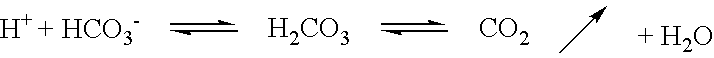Patents
Literature
382 results about "Dialysis solutions" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Two dialysis solutions for acute peritoneal dialysis Acute kidney injury (AKI) can be treated with either bicarbonate or lactate in acute peritoneal dialysis (PD). The aim of this review was to compare the effectiveness of bicarbonate versus lactate solution.
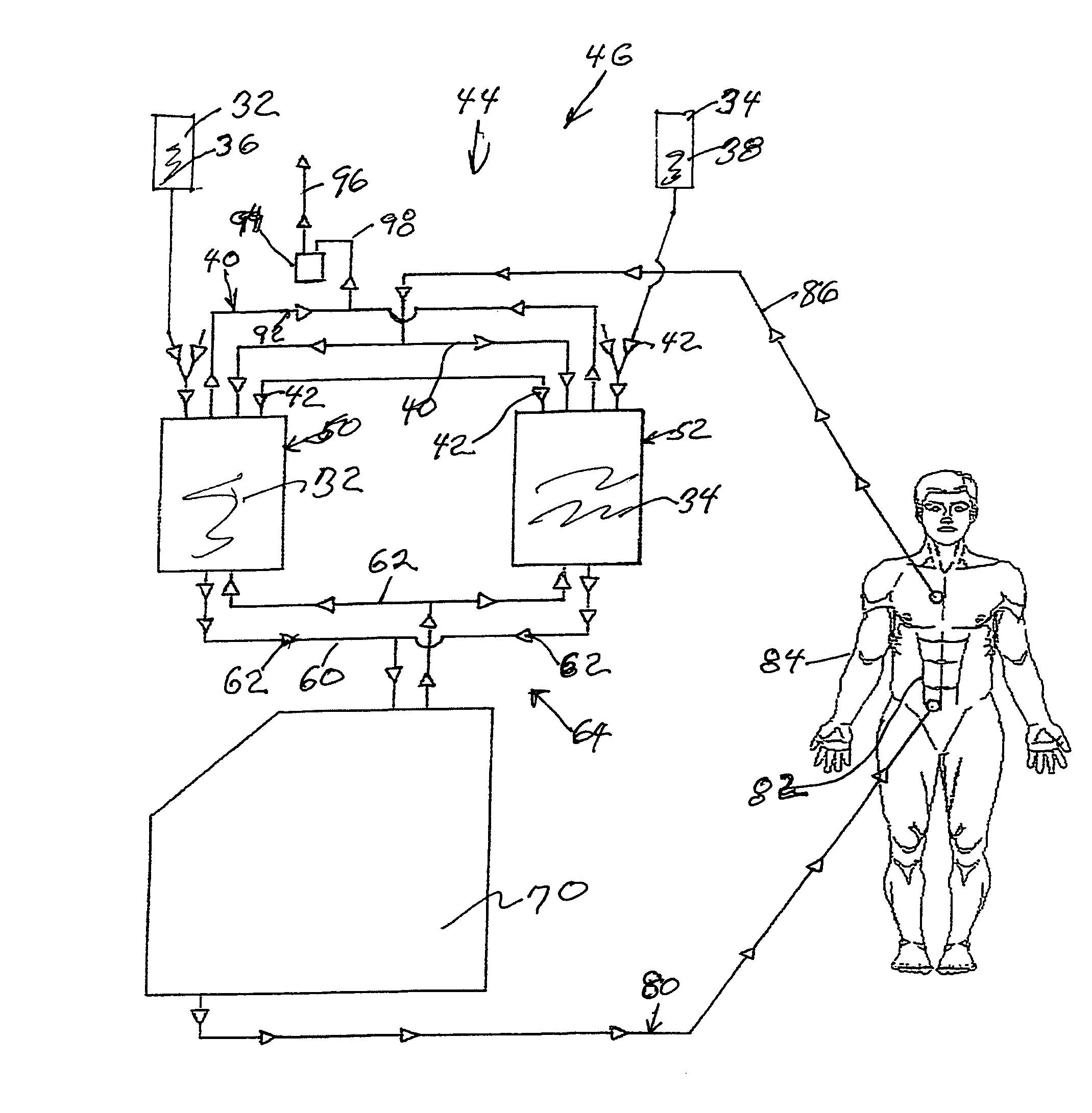
