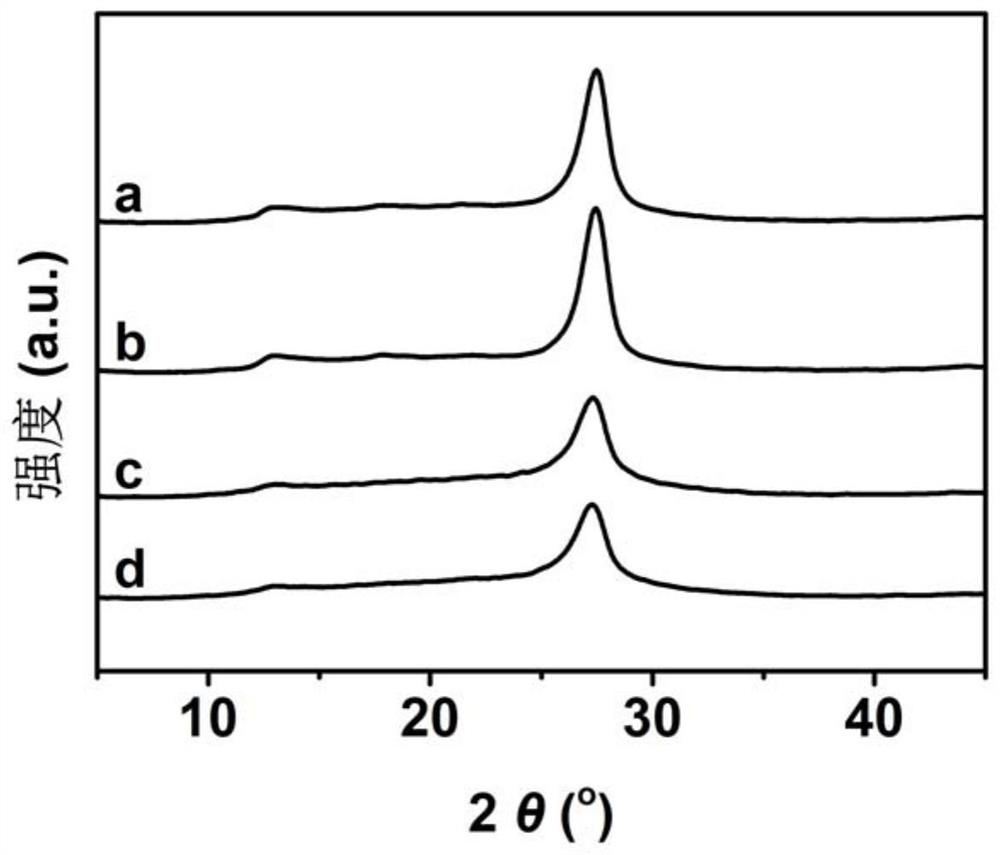
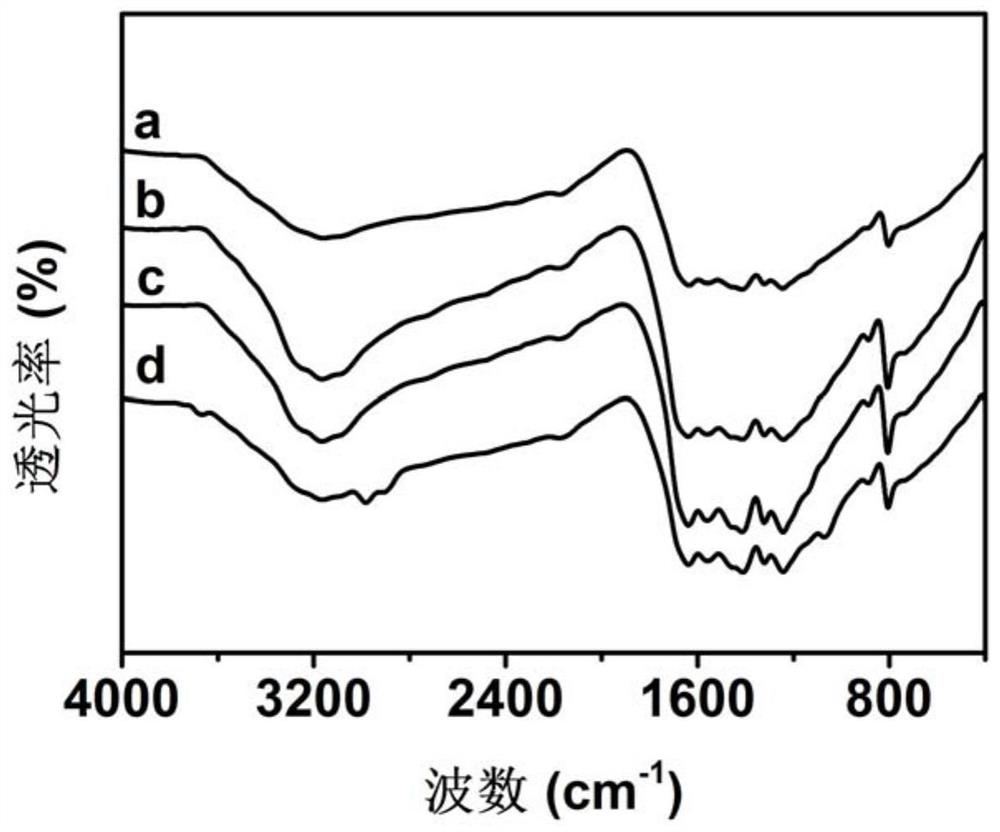
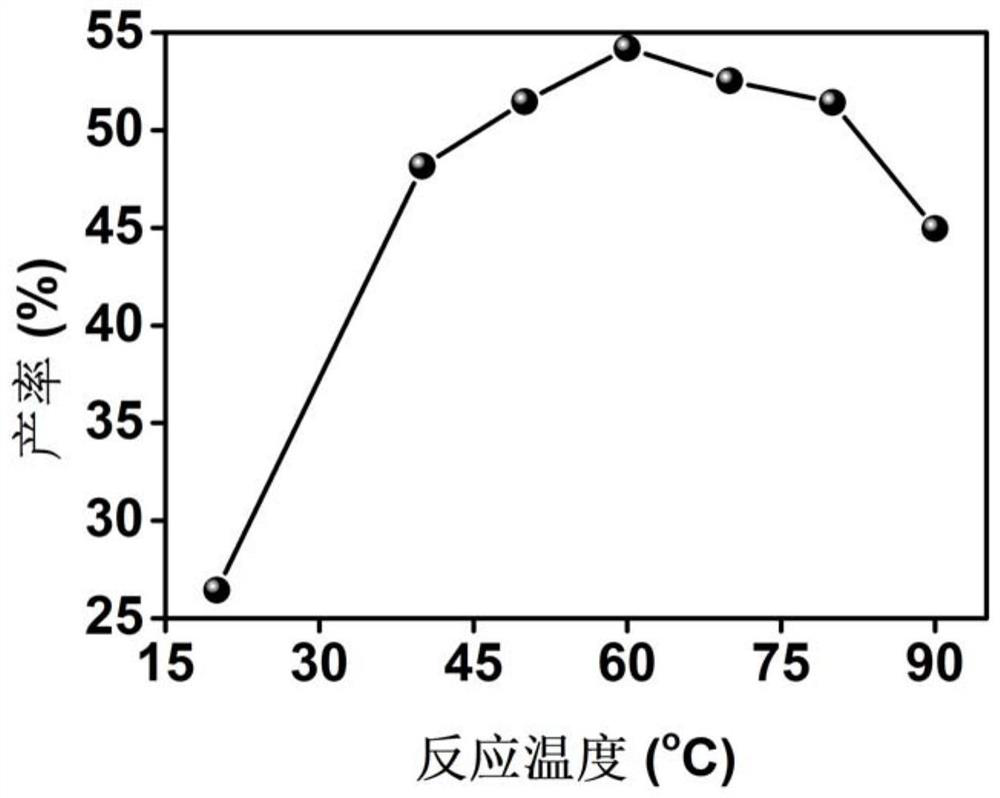
Preparation of modified carbon nitride photocatalyst and application of modified carbon nitride photocatalyst in synthesis of lactic acid by photocatalytic oxidation of glucose
A catalyst and glucose technology, applied in the field of catalysis, can solve the problems of cumbersome microbial population control, low yield, harsh reaction conditions, etc., and achieve the effect of recyclable catalytic activity, quick effect and good stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] (1) Accurately measure 1.0mL, 3.0mL, 5.0mL, 8.0mL, 10.0mL, and 15.0mL of glacial acetic acid, then add deionized water to prepare 200.0mL acetic acid solutions with different concentrations, and then accurately weigh 10.0g Boric acid is added to the above system, and boric acid-acetic acid solutions with different concentrations are prepared for subsequent use;
[0042] (2) Accurately weigh 3.0g of melamine and 3.0mL of the boric acid-acetic acid solution prepared in step (1) into the porcelain boat, and stir evenly at room temperature;
[0043] (3) Calcining the product obtained in step (2) at 400.0°C for 2.0 hours, and then grinding the obtained solid;
[0044] (4) Calcining the product obtained in step (3) at a temperature of 560.0° C. for 2.0 h, and then grinding the obtained product into powder to obtain an in-situ doped boron and oxygen heteroatom modified carbon nitride photocatalytic material.
Embodiment 2
[0046] (1) Accurately measure 10.0 mL of glacial acetic acid, then add deionized water to prepare 200.0 mL of acetic acid solution, then accurately weigh 10.0 g of boric acid and add it to the above system to prepare boric acid-acetic acid solution for later use;
