Nanovesicles derived from faecalibacterium prausnitzii, and uses thereof
A technology of Faecalibacterium Przewalskii and vesicles, which is applied to nanovesicles derived from Faecalibacterium Przetii and its application field, can solve the problem of unreported Faecalibacterium Przewalski releasing vesicles, and never reported Faecalibacterium Przewalski's cancer. or refractory disease diagnosis and treatment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
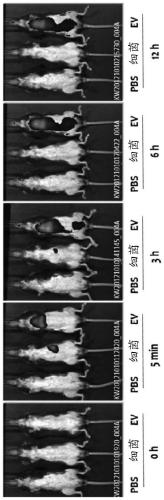
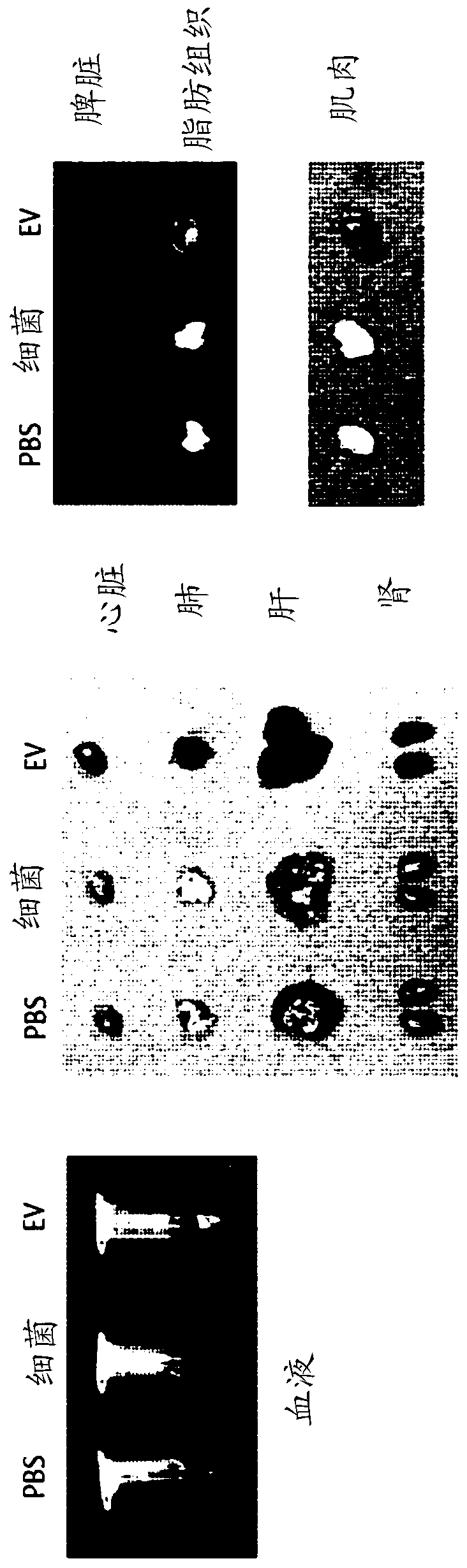
[0075] Example 1. Analysis of In vivo Absorption, Distribution and Excretion Patterns of Gut Bacteria and Bacteria-Derived Vesicles
[0076] To assess whether gut bacteria and bacterial-derived vesicles are absorbed systemically through the gastrointestinal tract, the following experiments were performed. First, a dose of 50 μg each of fluorescently labeled intestinal bacteria and vesicles derived from intestinal bacteria was administered to the stomach of the mouse through the gastrointestinal tract of the mouse, and the Fluorescence was measured after 1 hour, 6 hours and 12 hours. As a result of observing the whole image of the mouse, as Figure 1A As shown, the bacteria were not taken up systemically, but vesicles derived from the bacteria were absorbed systemically at 5 minutes after administration, and strong fluorescence was observed in the bladder at 3 hours after administration, making it possible to see that the vesicles were excreted into urinary tract. Furthermore...
Embodiment 2
[0078] Example 2. Metagenomic Analysis of Bacteria-Derived Vesicles in Clinical Samples
[0079] After first placing clinical samples (e.g. feces, blood, urine, etc.) middle. After removing bacteria and impurities using a 0.22-μm filter, transfer them to a Centriprep tube (centrifugal filter 50kD) and centrifuge at 1,500×g and 4°C for 15 minutes, discard the material smaller than 50kD, and The product was concentrated to 10ml. After bacteria and impurities were removed again using a 0.22-μm filter, ultracentrifugation was performed at 150,000×g and 4°C for 3 hours using a 90Ti-type rotor, the supernatant was discarded, and the aggregated pellets (pellets) were dissolved in in normal saline (PBS).
