A strain of myxobacteria and its application
A technology for myxobacteria and phytopathogenic bacteria, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve the problems of limited research and application of resistance to phytopathogens, and achieve the effects of being conducive to preservation and transportation, diverse inhibition strategies, and good application value.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Embodiment 1: Isolation and purification of bacterial strain
[0035] 1.1 Sample collection and pretreatment
[0036] Collect about 200g of soil in a 10-20cm soil layer from the furnace field of Nanling National Forest Park, remove visible roots, stones and other debris, pass through a 2mm sieve to mix the soil, and spread it at room temperature to dry naturally to reduce subsequent separation and purification Contamination by mold, protists and other miscellaneous bacteria in the process.
[0037] 1.2 Escherichia coli induction method to induce the formation of myxobacteria fruiting bodies
[0038] Take about 10 g of the air-dried soil sample and place it in a 50 mL centrifuge tube, add 15 mL of 100 μg / mL cycloheximide that has been filtered and sterilized, soak overnight, and pour off the liquid after centrifugation. The water agar medium (i.e. WCX medium, containing CaCl 2 2H 2 O 1g / L and agar 15g / L, the balance is water; pH 7.2) isolates phage myxobacteria, draw...
Embodiment 2
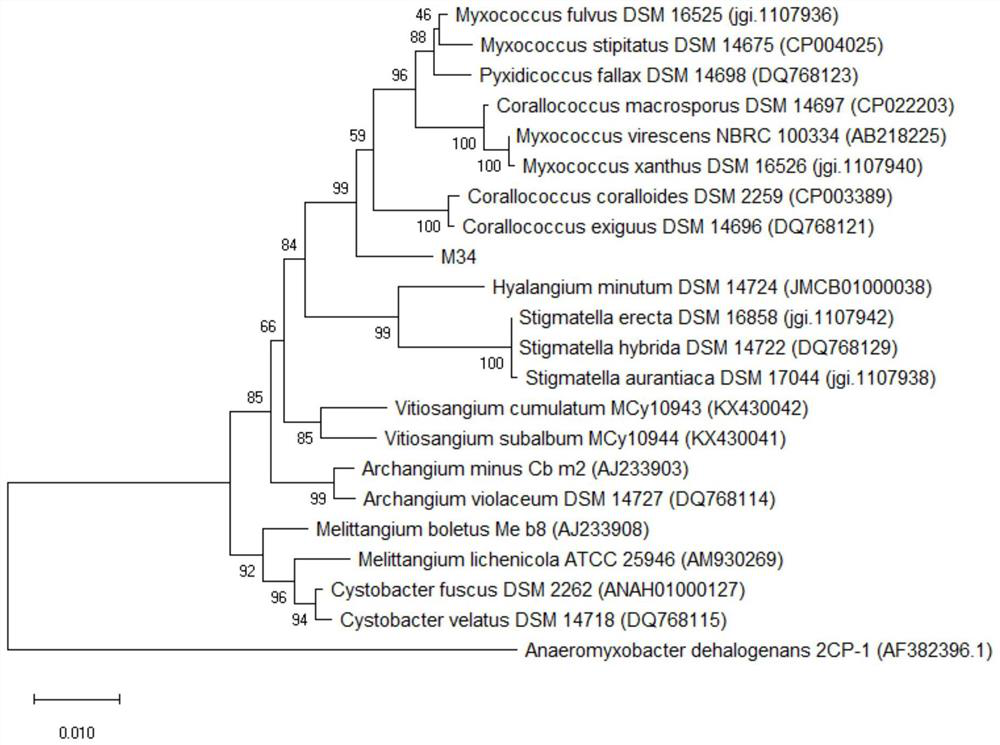
[0041] Embodiment 2: the identification of bacterial strain
[0042] 1. Morphological identification of strains
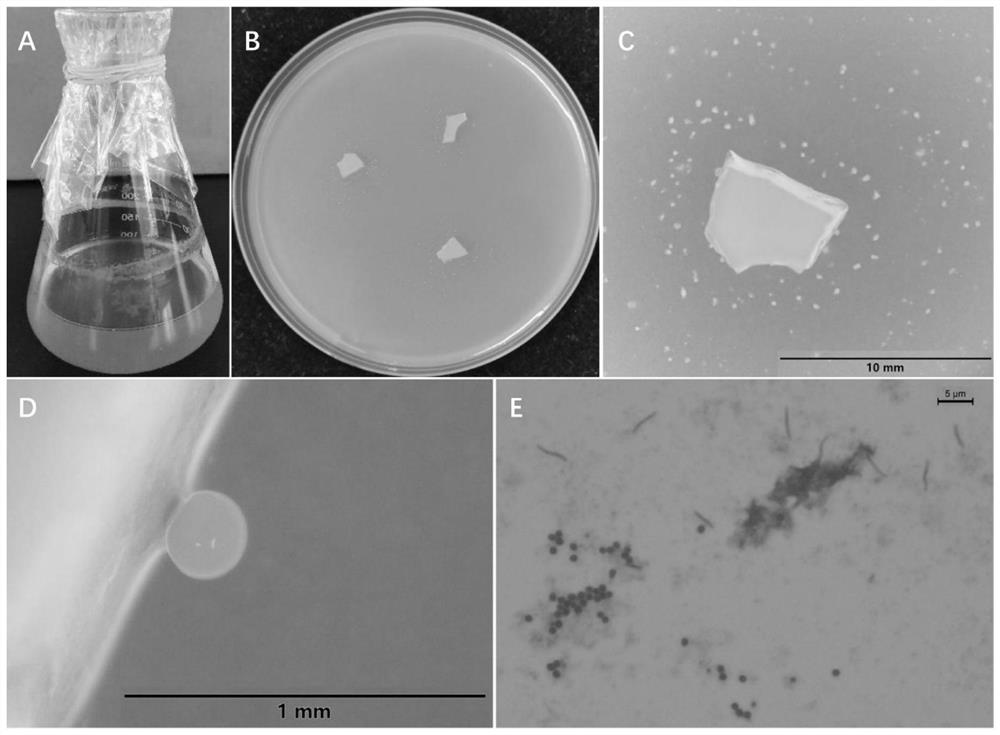
