Lithotripsy basket catheter with lithotripsy balloon
A technology of mesh basket and catheter, which is applied to the parts of surgical instruments, medical science, heating surgical instruments, etc., can solve the problems of common bile duct obstruction, difficulty in nursing, and difficulty in extracting huge common bile duct stones.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
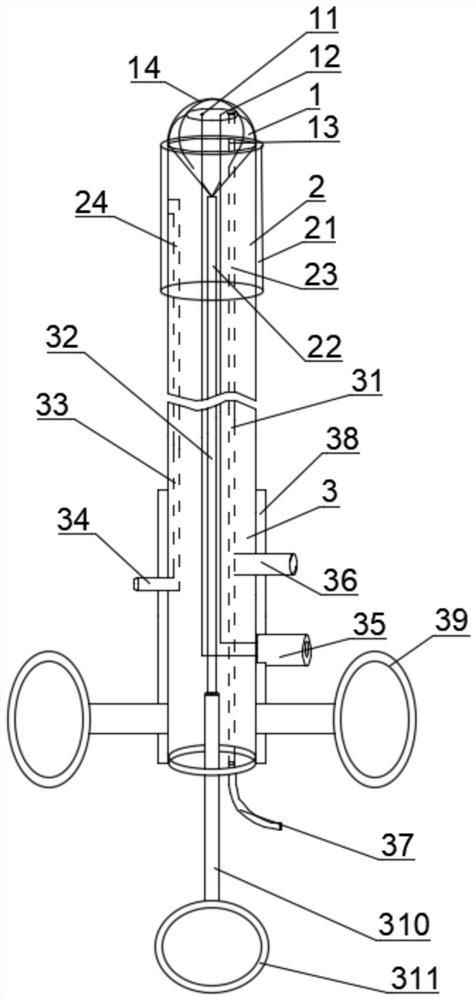
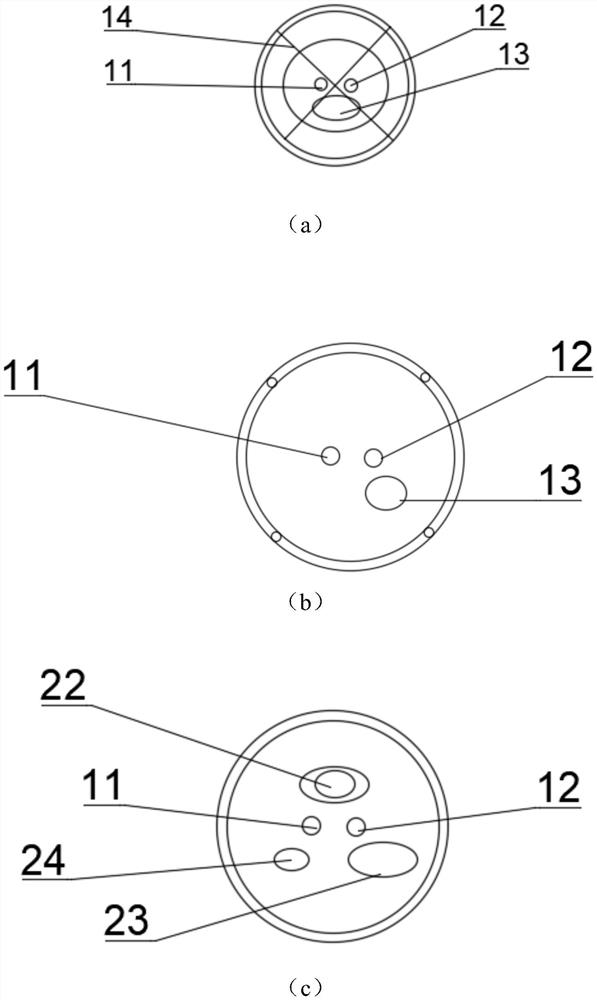
[0055] In this embodiment, the basket configuration of Scheme 1 is selected, and the total length of the catheter is 40-60 cm.
[0056] PTCD drainage of bile was performed first to control biliary infection and jaundice, and the PTCD tube was left in place for 2 months.
[0057] A zebra guide wire was inserted through the original PTCD tube, and the guide wire crossed the stone and entered the distal end of the duodenum through the duodenal papilla.
[0058] The guide wire was indwelled and the original PTCD tube was withdrawn, and the duodenal papilla balloon dilation catheter was inserted into the duodenal papilla through the guide wire to dilate the duodenal papilla.
[0059] Indwell the guide wire and withdraw the duodenal papilla balloon dilatation catheter, insert the guide wire through the tip of the crushed stone basket catheter, and send the crushed stone basket catheter into the common bile duct under the guidance of the guide wire, withdraw the guide wire, and relea...
Embodiment 2
[0065] In this embodiment, the basket configuration of Scheme 1 is selected, and the total length of the catheter is 2.2-2.8 m.
[0066] Such as Figure 7 As shown in (a) to (e), a duodenoscope was inserted through the mouth, and after successful bile duct intubation, endoscopic retrograde cholangiography was performed first to determine the number, location and size of stones, and then duodenal papillary sphincter A small incision was made and the duodenal papilla was dilated using a 1.0 cm diameter cylindrical balloon.
[0067] Under the guidance of the guide wire, the basket catheter is inserted through the duodenal clamp, the balloon is filled or the basket is released, and the small common bile duct stones are captured and directly dragged into the duodenum. When the diameter of the stone exceeds 1cm, release the basket catheter to collect the stone. When the basket is tightened, the stone is close to the electrode at the tip of the catheter, and the balloon is filled to...
Embodiment 3
[0070] In this embodiment, the basket configuration of Scheme 2 is selected, and the total length of the catheter is 40-60 cm.
[0071] PTCD drainage of bile was performed first to control biliary infection and jaundice, and the PTCD tube was left in place for 2 months.
[0072] Insert the cup-shaped crushed stone basket catheter into the common bile duct through the PTCD fistula tract, push the basket catheter forward, and release the basket.
[0073] Push the snare connecting rod forward, the head end of the net basket is open, and the net basket is cup-shaped.
[0074] Push the outer cannula forward, and the choledocholith enters the basket.
[0075] Pull back on the snare to tighten the mouth of the cup.
[0076] Pull back the gravel basket catheter, the basket is tightened, and the stone is fixed at the head end of the outer casing.
[0077] Inflate the balloon and secure the lithotripsy catheter.
[0078] Plasma, microelectrode or laser lithotripsy are performed, and...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com