Application of a new p-coumaroyl-coa ligase in the biosynthesis of phloretin
A technology of biosynthesis and ligase, which is applied in the field of enzyme engineering, can solve the problem of low activity of p-dihydrocoumaric acid, achieve good substrate selectivity and expand the application range
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] Example 1 Construction of expression vectors and recombinant strains of p-coumaroyl-CoA ligase
[0021] According to the amino acid sequence of HaCHS (AF315345) of Hypericum (Hypericum androsaemum), combined with the codon preference of Escherichia coli, and removing the commonly used enzyme cutting sites, the full-length Hypericum-derived Hachs gene was designed, and the Hachs gene was connected Between the NdeI / XhoI restriction sites of the pETDuet-1 plasmid, it is completely artificially synthesized to obtain the vector plasmid pPL1.
[0022] According to the amino acid sequence of Aa4CL (CAI09146.1) of nitrogen-fixing bacteria, combined with the codon preference of Escherichia coli, and removing the commonly used enzyme cutting sites, the full-length Aa4cl gene was designed, and its nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID No.3. It was shown that the Aa4cl gene was connected between the EcoRI / HindIII restriction sites of the pRSFDuet-1 plasmid and fully artificially s...
Embodiment 2
[0030] Embodiment 2 Recombinant strain biosynthesis of phloretin
[0031] Inoculate the recombinant strains BPL1-4 in LB liquid medium according to the inoculation ratio of 1%, add ampicillin and kana antibiotics, 37°C, 220rpm, shake culture for 12h, and then transfer to M9 fermentation medium containing antibiotics, 0.1 M IPTG, add 300mg / L p-dihydrocoumaric acid as a substrate, 30 ℃, 220rpm, shake and ferment for 48h, then detect the production of phloretin and the consumption of p-dihydrocoumaric acid.
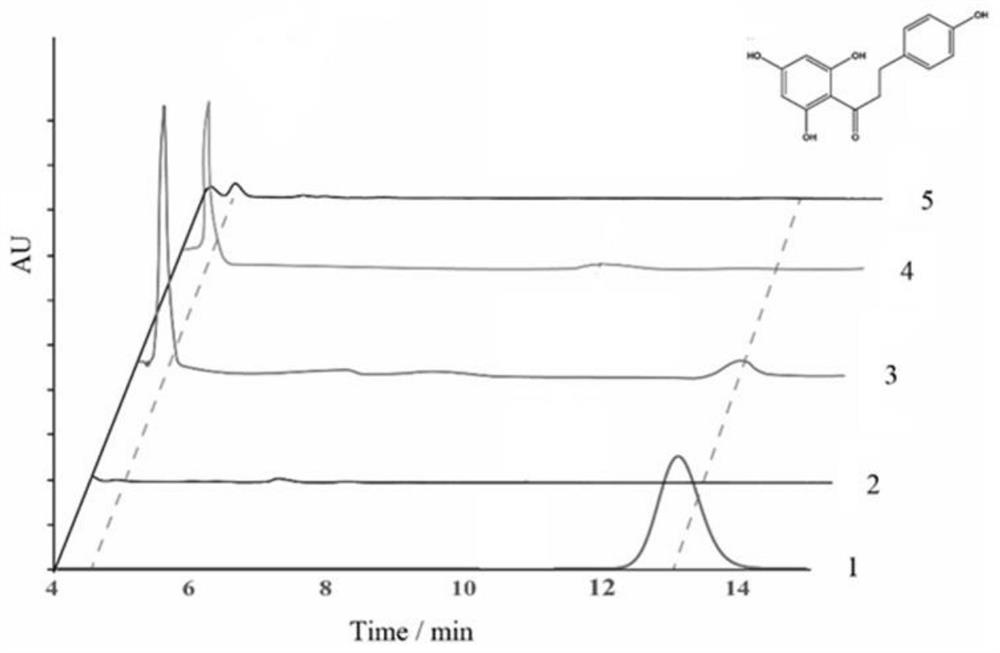
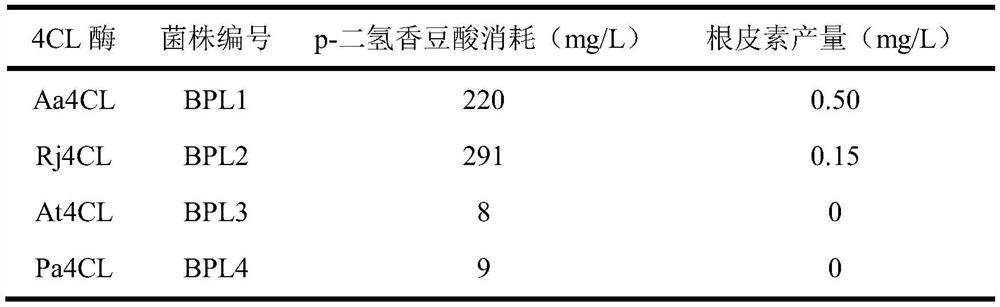
[0032] After HPLC detection, the strains BPL3 and BPL4 showed a small amount of background consumption of p-dihydrocoumaric acid, and no phloretin was detected. Strains BPL1 and BPL2 consumed 220 mg / L and 291 mg / L p-dihydrocoumaric acid, respectively, and produced 0.50 mg / L and 0.15 mg / L phloretin. Therefore, Aa4CL and Rj4CL can synthesize phloretin using p-dihydrocoumaric acid as a substrate, while At4CL and Pa4CL cannot catalyze the synthesis of phloretin (see Table 1 for...
Embodiment 3
[0036] Example 3 Recombinant strain biosynthesis of naringenin
[0037] The recombinant strains BPL1-4 were inoculated in LB liquid medium according to the inoculation ratio of 1%, added ampicillin and kana antibiotics, 37°C, 220rpm, shaking culture for 12h, and then transferred to M9 fermentation medium containing antibiotics, 0.1 M IPTG, add 300mg / L p-coumaric acid as substrate, 30℃, 220rpm, shake flask fermentation for 48h, detect the production of naringenin and the consumption of p-coumaric acid.
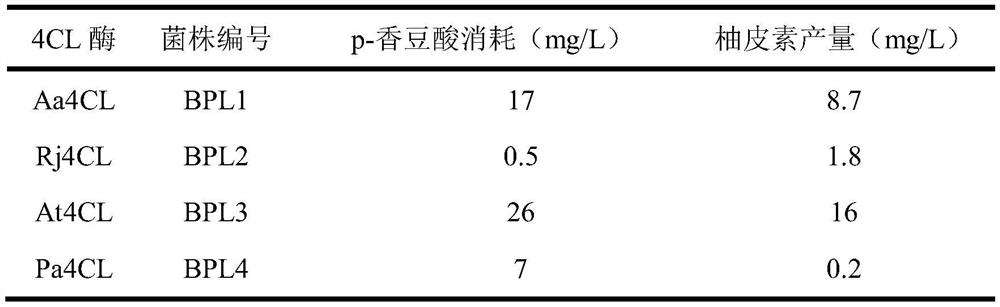
[0038] After HPLC detection, the strain BPL3 consumed 26 mg / L of p-coumaric acid and synthesized 16 mg / L of naringenin. Strains BPL1 and BPL2 consumed 17 mg / L and 0.5 mg / L of p-coumaric acid, respectively, and synthesized 8.7 mg / L and 1.8 mg / L of naringenin (see Table 2 for details). Therefore, Aa4CL and Rj4CL were able to synthesize naringenin from p-coumaric acid, but not as efficiently as At4CL.
[0039] Table 2 Fermentative synthesis of naringenin by recombinant strains ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com