A method of ink direct writing three-dimensional printing based on near-infrared photopolymerization
A near-infrared light and three-dimensional printing technology, which is applied in processing and manufacturing, manufacturing tools, additive manufacturing, etc., can solve problems such as limitation, short wavelength of light, unfavorable mechanical properties, etc., achieve good penetration, improve mechanical properties, and avoid structure The effect of collapse
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
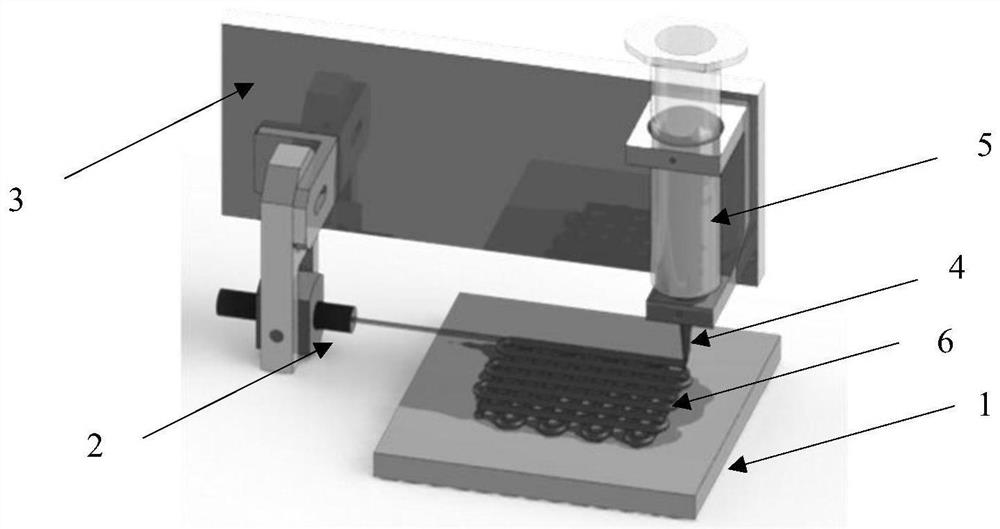
[0037] figure 1 It is a near-infrared photopolymerized ink direct-writing three-dimensional printing device, which is composed of a support table 1, a near-infrared light emitting structure 2, a controller 3, a direct-writing nozzle 4, and an ink storage tank 5.
[0038] Among them, the support platform 1 is used to support the three-dimensional object 6; the near-infrared light emission structure 2 is located above the support platform 1, and is fixedly connected with the controller 3, and the controller 3 drives the near-infrared light emission structure 2 to move or remain still; the direct writing nozzle 4 is located on the Above the support table 1, the direct writing nozzle 4 is sealed and connected to the ink storage tank 5, and the direct writing nozzle 4 and the ink storage tank 5 are fixedly connected to the controller 3, and the controller 3 drives the direct writing nozzle 4 and the ink storage tank 5 to move or stay still.
[0039] The raw material 1.0wt% initiato...
