Artificial inoculation identification method for stalk rot resistance of corn varieties
A technology of stem base rot and artificial inoculation, applied in the agricultural field, can solve the problems of difficult control of inoculation amount, unsuitable for identification of large-scale resistant materials, poor stability of inoculation effect, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
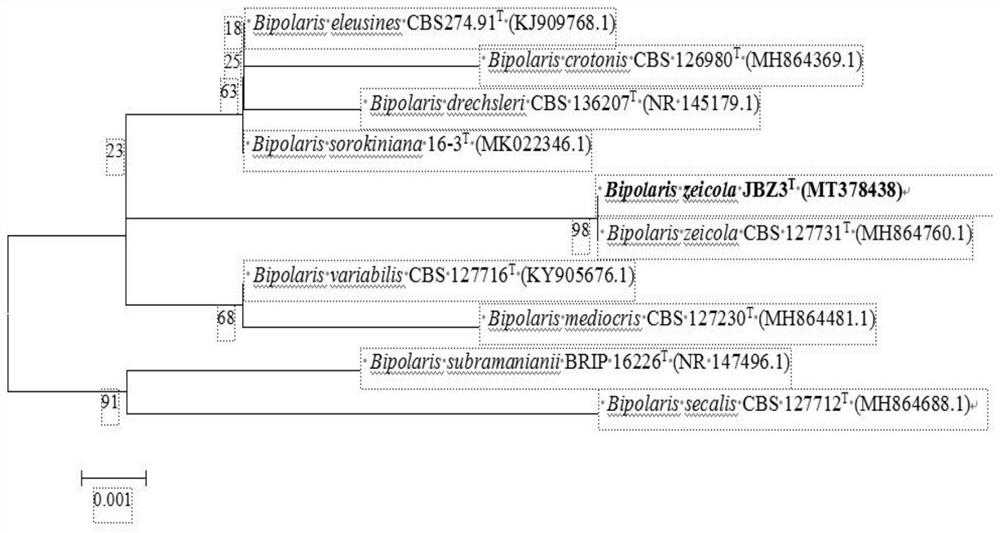
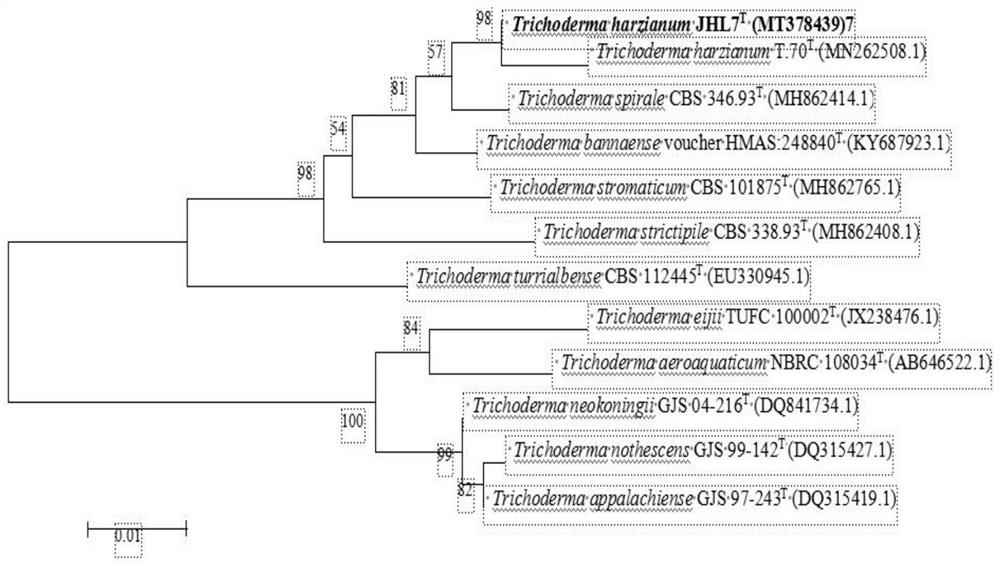
[0036] Isolation and Identification of Maize Stem Root Rot Pathogen
[0037] 1. Collection of corn stalk rot samples
[0038] Corn stover samples were collected at 15 sites in 6 prefecture-level cities in Heilongjiang Province, China, showing light brown lesions in the lower part of the stem nodes and dark brown pith tissue or disintegration of the stem pith. More than 10 disease samples were collected from each site and brought back to the laboratory for isolation.