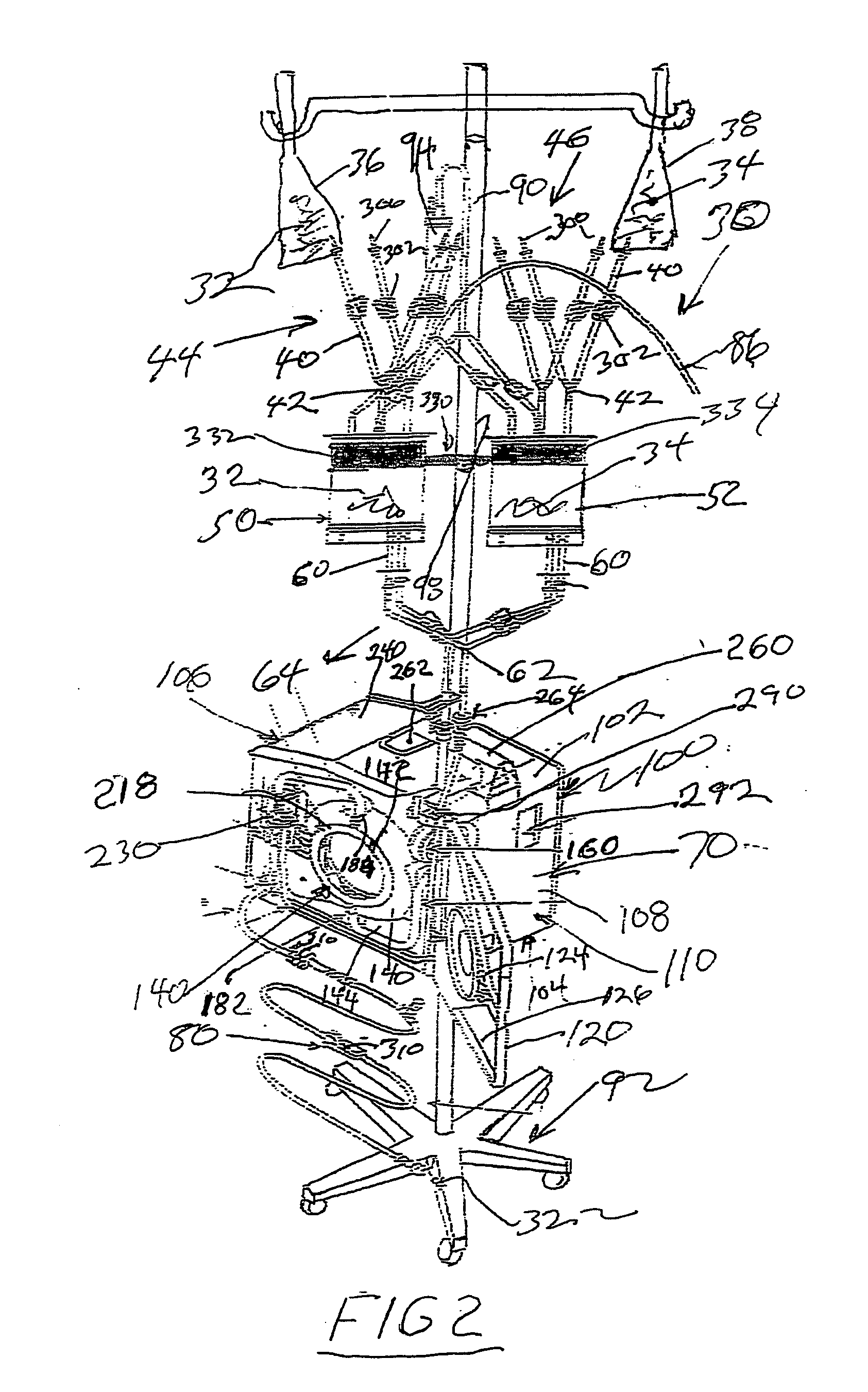
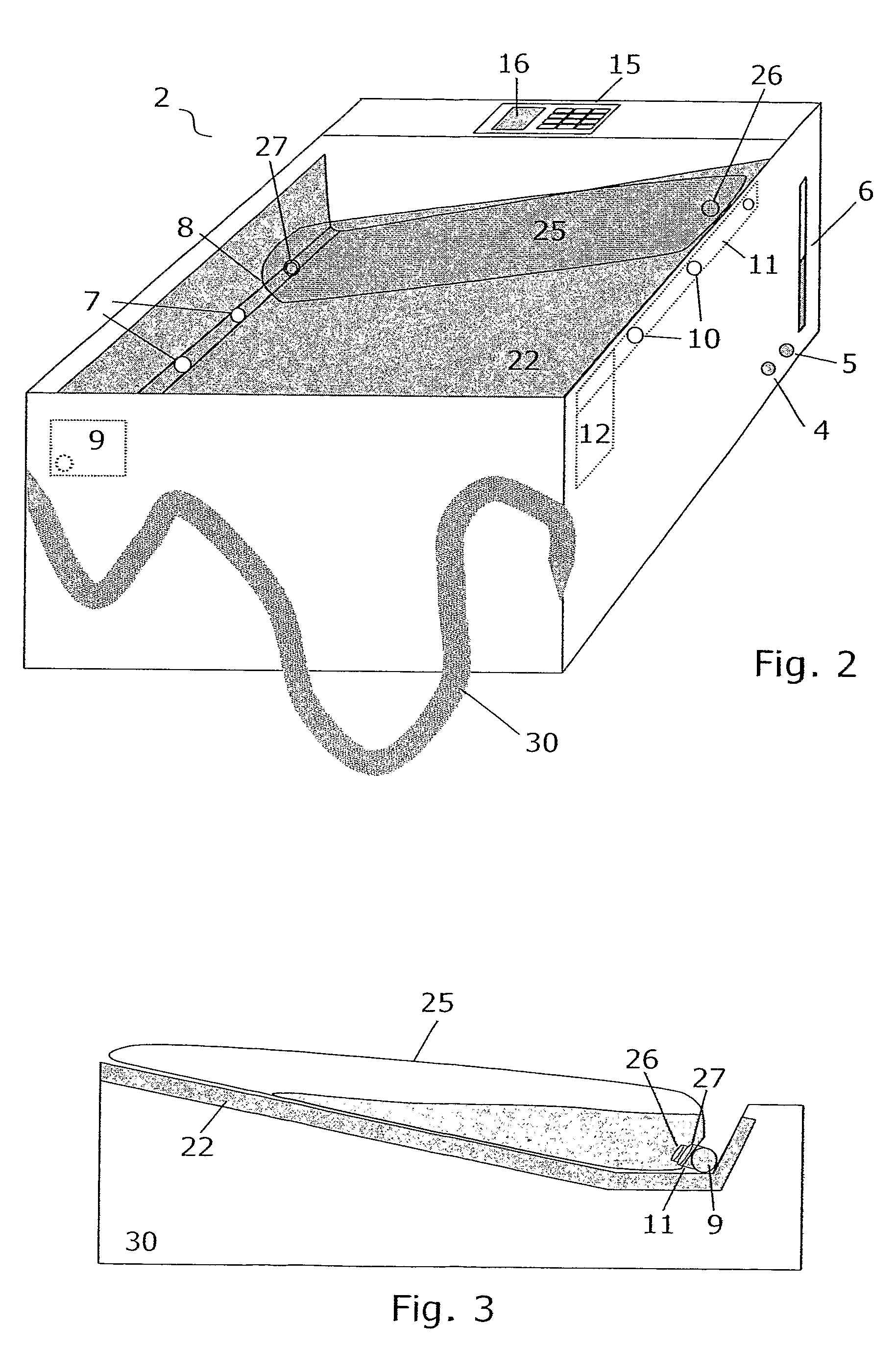
High convection home hemodialysis/hemofiltration and sorbent system
InactiveUS20050131332A1Easily set up sterile blood therapy