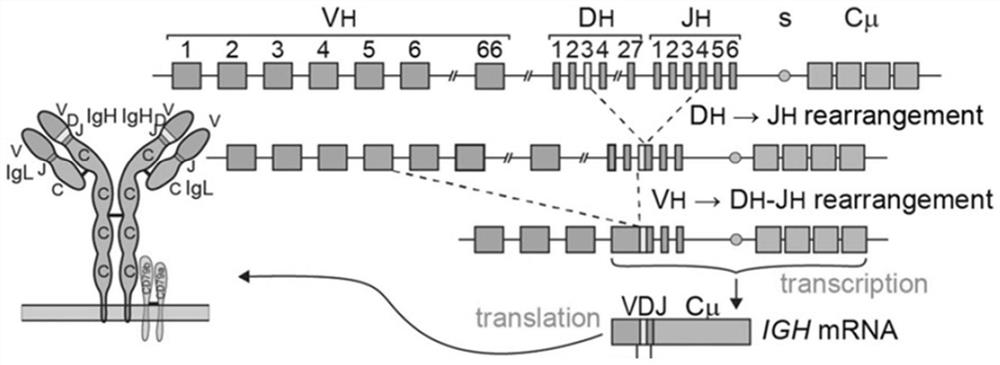
[0108] 1. Capture amplification: based on the antibody VDJ rearrangement process (see figure 1 ), for the primer pools designed for the V and J regions of B cells, two primer pools were used in this application, one was composed of 34 primers designed in the FR2 region of the V region and 4 primers designed in the J region The other is a primer pool composed of 33 primers designed in the FR3 region of the V region and 4 primers designed in the J region. These two primer pools can perform specificity with all the V and J regions. Combined, it can comprehensively and specifically capture and amplify the VDJ region. The first round of PCR amplification is performed on the V / J region of the B cell by using the above primer pool to obtain the amplification product.
[0109] 2. Library construction and sequencing: Perform two rounds of PCR amplification on the above-mentioned amplification products, construct an on-board library b...
Embodiment 2
[0145] Embodiment 2 parameter optimization
[0146] This application optimizes the conditions and parameters of each step in the analysis method, and some examples of optimization tests are as follows:
[0147] Optimize the identity and coverage parameters in the sequence clustering step:
[0148] The identity selection parameters are 0.8, 0.85, 0.9, 0.95, and 1; the parameters s, aL, and aS in coverage are respectively selected as 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6, 0.7, 0.8, and 0.9. Use the combination of two parameters to verify, and the specific results are shown in the following table:
[0149] Table 1 Sample cdhit clustering results
[0150]
[0151]
[0152] The values in the above table represent the sequence numbers of the dominant clones of the sample obtained after clustering and merging the same CDR3 classes, and the actual number of dominant clone sequences of the sample is 36767 (that is, the real result of separate statistics without clustering) . It can be seen fr...
Embodiment 3
[0153] Embodiment 3 verification experiment
[0154] The method steps of Example 1 were used to detect and analyze the bone marrow samples of 5 leukemia patients, and the sample number was named: (number of times of inspection +) sending hospital + sample number + name of person.
[0155] Two groups were set up in the experiment: Group 1: NGS workflow optimized for analysis in this application; Group 2: ddPCR (Droplet DigitalPCR) control group. ddPCR is to divide the sample into a large number of reaction wells and perform PCR on the target gene. The wells containing the target gene are counted as positive by PCR amplification, and the wells not containing the negative count are counted. Since ddPCR involves counting positive wells (positive rate), it has the advantage of being able to perform direct and absolute quantification without direct comparison with a reference sample or standard sample, which can be used as a reference control for this application. Table 1 compares ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com