[0080] Internal DNA was extracted from lipids by boiling 100 μl of vesicles isolated by the method described above at 100 °C, followed by cooling on ice for 5 min. Then, in order to remove the residual suspension, the DNA was centrifuged at 10,000×g and 4°C for 30 minutes, and o...
Embodiment 3
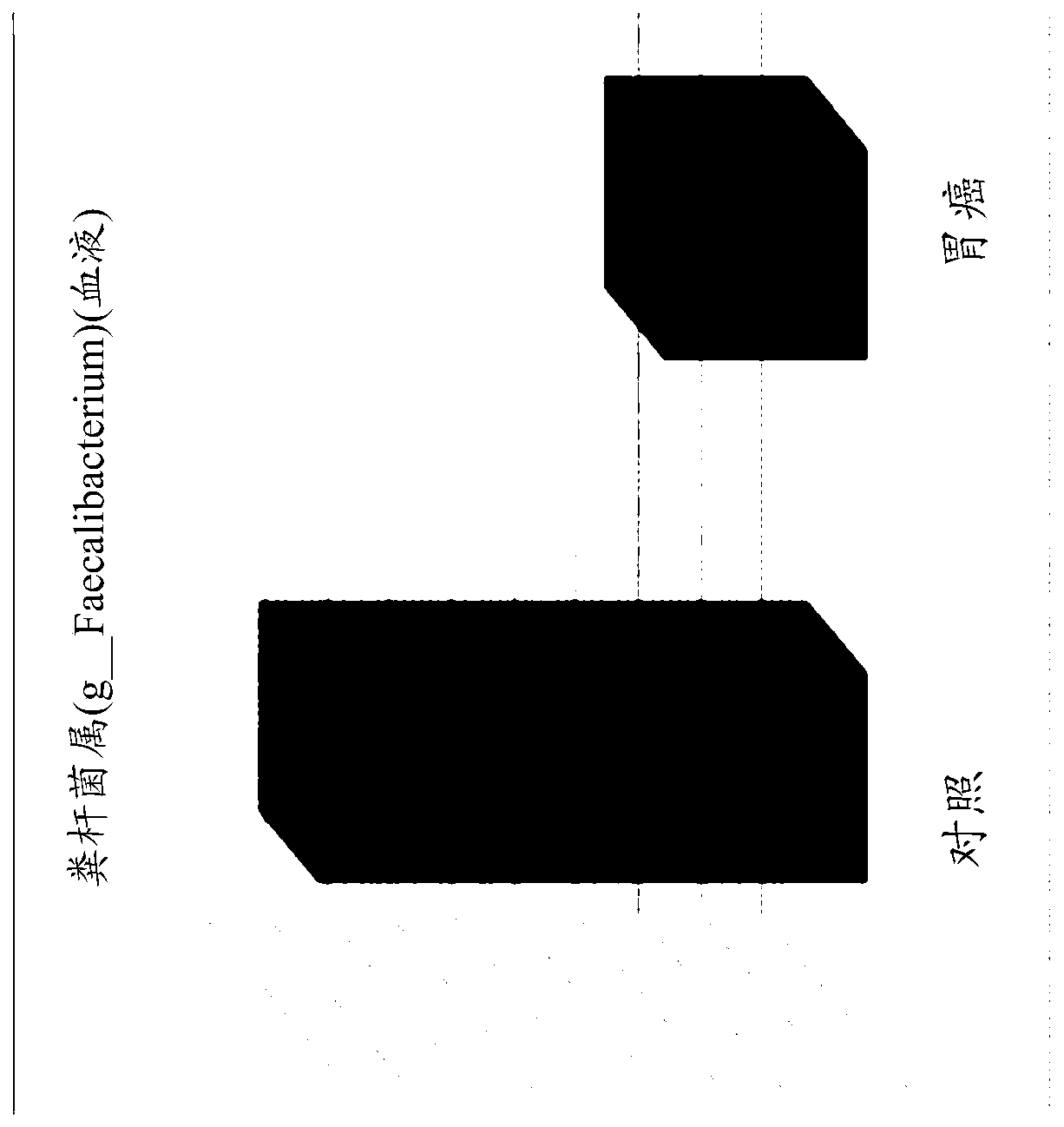
[0084] Example 3. Metagenomic analysis of bacterial-derived vesicles in the blood of patients with gastric cancer
[0085] After performing metagenomic analysis of blood from 66 gastric cancer patients and 198 age- and sex-matched normal individuals by extracting genes from vesicles present in blood using the method of Example 2, the source of Distribution of vesicles in F. prausnitzii. As a result, it was confirmed that compared with the blood of normal individuals, the vesicles derived from Faecalibacterium prausnitzii were significantly reduced in the blood of patients with gastric cancer (see Table 2 and figure 2 ).
[0086] [Table 2]
[0087]
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| absorbance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com