Palmitic anti-enzymolysis antibacterial peptide, and preparation method and application thereof
A technology of palmitic acidification and antimicrobial peptides, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of loss of activity and limited therapeutic efficacy of natural antimicrobial peptides, and achieve the effect of low hemolytic toxicity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
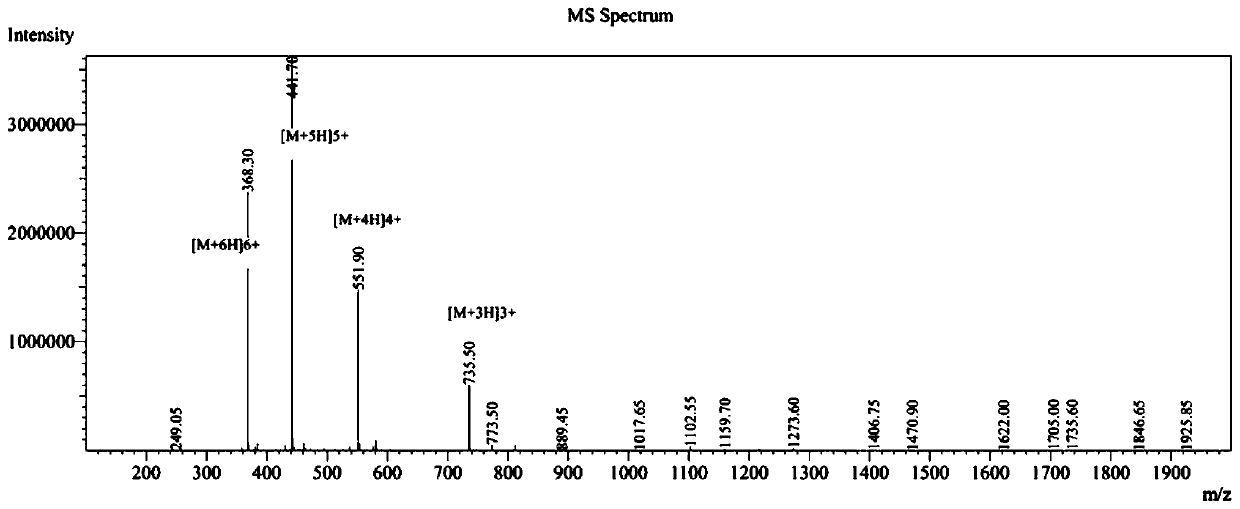
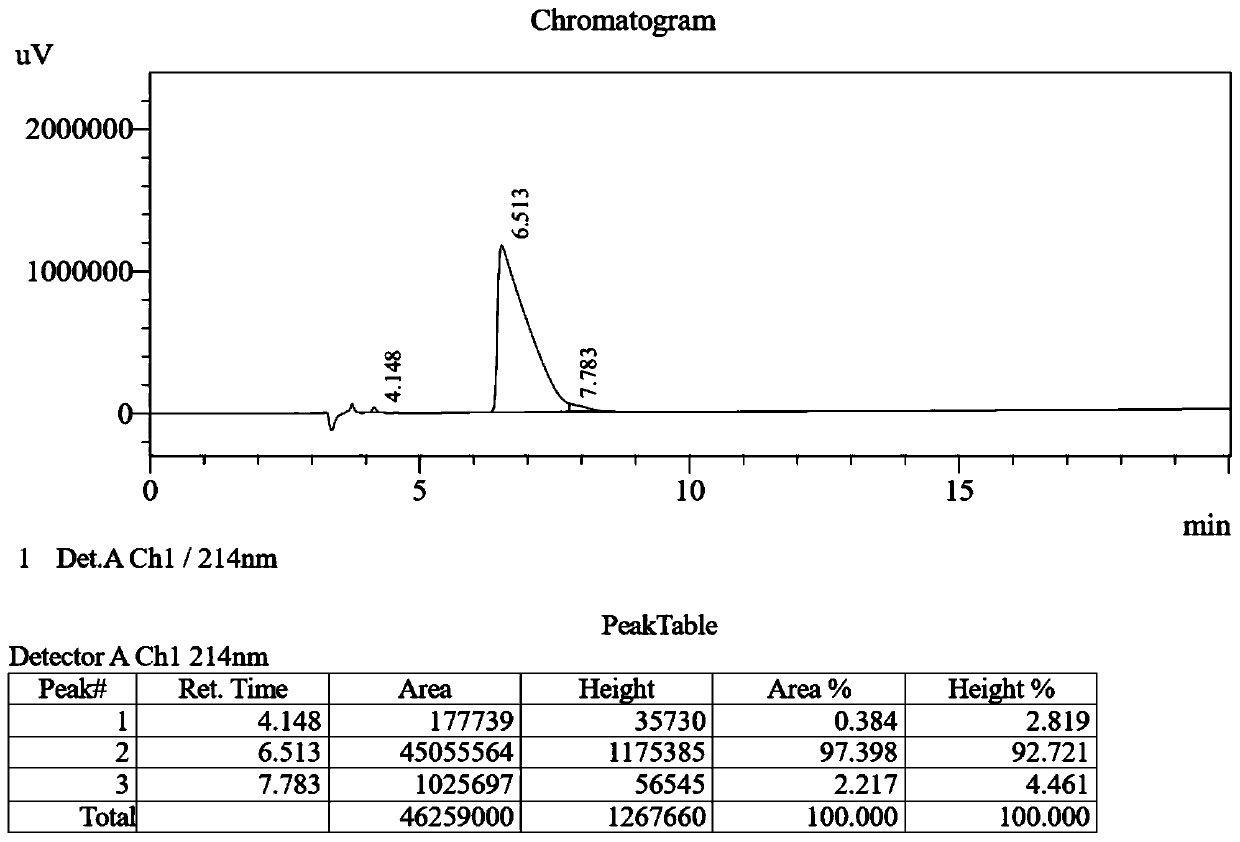
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0018] Antimicrobial Peptide Design:
[0019] palmitoylated anti-enzyme antimicrobial peptide B 3 C 16 The sequence is:
[0020] C 16 -GGGK(PRPR)K(PRPR)RPRP
[0021] The hydrolysis of trypsin is avoided by means of steric hindrance, that is, the protective amino acid proline (Pro) is placed on the carboxyl terminal of each positively charged amino acid arginine (Arg) to form steric hindrance between amino acids, and at the same time Use lysine (Lys) to add two branched peptide chains on the polypeptide main chain, such as Figure 4 As shown, the dendritic structure and the steric hindrance between the peptide chains are formed, palmitic acid is further used as the main source of hydrophobicity of the antimicrobial peptide sequence, which perfectly avoids the hydrolysis of hydrophobic amino acids by all proteases, and finally the flexible amino acid linker is used GGG linked palmitic acid with branched peptides to form a perfect amphiphilic structure, and named the newly d...
Embodiment 2
[0028] The above-mentioned antimicrobial peptides were synthesized using a peptide synthesizer. The method was solid-phase chemical synthesis, and the specific steps were:
[0029] 1. The preparation of the polypeptide main chain is carried out one by one from the C-terminal to the N-terminal, and is completed by a polypeptide synthesizer. First, Fmoc-X (X is the first amino acid at the C-terminal of each antimicrobial peptide) is inserted into Wang resin, and then the Fmoc group is removed to obtain X-Wang resin; then Fmoc-Y-Trt-OH (9 -Fmoxy-trimethyl-Y, Y is the second amino acid at the C-terminus of each antimicrobial peptide); according to this procedure, it is synthesized from the C-terminus to the N-terminus until the synthesis is completed, and the side of the Fmoc group is removed chain protection resin;
[0030] 2. Use hydrazine hydrate to remove the Fmoc-Lys(Dde)-OH side chain Dde protecting group, and repeat step 1 to complete the branched-chain amino acid linkage....
