Acid-base regulation solution used for dialysate regeneration and dialysate regeneration method
A technology of acid-base adjustment and dialysate, applied in the field of hemodialysis, can solve problems such as excessive fluctuation of bicarbonate ion concentration, achieve the effect of simplifying the control unit and ensuring the quality of dialysis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0051] Embodiment 1: B liquid (acid-base adjustment liquid) is the aqueous solution of 6% sodium carbonate+1% sodium hydroxide
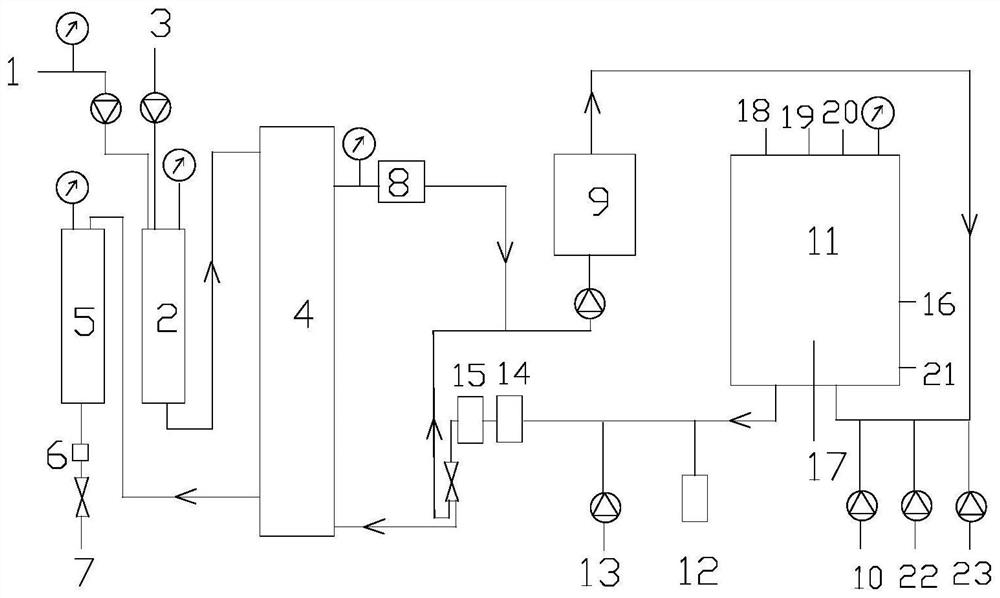
[0052] use as figure 1 As shown in the dialysate regeneration system, a simulated dialysate regeneration cycle test was carried out. details as follows:
[0053] Take 4L of simulated liquid, add 8g of urea to it, stir evenly, place it in arterial blood end 1 to simulate arterial blood, and flow into arterial jug 2 through the blood pump, set the blood pump flow rate to 150mL / min, and flow from inlet 3 to arterial jug 2 Continuously replenish urea solution (150mg / mL, total amount 100mL), and set the flow rate of the peristaltic pump to 0.5mL / min.
[0054] The blood flows from the arterial jug 2 into the dialyzer 4, and undergoes material exchange with the dialysate. The flow rate of the dialysate is 300mL / min. After the material exchange, the blood flows into the venous jug 5, and returns to the venous blood end after passing through the gas detecto...
