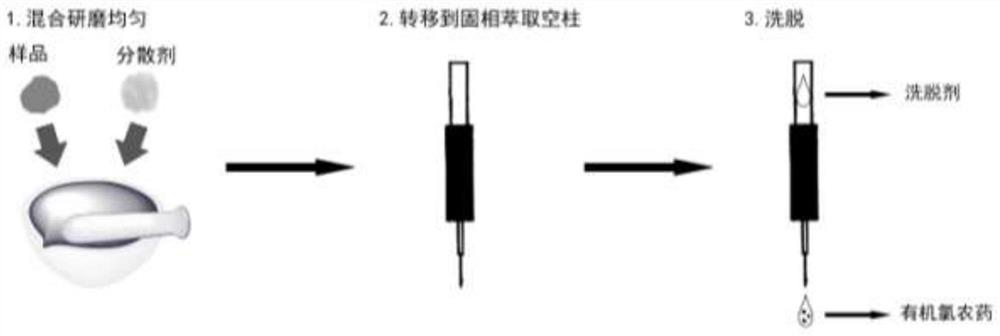
Method for detecting organochlorine pesticide in soil
A detection method and organochlorine technology, applied in the field of analysis and detection, can solve the problems of expensive instruments and equipment, low analyte concentration, short operation time, etc., and achieve the effects of high efficiency, accurate qualitative and quantitative, and less solvent.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] 1.1 Blank soil sample preparation
[0032] Collect a batch of soil near the drinking water source, remove impurities such as grass roots, sand and gravel, put it on the sample tray, spread it to a thickness of about 20mm, freeze-dry it, pass it through a 60-mesh sieve, and grind it evenly to obtain the soil sample to be tested. The traditional method of rapid solvent extraction-solid phase extraction column purification was used to test the 8 kinds of organochlorine pesticides in the samples, and the soil samples whose detection concentration was lower than the detection limit of the method were selected as the blank soil samples for testing.
[0033] 1.2 Preparation of spiked soil for testing
[0034] Accurately weigh 50.0 g of the blank soil for testing, add 10 mL of mixed standard solution of 8 kinds of organochlorine pesticides in n-hexane with a concentration of 1.0 mg / L, add 10 mL of n-hexane solvent to immerse the soil, stir under a fume hood to mix evenly, Then...
Embodiment 2
[0038] The application has also tested the chromatographic condition optimization and internal standard selection of above-mentioned detection method, and test result is as follows.
[0039] 2.1 Optimization of chromatographic conditions
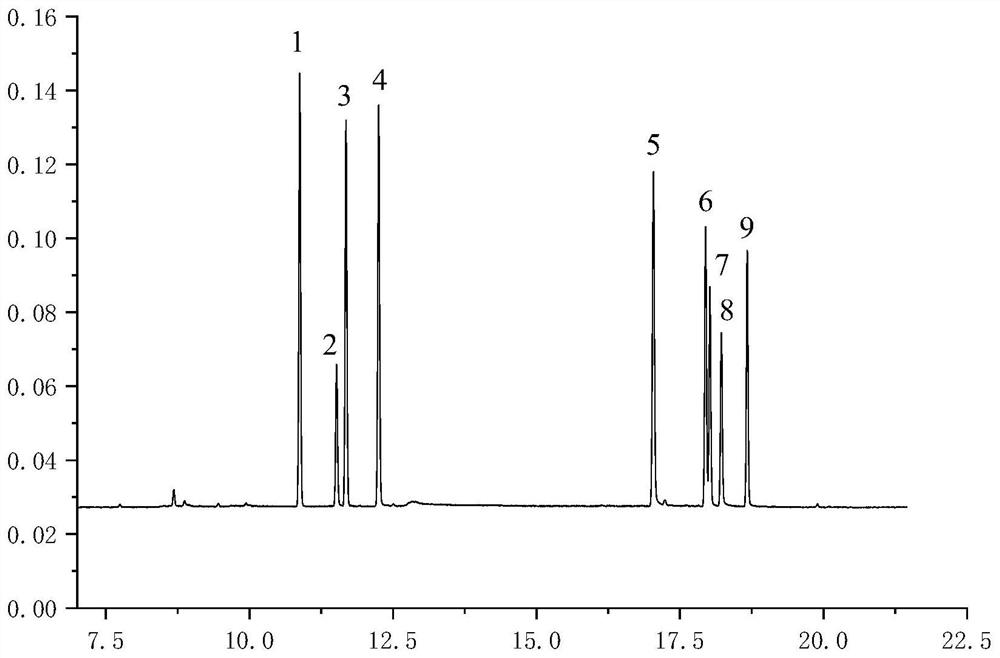
[0040] The purpose of optimizing the chromatographic conditions is to make the separation and detection time the shortest and the effect the best, and at the same time make the detection sensitivity of the chromatogram reach the highest. According to the principle of similar miscibility, since organochlorine pesticides are weakly polar substances, HP-5 capillary column was selected. The gas chromatogram of the standard mixed solution of 8 kinds of organochlorine pesticides is as follows: figure 2 As shown, the experimental results show that under the chromatographic conditions, the target compound and the internal standard can be separated well, which can meet the experimental requirements.