[0043] figure 1 The morphological characteristics of the isolated myxobacteria M34 are shown, among which figure 1 A and figure 1 B is respectively that this bacterial strain is in MD1 liquid culture medium (contains casein peptone 6g / L, soluble starch 2g / L, MgSO 4 .7H 2 O 2g / L and CaCl 2 2H 2 (0.4g / L, the balance is water; pH 7.2) and VY / 2 solid medium after cultivating 5 days aggregation growth characteristics and bacterium colony form, on the VY / 2 plate, show as the light lemon yellow transparent bacterium colony that slides to expand, overall Bacterial colony is moist; Vegetative cells begin to gather and form fruiting body after cultivating 5 days ( figure 1 C and figure 1 D), mature fruiting body is spherical, light lemon yellow, sessile. Crystal violet staining observed under a 100 times oil microscope that the vegetative cells of the strain were lo...
Embodiment 3
[0050] Example 3: Research on anti-phytopathogenic activity of myxobacteria Corallococcus sp.M34 strain
[0051] 3.1 Inhibition of myxobacteria Corallococcus sp.M34 on plant pathogenic fungi
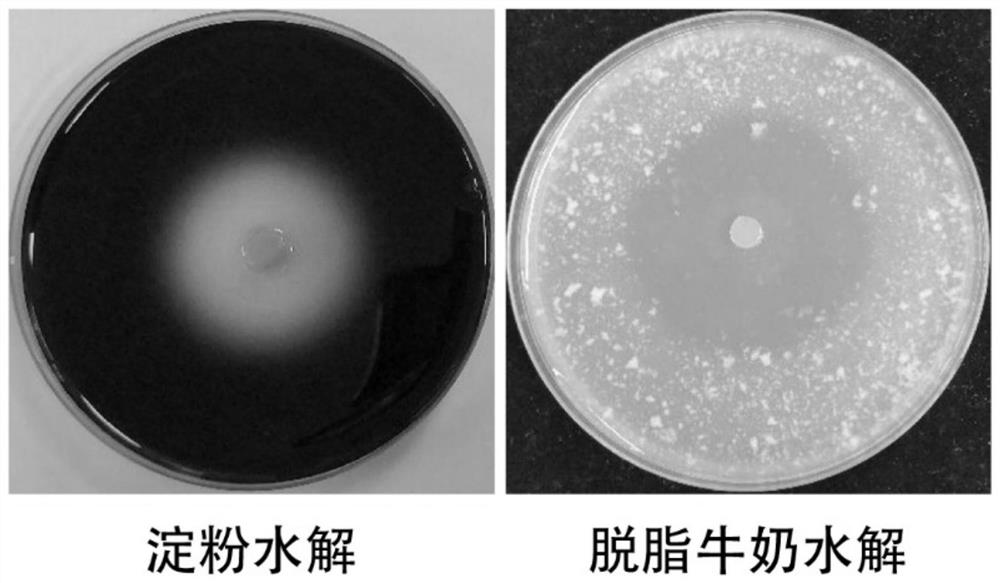
[0052] Pick the rice sheath blight pathogen Rhizoctonia solani Kühn, the banana wilt pathogen Fusarium oxysporum f.sp.cubense race 4, and the banana wilt pathogen Colletotrchum musarum Cooke et Mass Three kinds of phytopathogenic fungal filaments were inoculated on the VY / 2 solid medium at about 2 cm from the edge, and myxobacteria M34 were inoculated at the opposite position on the other side of the plate. Each pathogenic fungus was set for 5 repetitions, and no sticky bacteria was inoculated at the same time. Five bacterial M34 plates were used as controls. Cultivated at 30°C, on the 3rd to 5th day of culture, it was found that it significantly inhibited the growth of Rhizoctonia solani and Discospora banana, while Fusarium oxysporum was less inhibited by Myxobacterium M34 due to its ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com