[0039] 2. Make culture medium
[0040] Potato agar (PDA) medium: Take 200g peeled potato pieces, cut into small pieces, add less than 1000mL of water to boil for 30min, filter with double gauze, make up 1000mL with distilled water, add 20g of glucose, a small amount of multiple additions for a total of 18g Agar powder, stirred continuously, divided into test tubes and Erlenmeyer flasks, and then placed in a heat sterilizer at 121°C for 20 minutes to sterilize, and set aside.
[0041] Carnation leaf (CLA) cultu...
Embodiment 2
[0069] Resistance Identification of Maize Varieties to Stem Rot
[0070] 1. Preparation of Inoculum
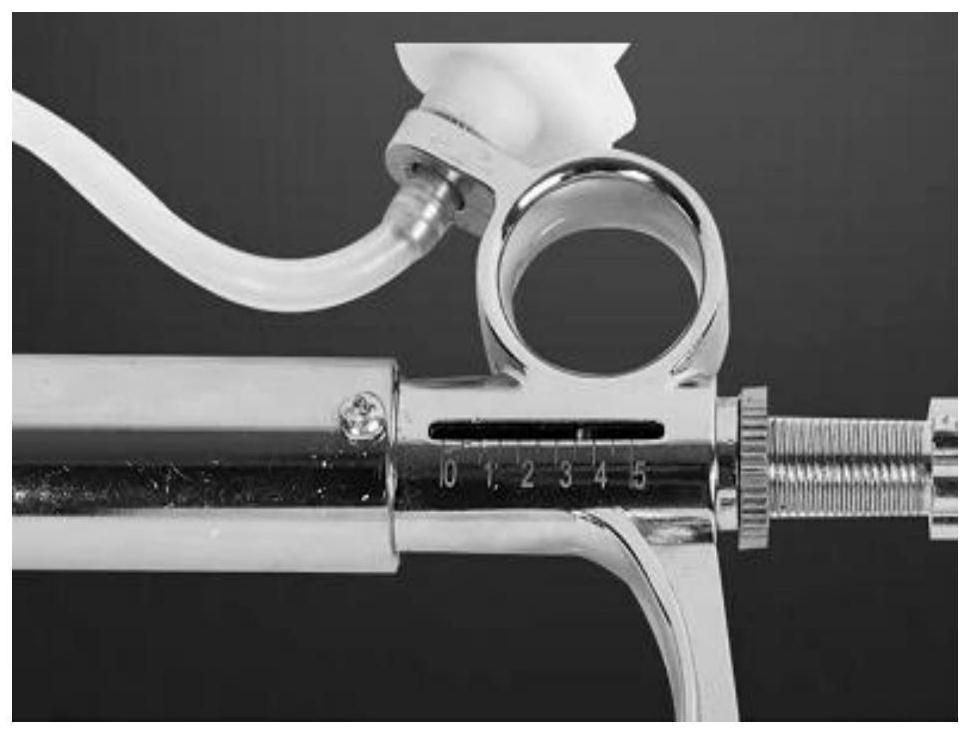
[0071] Since Fusarium graminearum and Fusarium laminarum are the dominant bacteria of maize stalk rot in Heilongjiang Province, representative strains were purchased from commercial channels and re-cultivated on PDA plates for 5 days, and then inoculated into sorghum with a 7 mm diameter bacterial plate Grain culture medium (sorghum grains boiled in boiling water for 20 minutes, then transferred to Erlenmeyer flasks for sterilization at 121°C for 45 minutes), inoculated 5 to 7 bacterial plates in each Erlenmeyer flask, cultivated in the dark at 26°C, and shook the Erlenmeyer flasks 1 to 2 times a day. For the second time, the surface of each sorghum grain is covered with mycelium. Then, rinse the sorghum grains with bacteria with sterile water, filter with sterile double-layer gauze, and adjust the concentration of the spore suspension to 1×10 using a hemocytometer. 6 Spores...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com