[0041] 2.2 Internal standard selection
[004...
Embodiment 3
[0044] The present application has also tested the above-mentioned detection method. By investigating the type of dispersant, eluent and elution volume, the ratio of sample to dispersant, the recovery rate and standard deviation of organochlorine pesticides under different conditions are measured. The test results are as follows.
[0045] 3.1 Drawing of standard curve
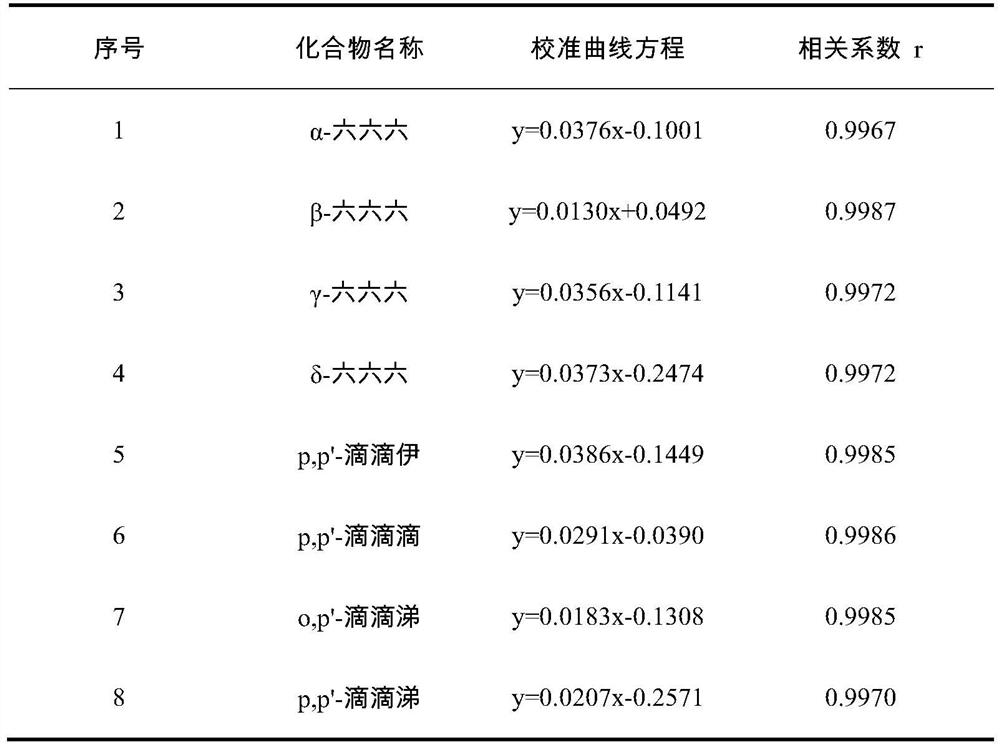
[0046] Using n-hexane as a solvent, accurately pipette the stock solutions of 8 kinds of mixed organochlorine pesticides, prepare standard solutions with concentrations of 50, 100, 150, 200, and 250 μg / L, and add 80 ppb of 13 C 12 -PCB-153 is used as an internal standard, with the concentration ratio as the abscissa and the peak area as the ordinate to draw a standard curve. The calculated standard curve equation and correlation coefficient are shown in Table 1. As can be seen from the data in Table 1, at 50 The linear correlations of the eight organochlorine pesticides within the mass concentration range of ~...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com