Embodiment 2
[0061] Embodiment 2: B liquid is the aqueous solution of 2% sodium carbonate+1% sodium hydroxide
[0062] Adopt the same flow process as embodiment 1 to carry out the simulated dialysate regeneration cycle test, the difference is:
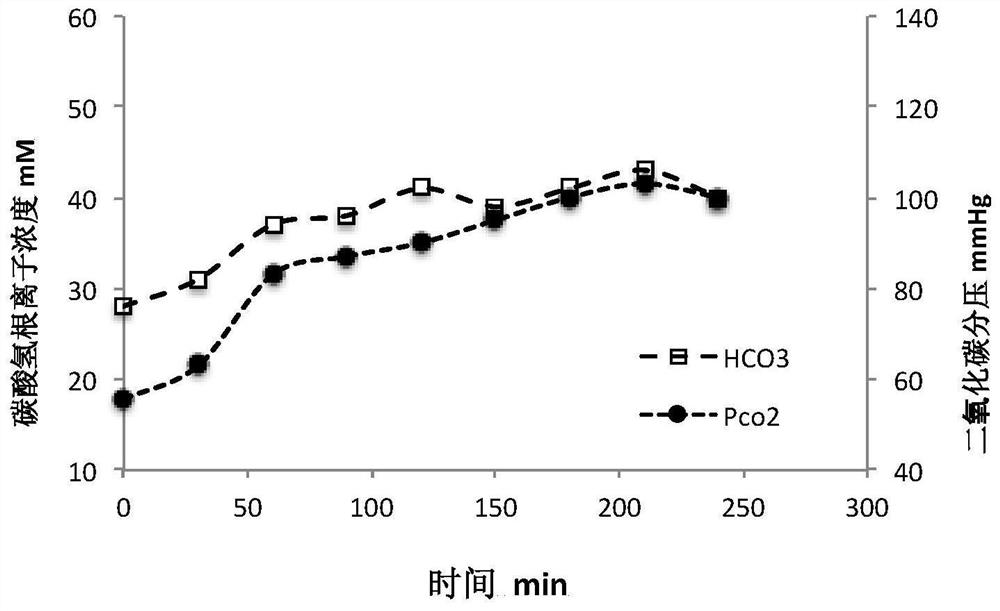
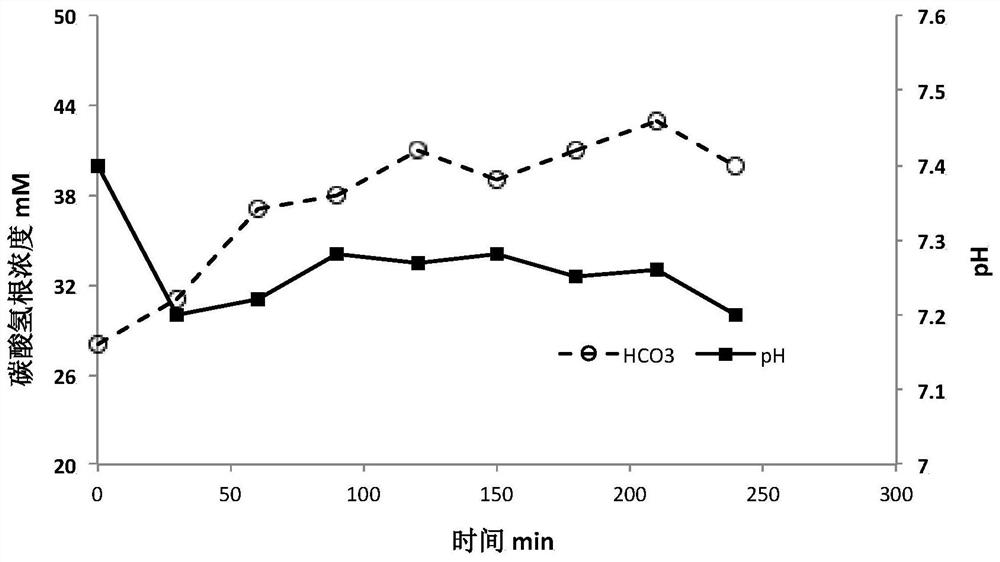
[0063] Take 4L of simulated solution, add 8g of urea to it, stir evenly, and place it on the arterial blood side. Set blood pump flow rate to 200mL / min, dialysate flow rate to 300mL / min, and treat for 240 minutes. After starting the treatment, a peristaltic pump was used to continuously supplement the blood end with urea solution (150 mg / mL, total 100 mL) at a flow rate of 0.5 mL / min. Imported dialysate samples were taken, and changes in bicarbonate ions and partial pressure of carbon dioxide were measured using a blood gas analyzer (Radiometer, ABL80).
[0064] The result is as Figure 4 and Figure 5 As can be seen from the figure, when the aqueous solution of 1% sodium hydroxide and 2% sodium carbonate is used as liquid B, the pH of the dial...
Embodiment 3
[0065] Embodiment 3: B liquid is the aqueous solution of 1.2% sodium carbonate+2% sodium hydroxide
[0066] Adopt the same flow process as embodiment 1 to carry out the simulated dialysate regeneration cycle test, the difference is:
[0067] Take 4L of simulated solution, add 8g of urea to it, stir evenly, and place it on the blood side. Set blood pump flow rate to 200mL / min, dialysate flow rate to 300mL / min, and treat for 240 minutes. After starting the treatment, a peristaltic pump was used to continuously supplement the blood end with urea solution (150 mg / mL, total 100 mL) at a flow rate of 0.5 mL / min. Imported dialysate samples were taken, and changes in bicarbonate ions and partial pressure of carbon dioxide were measured using a blood gas analyzer (Radiometer, ABL80).
[0068] The result is as Figure 6 and Figure 7 As can be seen from the figure, when the aqueous solution of 2% sodium hydroxide and 1.2% sodium carbonate is used as liquid B, the pH of the dialysate...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com