3D bioprinting ink and its preparation method and application
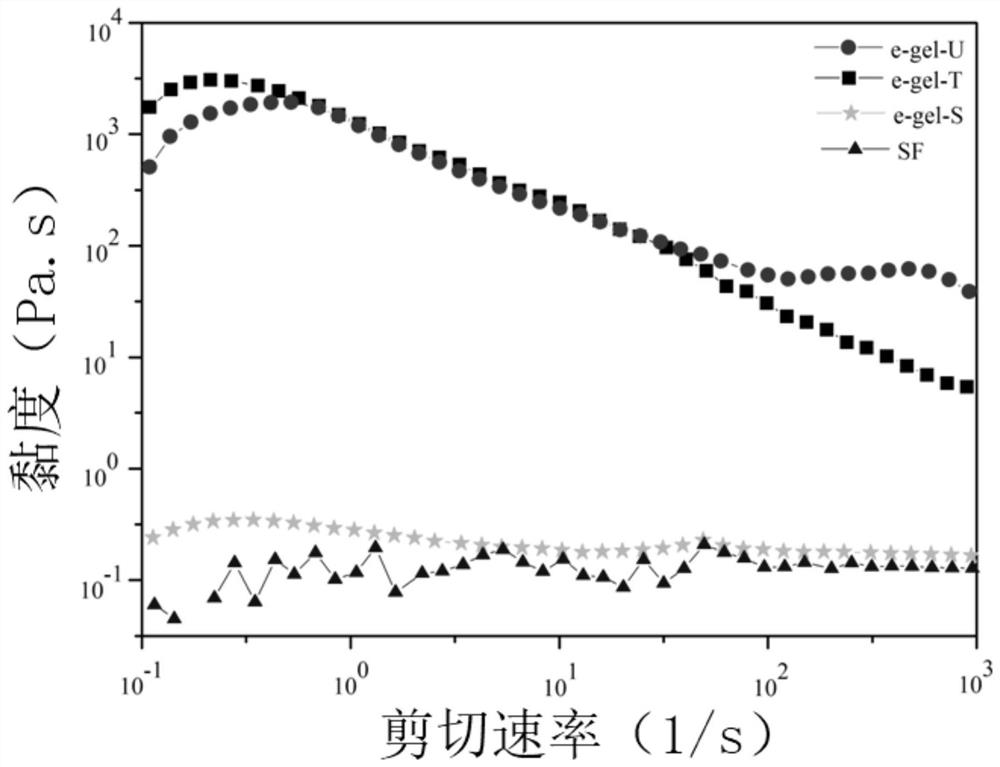
A bioprinting and 3D printing technology, applied in the field of 3D printing, can solve problems such as the reduction of silk fibroin content, the adverse effects of chemical reagents on the long-term growth of cells, and the inability to fully demonstrate the biological characteristics of silk fibroin materials, etc., to achieve high mechanical properties , optimize the rheological properties, improve the effect of printability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0050] In this embodiment, a method for preparing a 3D bioprinting ink for 3D bioprinting a bone defect scaffold is provided, and the method includes the following steps:
[0051] Step 1, prepare silk fibroin aqueous solution;
[0052] Silk fibroin aqueous solution is obtained after degumming, dissolving, dialysis and centrifugation of silk. The degumming, dissolving and dialysis processes all adopt common technical means in the field. For details, please refer to the references Rockwood D N, Preda R C, Yücel, Tuna, et al. Materials fabrication from Bombyx mori silk fibroin[J].Nature Protocols,2011,6(10) : 1612-1631.. Wherein, the molecular weight cut-off of the dialysis bag used in the dialysis process is 3500kDa. The concentration of the final prepared silk fibroin aqueous solution was 10 wt%.
[0053] Step 2, the silk fibroin aqueous solution is made into a silk fibroin electrogel under the action of a stable electric field;
[0054] The silk fibroin aqueous solution pr...
Embodiment 2
[0059] In this example, the pure silk fibroin 3D bioprinting ink 3D printing gel scaffold prepared by Example 1 is provided.
[0060] Put the pure silk fibroin 3D bioprinting ink prepared in Example 1 on the 3D printer, open the 3D printer control panel, set the temperature of the nozzle to 5°C, and place the pure silk fibroin 3D bioprinting ink on the nozzle for temperature pre-control for 15 minutes. , so that the pure silk fibroin 3D bioprinting ink reaches the preset nozzle temperature. Use the platform to receive the print holder with the platform temperature set to 5°C. 3D print pure silk fibroin gel scaffolds according to the model set by the 3D printer, see 3D printed pure silk fibroin gel scaffolds Figure 5 , the number of layers is 10.
Embodiment 3
[0062] This embodiment provides the application of a pure silk fibroin 3D printing scaffold in 3D bioprinting bone defect materials, including:
[0063] The pure silk fibroin gel scaffold prepared in Example 2 was frozen at -20°C for four to five hours, and then placed in a freezer at -80°C for overnight freeze-drying to obtain pure silk fibroin 3D printing. Freeze-dried scaffolds.
[0064] Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) was used to observe the 3D printed scaffolds prepared above. The freeze-dried scaffolds had micro-scale microporous structures. For details, please refer to the structure. Image 6 .
[0065] The 3D printed scaffolds prepared above were used for in vitro cell culture, and the cultured cells were pre-osteoblasts MC3T3, and the cultured cells were labeled with fluorescent proteins. Figure 7 It is a confocal image of the 7th day of cell culture. It can be seen from the figure that a lot of fluorescence is displayed inside and on the surface of the scaffold...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com