[0047](2) Accurately weigh 3g of nitrogen-containing compound precursors (melamine, thiourea, urea and dicyandiamide respectively) and 2mL of boric acid-acetic acid solution prepared in step (1), add 1mL of water into the porcelain boat, Stir well at room temperature;
[0048] (3) Calcining the product obtained in step (2) at 400.0°C for 2.0 hours, and then grinding the obtained solid;
[0049] (4) Calcining the product obtained in step (3) at a temperature of 560.0° C. for 2.0 h, and then grinding the obtained product into powder to obtain an in-situ doped boron and oxygen heteroatom modified carbon nitride photocatalytic material.
Embodiment 3
[0051] (1) Accurately measure 10.0 mL of glacial acetic acid, then add deionized water to prepare 200.0 mL of acetic acid solution, then accurately weigh 10.0 g of boric acid and add it to the above system to prepare boric acid-acetic acid solution for later use;
[0052] (2) Accurately weigh 3g of nitrogen-containing compound precursors (melamine, thiourea, urea and dicyandiamide respectively) and 1mL of boric acid-acetic acid solution, add 2mL of water into the porcelain boat, and stir evenly at room temperature;
[0053] (3) Calcining the product obtained in step (2) at 400.0°C for 2.0 hours, and then grinding the obtained solid;
[0054] (4) Calcining the product obtained in step (3) at a temperature of 560.0° C. for 2.0 h, and then grinding the obtained product into powder to obtain an in-situ doped boron and oxygen heteroatom modified carbon nitride photocatalytic material.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com