Embodiment 2
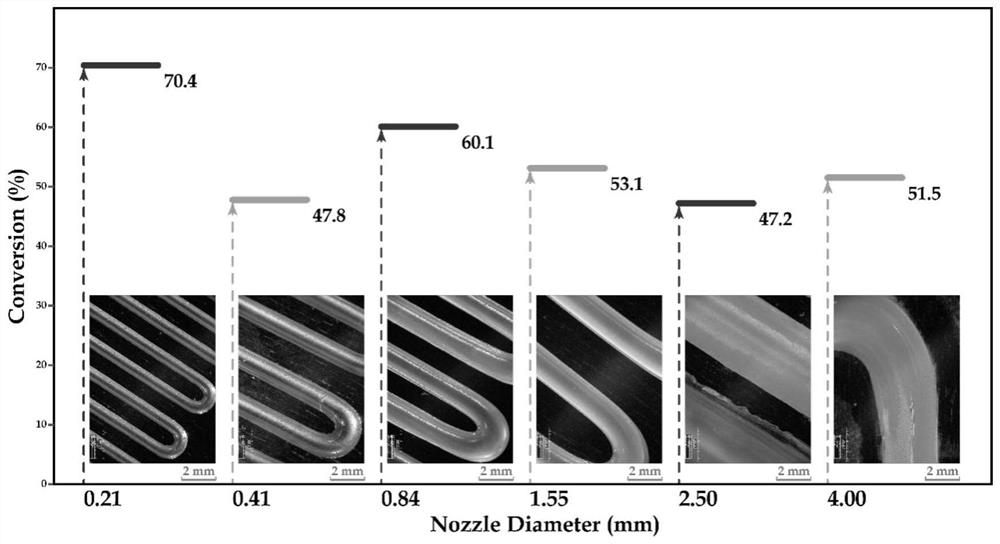
[0041] Utilize near-infrared light to solidify in real time: adopt the same process parameters of the ink in Example 1, the direct writing printing equipment and its working parameters, and only use the 0.41mm nozzle for grid printing (first control the direct writing nozzle to reciprocate in the horizontal plane, and then control The direct writing nozzle is lifted up and the original direction of motion is changed to continue the reciprocating motion), and the following is obtained: image 3 The 3D printed object shown on the right.
[0042]For curing after printing by using near-infrared light: using the same ink process parameters, direct writing printing equipment and its working parameters as above, using a 0.41mm nozzle for grid printing, the ink moves and extrudes with the direct writing nozzle to obtain a shape, And use near-infrared light to cure after the end of extrusion, to obtain such as image 3 The 3D printed object shown on the left.
[0043] A comparison is...
Embodiment 3
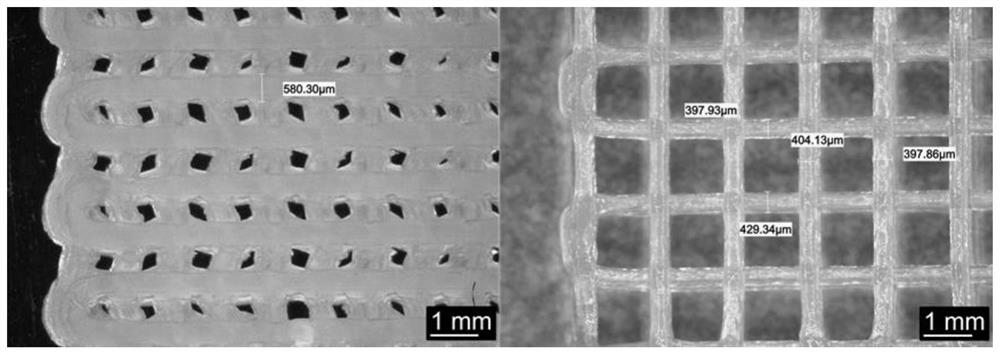
[0045] The working setting of the ink direct writing three-dimensional printing equipment of near-infrared photopolymerization is the same as embodiment 1. With 1.0%wt initiator (Irgacure784), 1.0wt%NaYF4:Yb, Tm up-converting nanoparticles, 0.5wt% color paste (red, Yellow, blue, white), 12.5wt% thixotropic agent (gas silicon, Evonik TS100), 42.5wt% epoxy acrylate resin and 42.5wt% monomer trimethylolpropane acrylate (TMPTA) weighed in The mixing and defoaming machine is fully mixed to obtain ink (elastic modulus G' is 0.49kPa, loss modulus G" is 0.25kPa). Fill the ink into the printer, control the extrusion pressure to 50kPA, and use a 1.55mm direct writing nozzle , the laser power is 3.5W, and the printing speed is controlled at 1.0mm / s. Lines of different colors can be obtained, and the results are as follows Figure 4 shown. Such as Figure 5 As shown, according to the ultraviolet-visible light absorption spectrum, the absorption band (300-500nm) of the initiator used ove...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| elastic modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com