Astaxanthin nano-emulsion with good blending properties, and preparation method for astaxanthin nano-emulsion
A technology of nanoemulsion and astaxanthin, which is applied to medical preparations with no active ingredients, medical preparations containing active ingredients, dairy products, etc., can solve problems such as emulsifier poisoning, complicated process, and unclear application characteristics. To achieve the effect of improving the stability of brewing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Example 1: Effect of diluent on emulsion formation
[0036] (1) Mix 30 g of octenyl succinic acid mono-arabic gum ester, 25 g of glucose syrup and 45 g of glycerin and stir evenly, add 10 g of astaxanthin, 0.1 g of mixed tocopherol, stir, the viscosity of the emulsion is 10000 mcp.s, the state is viscous and not Homogeneous, and could not be homogenized to obtain an emulsion.
[0037](2) Mix 30 g of octenyl succinic acid monoarabic gum ester, 25 g of glucose syrup and 45 g of water and stir evenly, add 10 g of astaxanthin, 0.1 g of mixed tocopherol, stir, the emulsion viscosity is 2000 mcp.s, the state is uniform, and the state is uniform at 100 Mpa. After the astaxanthin emulsion was obtained, its particle size was 3.5 microns; its ZETA potential was -15mV (the system was considered to be stable when the absolute value was greater than 30), and delamination appeared when placed at 37°C for 3 days.
[0038] (3) Mix 30 g of octenyl succinic acid mono-arabic gum ester, 2...
Embodiment 2
[0041] Example 2: Screening of Embedding Wall and Filling Materials
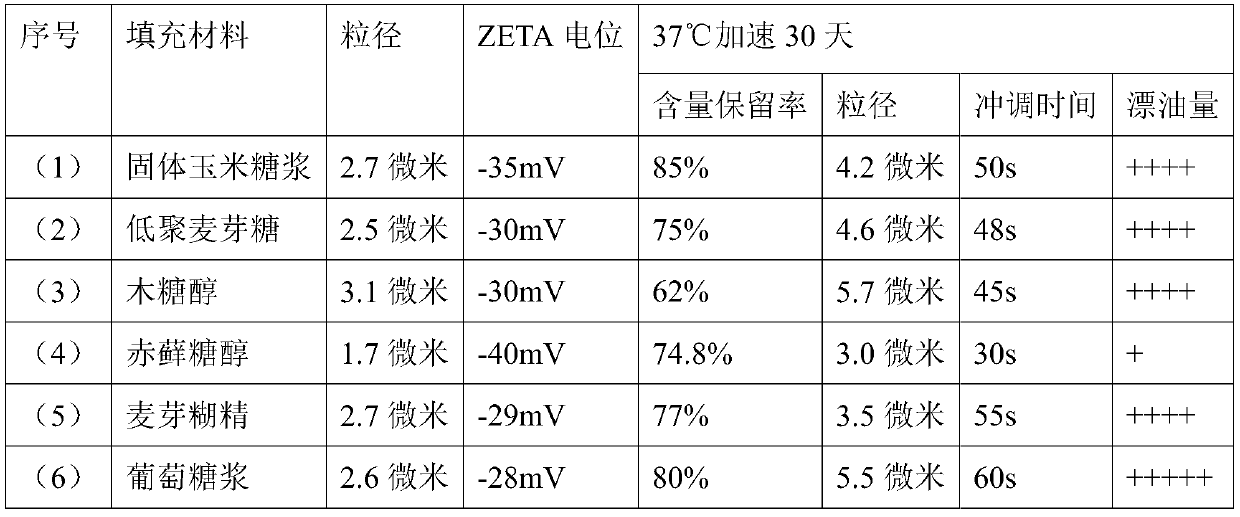
[0042] Mix 100 g of octenyl succinic acid monoarabic gum ester, 80 g of filler material with 450 g of water and stir evenly, add 100 g of astaxanthin, 1 g of mixed tocopherol, and 2 g of potassium sorbate, stir and dissolve, and homogenize at 60 Mpa to obtain astaxanthin emulsion , different filling materials, the obtained emulsion index is shown in Table 1 below:
[0043] Table 1. Emulsion Specifications
[0044]
[0045] (7) 100 g of sodium starch octenyl succinate (a kind of modified starch), 80 g of erythritol and 450 g of water were mixed and stirred evenly, 100 g of astaxanthin was added, 5 g of mixed tocopherols, and 0.5 g of potassium sorbate were stirred. Dissolved and homogenized at 45Mpa to obtain astaxanthin emulsion with a particle size of 8.3 microns; its ZETA potential was 21mV (the system was considered stable when the absolute value was greater than 30); accelerated at 37°C for 30 days, ...
Embodiment 3
[0047] Example 3: Selection of emulsifier and co-emulsifier, and selection of oil-phase co-dispersant.
[0048] The phospholipids described in Example 3 below are concentrated phospholipids with an acetone-intolerant content of more than 50%, including concentrated sunflower phospholipids and concentrated soybean phospholipids.
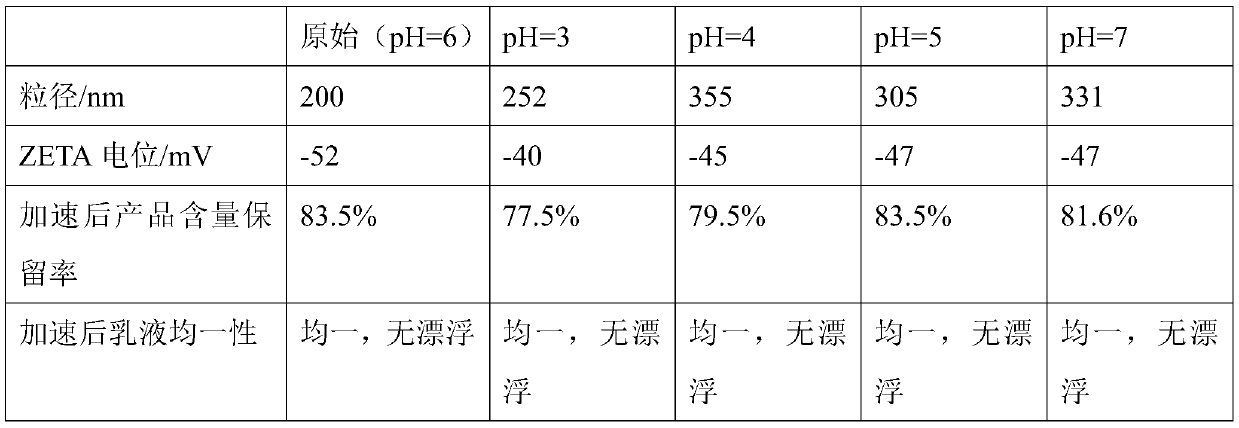
[0049] (1) Mix 250 g of octenyl succinic acid mono-arabic gum ester, 100 g of erythritol, 5 g of sucrose fatty acid ester and 500 g of water and stir well, add 120 g of astaxanthin, 20 g of mixed tocopherol, 0.1 g of potassium sorbate, After stirring evenly, shear pre-emulsification at 10,000 rpm for 1min, and homogenize at 45Mpa to obtain astaxanthin emulsion with a particle size of 1.2 microns; its ZETA potential is -25mV (when the absolute value is greater than 30, the system is considered to be stable); 37 ℃ accelerated 30 Days, the content retention rate is 81%, the particle size is 1.9 microns, the preparation time is 32s, there is a trace amoun...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com