Underground water remediation method for pesticide contaminated site
A technology for groundwater remediation and pesticide pollution, which is applied in the field of water treatment, can solve the problems of low removal efficiency, long cycle, and inability to fully decompose organic pollutants, and achieves reduced investment and operating costs, simple operation, and high treatment efficiency. good effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
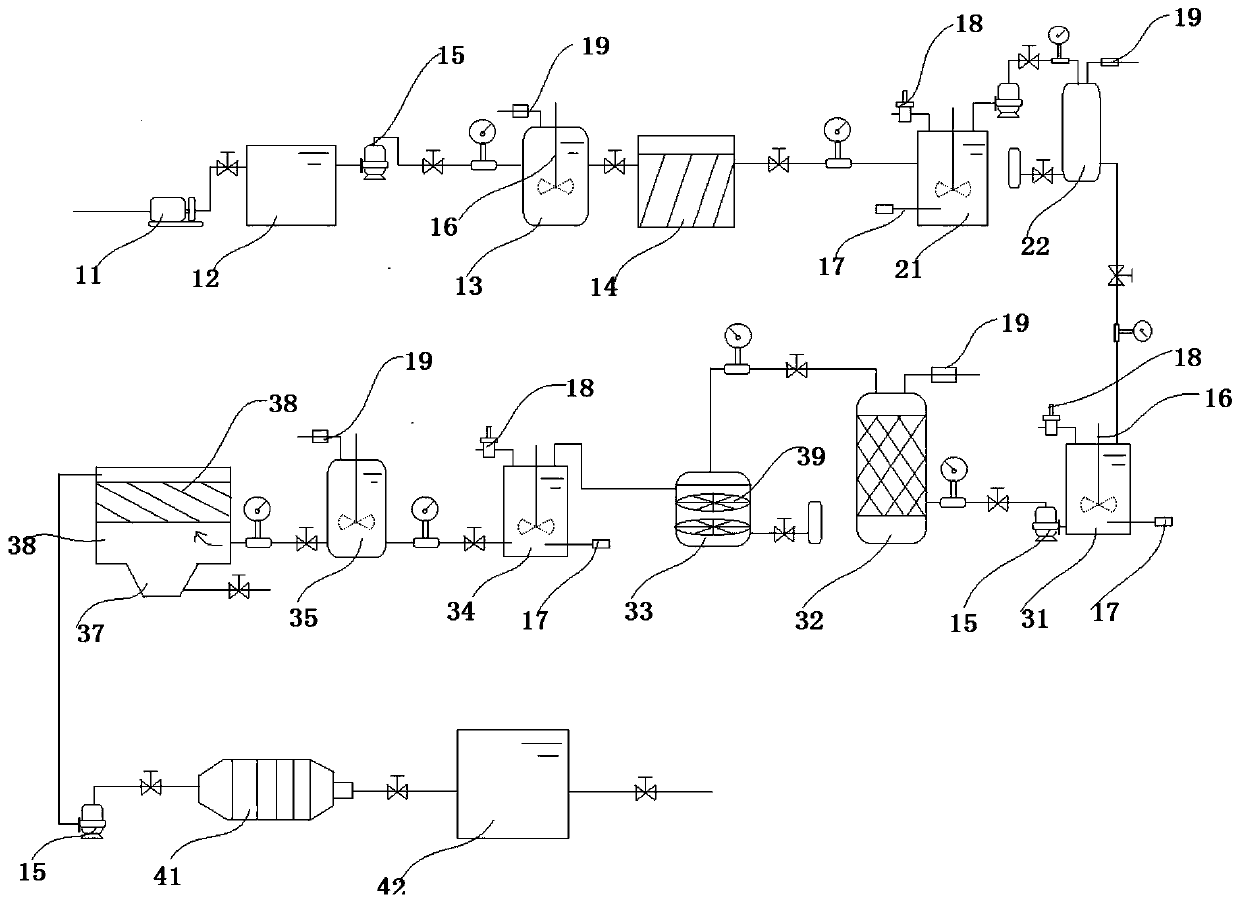
[0050] Homogenize the groundwater in the pesticide-contaminated site for 12 hours; coagulate polyacrylamide and magnetic seeds for 45 minutes; then discharge it into a supermagnetic separator to separate the magnetic seeds and coagulation sediments, and the speed of the supermagnetic separator is 0.1r / min; adjust the pH of the water treated by the ultra-magnetic separator to 3, then pump it into the micro-electrolysis reaction tower, and add iron filings and carbon particles for micro-electrolysis treatment for 50 minutes; adjust the pH of the water after the micro-electrolysis treatment to 5, and then pump into the heterogeneous reaction tower, and add Al-Mn catalyst and Fenton's reagent to carry out the heterogeneous catalytic oxidation reaction for 1 h; pump the effluent into the degassing tower, and remove the gas generated in the reaction through air aeration, and the aeration time is 2.5h; adjust the pH of the effluent from the degassing tower to 10.5, and then drain it ...
Embodiment 2
[0052] Homogenize the groundwater in the pesticide-contaminated site for 15 hours; coagulate polyacrylamide and magnetic seeds for 60 minutes; then discharge it into a supermagnetic separator to separate the magnetic seeds and coagulation sediments, and the speed of the supermagnetic separator is 1.0r / min; adjust the pH of the water treated by the ultra-magnetic separator to 4, then pump it into the micro-electrolysis reaction tower, and add iron filings and carbon particles for micro-electrolysis treatment for 110 minutes; adjust the pH of the water after the micro-electrolysis treatment to 6, and then pump into the heterogeneous reaction tower, and add aluminum manganese catalyst and Fenton reagent to carry out the heterogeneous catalytic oxidation reaction for 2 hours; pump the effluent into the degassing tower, and remove the gas generated in the reaction through air aeration, and the aeration time is 3h; adjust the pH of the effluent from the degassing tower to 11.5, and ...
Embodiment 3
[0054] Homogenize the groundwater in the pesticide-contaminated site for 14 hours; coagulate polyacrylamide and magnetic seeds for 50 minutes; then discharge it into a supermagnetic separator to separate the magnetic seeds and coagulation sediments, and the speed of the supermagnetic separator is 0.5r / min; adjust the pH of the water treated by the ultra-magnetic separator to 3.5, then pump it into the micro-electrolysis reaction tower, and add iron filings and carbon particles for micro-electrolysis treatment for 50 minutes; adjust the pH of the water treated by the micro-electrolysis to 5.5, and then pump into the heterogeneous reaction tower, and add aluminum manganese catalyst and Fenton's reagent to carry out the heterogeneous catalytic oxidation reaction for 1.5h; pump the effluent into the degassing tower, and remove the gas generated in the reaction through air aeration, and the aeration time 2.5h; adjust the pH of the effluent from the degassing tower to 11, and then d...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com