Anti-bacteriophage lactobacillus plantarum strain and application thereof in fermented soybean milk
A technology of Lactobacillus plantarum and anti-phage, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve problems such as phage pollution, economic loss, and increased production costs of fermented products.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Lactobacillus plantarum anti-phage mutant strain IMAU10120-1 is isolated and identified by the following method:
[0038] A. Induction and isolation of anti-phage strains
[0039] Phage-resistant mutant strains of Lactobacillus plantarum were obtained by secondary infection method.
[0040] Inoculate Lactobacillus plantarum IMAU10120 in MRS-Ca medium with 2% inoculum, and cultivate to OD at 37°C 600 ≈0.5, insert phage P1 at the best multiplicity of infection, culture at 37°C until clear, continue to culture for 20-24 hours, dip a small amount of mixed culture solution with an inoculation loop and inoculate it on the MRS agar medium, and culture Place the plate at 37°C and incubate for 48 hours. After the colony is formed, pick a single uniform colony with an inoculation loop and inoculate it on the MRS agar medium by drawing a line. Continue to cultivate under the above conditions, and after the bacterial strain grows well, observe and record the colony morphology and...
Embodiment 2
[0044] Method for Determination of Bile Salt Tolerance of Lactobacillus Plantarum Strain IMAU10120-1
[0045] A. Activation of bacteria
[0046] Prepare 10% reconstituted skim milk and sterilize it at a temperature of 115°C for 7 minutes to obtain an activated medium; according to the inoculation amount of 2% by weight of the activated medium, the anti-phage strain of Lactobacillus plantarum frozen and preserved at a temperature of -80°C IMAU10120-1 was inoculated in the above-mentioned activation medium, cultured at 37°C for 20-24 hours, and then activated Lactobacillus plantarum anti-phage strain IMAU10120- 1 Inoculate in MRS broth medium, culture at 37°C for 20-24 hours, and subculture 2-3 times in the same way to make the number of viable bacteria reach 10 8 More than CFU / mL;
[0047] The activation medium used is a skimmed milk powder medium sold by Fonterra, which needs to be sterilized at a temperature of 115° C. for 7 minutes before use. The MRS broth medium and MRS...
Embodiment 3
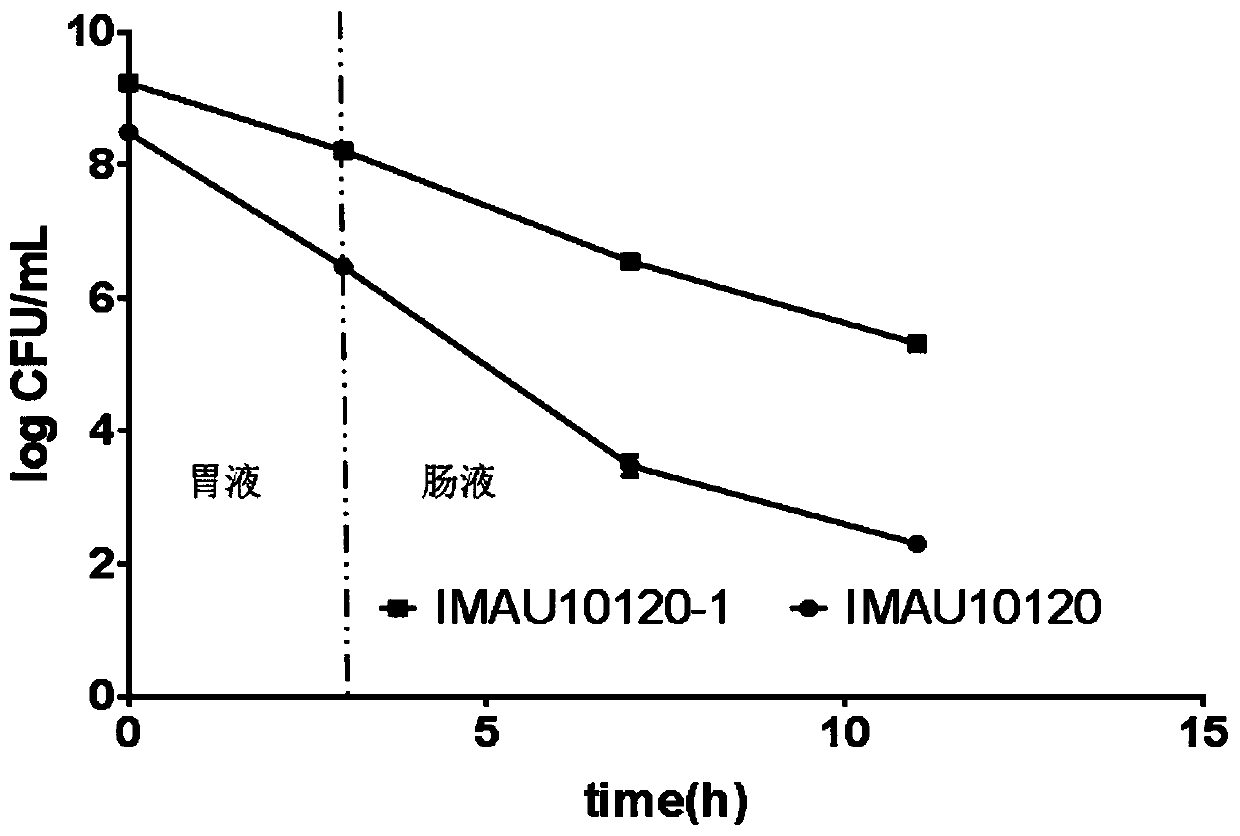
[0058] Determination method for tolerance of Lactobacillus plantarum strain IMAU10120-1 to artificial gastrointestinal fluid
[0059] A. Activation of bacteria
[0060] Prepare a 10% reconstituted skim milk solution, sterilize at a temperature of 115°C for 7 minutes to obtain an activated medium; according to an inoculation amount of 2% by weight of the activated medium, freeze-preserved Lactobacillus plantarum anti-phage at a temperature of -80°C The strain IMAU10120-1 was inoculated in the above-mentioned activation medium, and cultured at a temperature of 37°C for 20-24 hours, and then the activated Lactobacillus plantarum anti-phage strain IMAU10120 -1 was inoculated in MRS broth medium, cultured at 37°C for 20-24 hours, subcultured in the same way for 2-3 times, and the number of viable bacteria reached 10 8 More than CFU / mL;
[0061] B. Preparation of artificial gastrointestinal juice
[0062]Add sterilized pepsin 3.0g / L to sterilized PBS (adjusted with 0.1mol / L HCl) ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com