Probe with functions of successive imaging and killing of bacteria and cancer cells and application thereof
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0053] Example 1 Preparation of AIE-Mito-TPP probes with sequential imaging and killing functions for bacteria and cancer cells
[0054] (1) Add 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde (690mg, 5.0mmol) and 1,6-dibromohexane (1.22g, 5.0mmol) into 20mL of acetonitrile, then add potassium carbonate (690mg, 5.0mmol) in N 2 Under reflux, the reaction was stirred for 6 h, the solvent was spin-dried, and the compound IX was obtained by separation through a silica gel column (PE:EA=80:1).
[0055] (2) Compound IX (300mg, 1.0mmol) and triphenylphosphine (262mg, 1.0mmol) were dissolved in 5mL of acetonitrile, under N 2 Under reflux, stir the reaction for 5h, rotary evaporate under reduced pressure, remove the solvent, and recrystallize to obtain compound X.
[0056] (3) Compound X (250mg, 0.44mmol) was dissolved in ethanol, then hydrazine hydrate (11mg, 0.22mmol) was added, and the 2 Under reflux, stir the reaction for 4h, filter, wash with absolute ethanol three times, and dry in vacuum to obtain...
Embodiment 2
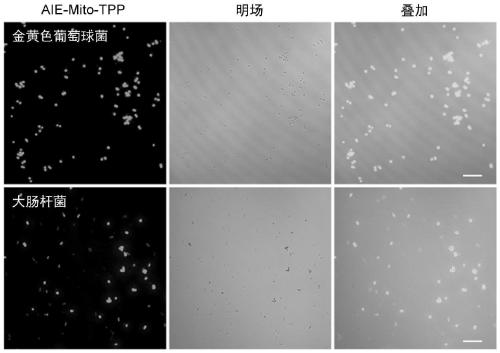
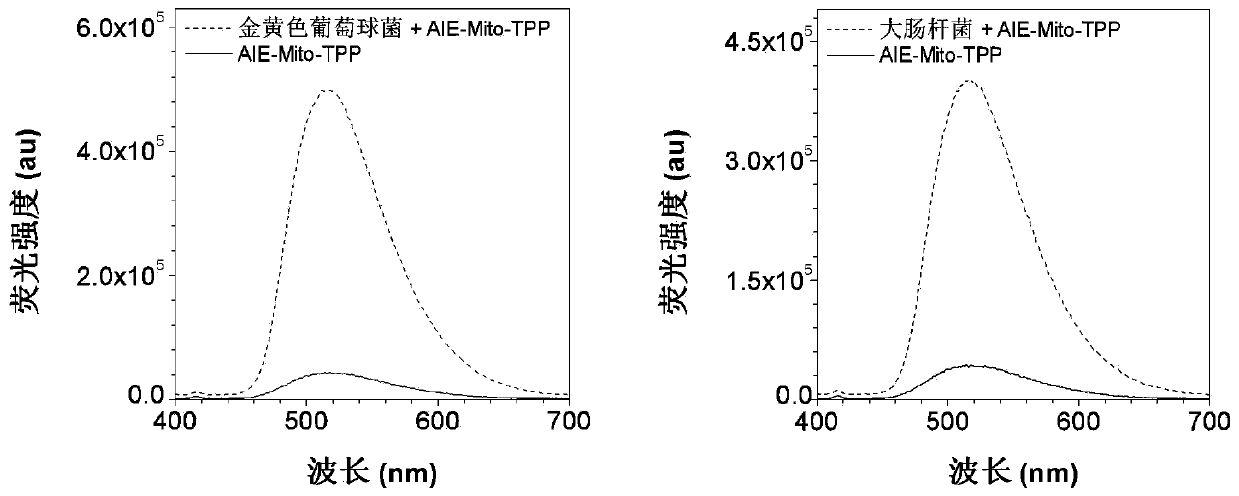
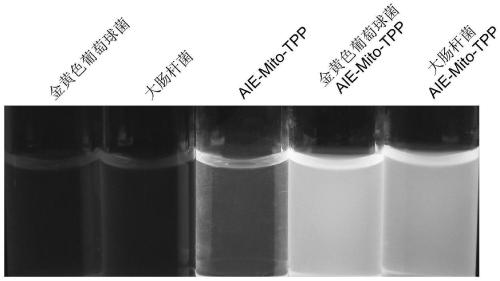
[0059] Example 2 Fluorescence imaging of bacteria
[0060] (1) Culture and dilution of bacteria
[0061] A single clone of Staphylococcus aureus (Gram-positive bacteria) on the agar plate was added to 5 mL of NB liquid medium, and placed on a shaker with a temperature of 37° C. and a rotation speed of 180 rpm for 12 hours. Then the bacterial suspension was centrifuged at 7100g for 3 minutes, washed 3 times with PBS, the supernatant was discarded, and the remaining bacteria were resuspended in PBS. Then the bacterial suspension was diluted to an absorbance value of 1.0 (OD 600 = 1.0). For the cultivation of Escherichia coli (Gram-negative bacteria), except that LB liquid medium is used as the culture medium, other experimental conditions and operations are the same as those of Staphylococcus aureus.
[0062] (2) Fluorescence imaging experiment of bacteria
[0063] 100 μL of bacterial suspension (OD 600 =1.0) into the PBS (400 μL) solution containing AIE-Mito-TPP, so that t...
Embodiment 3
[0072] Embodiment 3 antibacterial activity experiment
[0073] Bacterial (Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli) suspension (10 6 CFU mL -1 ) were mixed evenly with different concentrations of AIE-Mito-TPP, placed on a shaker with a temperature of 37°C and a rotation speed of 180rpm, and incubated for 30 minutes; 4 CFU mL -1 ; Then take 10 μ L and drop it on the agar plate, and smear it gently on the agarose gel plate with a bacterial coating stick, in order to disperse the bacterial solution evenly on the agar plate; When the friction force increased, stop smearing; finally, these agar plates were incubated at 37°C for 18 hours, and the number of bacterial colonies was recorded. The antibacterial experimental operation of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus is the same as the above operation.
[0074] Figure 7 Bacterial survival graphs and agarose plate photos of Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli treated with AIE-Mito-TPP at different concentration...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com