Embodiment 3
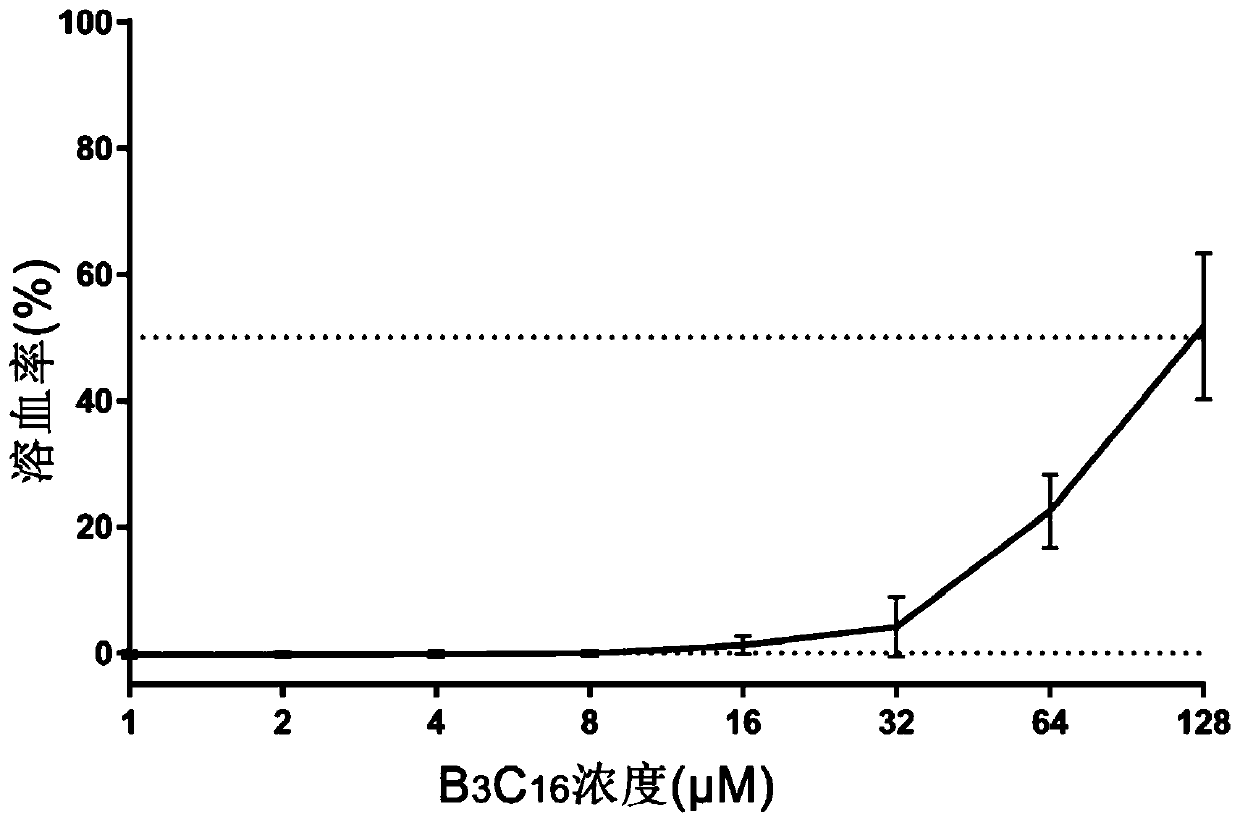
[0035] Detect the antibacterial activity, hemolytic activity and protease hydrolysis ability of the designed and synthesized antimicrobial peptide in vitro;
[0036] 1. Determination of antibacterial activity: The minimum inhibitory concentration of several antibacterial peptides was determined by the micro broth dilution method. Bacterial single colonies were picked and cultured overnight in MHB medium, and transferred to new MHB to grow to mid-logarithmic phase. The above bacterial solution was then centrifuged and resuspended in MHB to a final concentration of 1 × 10 5 CFUml -1, and transferred to a 96-well plate, 50 μl per well. 50 μl of BSA containing different concentrations of peptides were added to the above-mentioned 96-well plate, and the final peptide concentration in the 96-well plate ranged from 0.125 to 64 μM. After incubating at 37° C. for 22-24 hours, measure the light absorption value at 492 nm (OD=492 nm) with a microplate reader to determine the minimum i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com