systemImprove efficiencySemi-permeable membranesHaemofiltrationPositive pressureSorbent
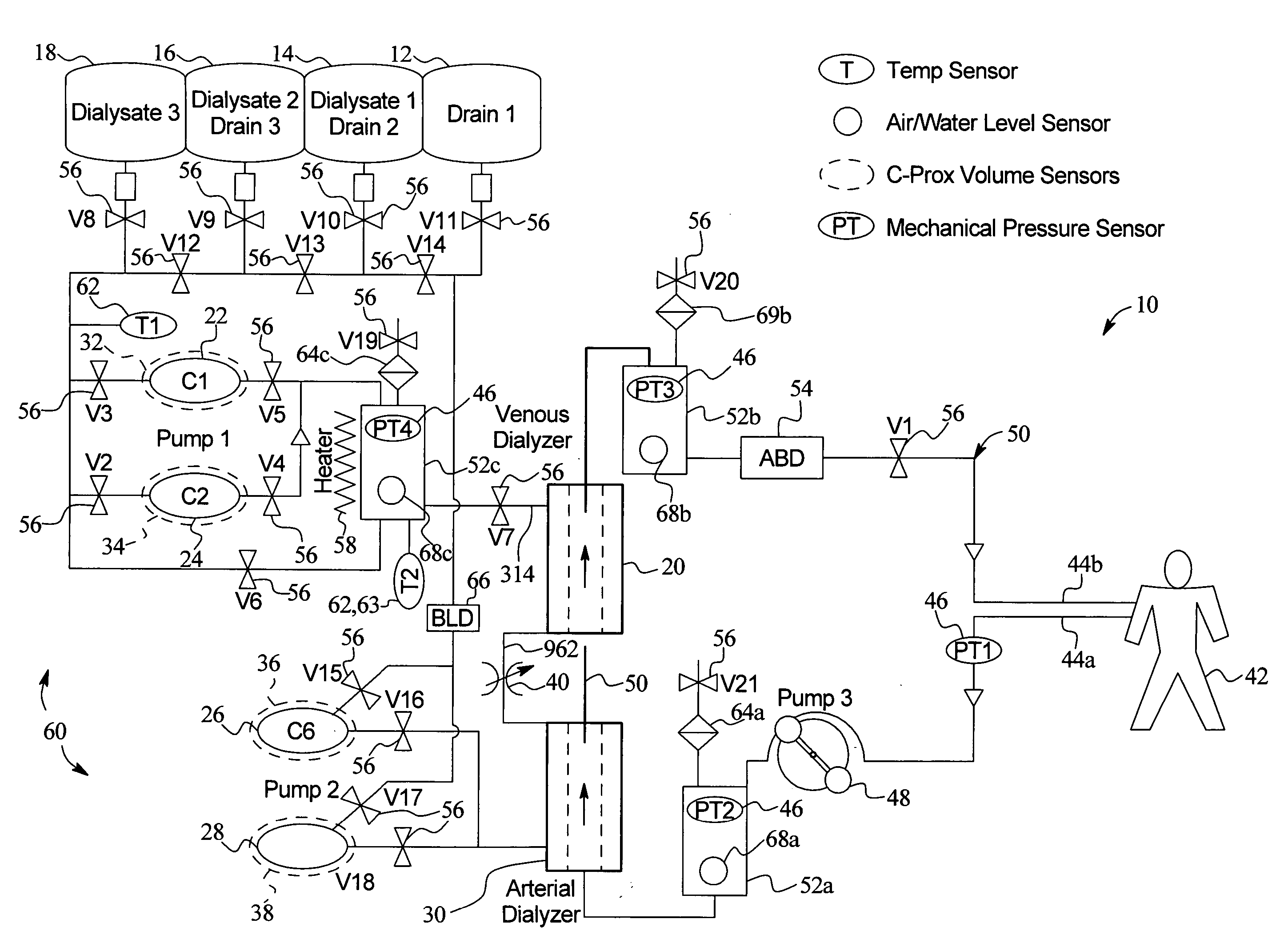
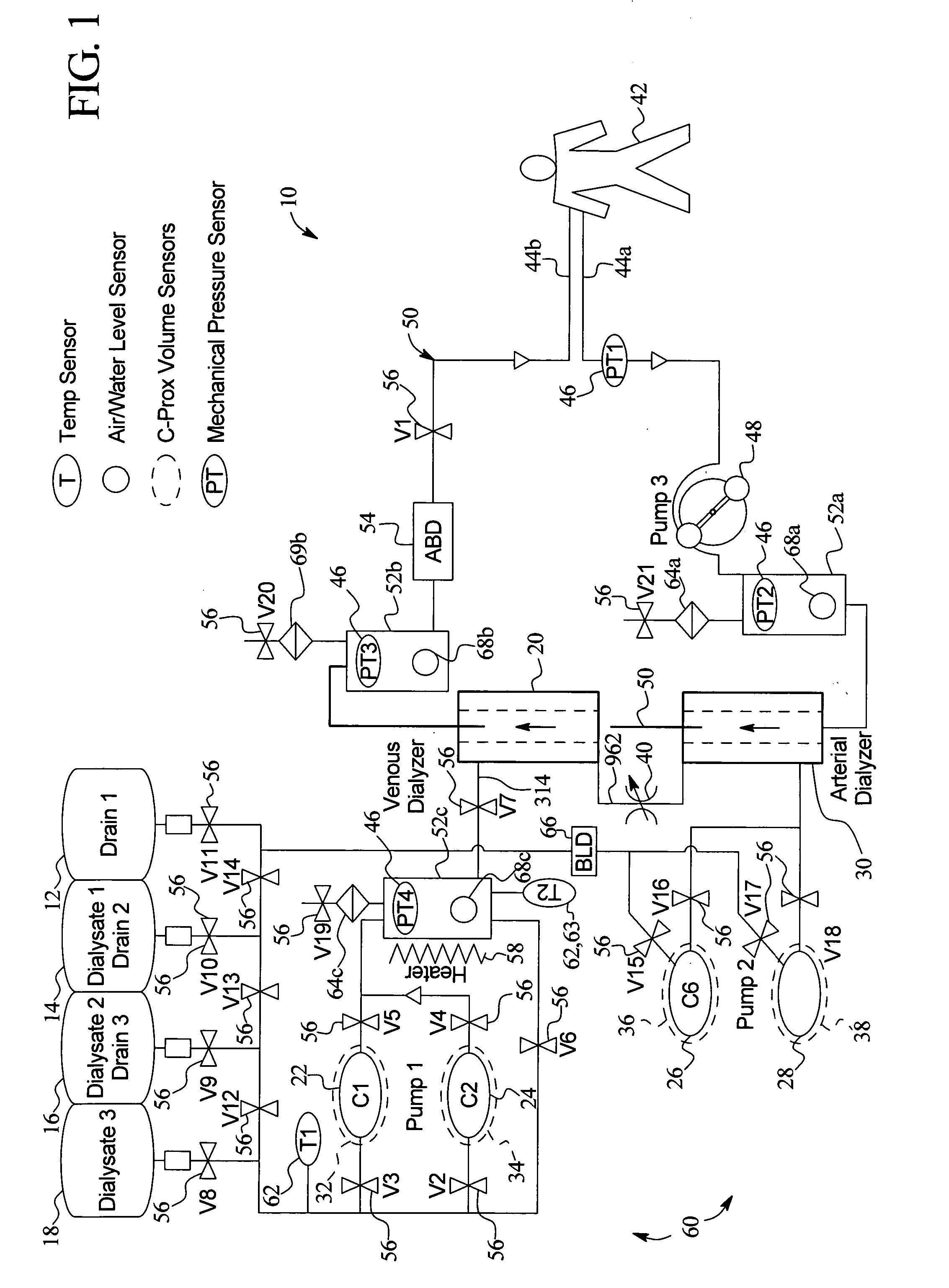
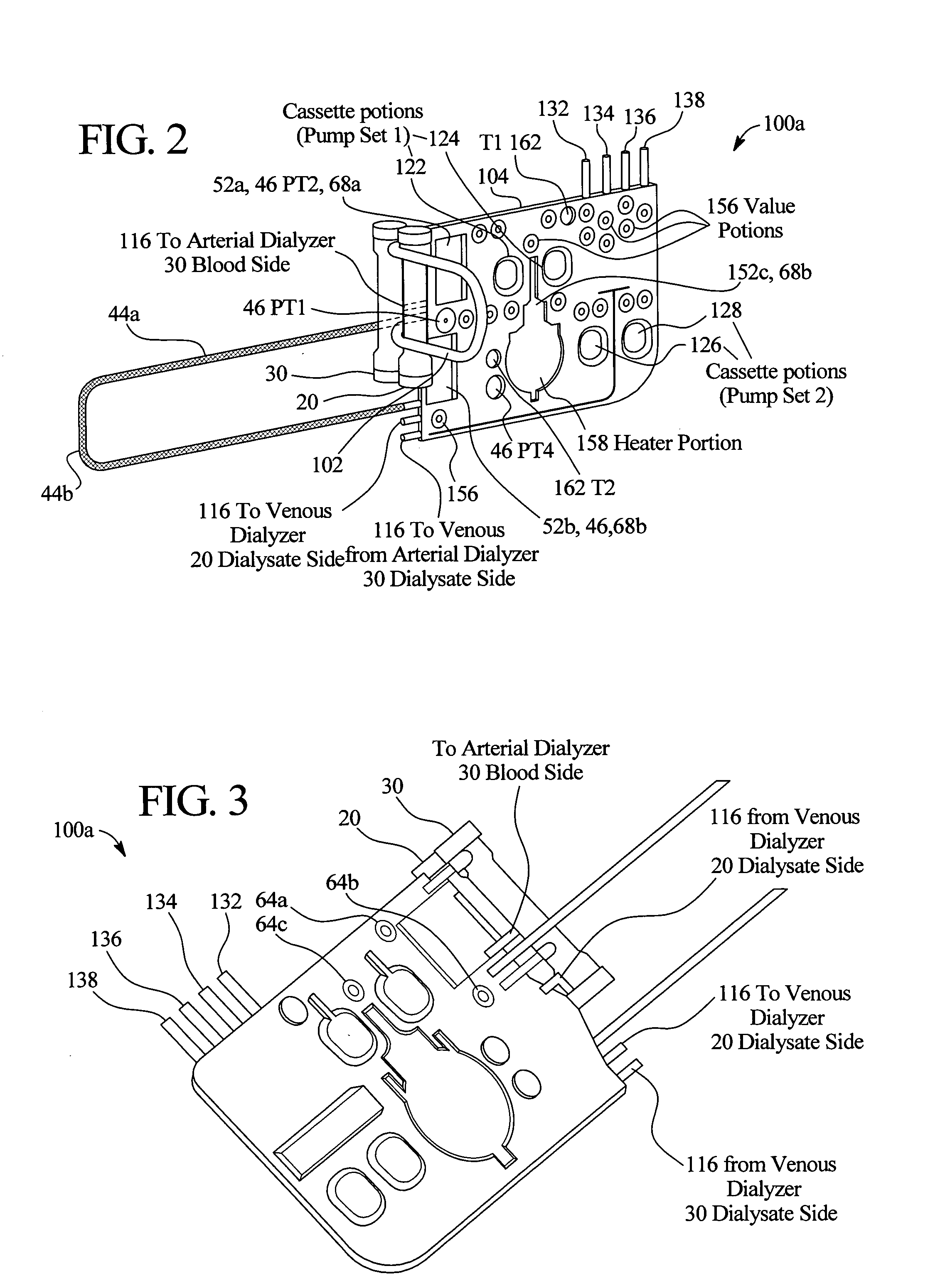
A system, method and apparatus for performing a renal replacement therapy is provided. In one embodiment, two small high flux dialyzers are connected in series. A restriction is placed between the two dialyzers in the dialysate flow path. The restriction is variable and adjustable in one preferred embodiment. The restriction builds a positive pressure in the venous dialyzer, causing a high degree of intentional backfiltration. That backfiltration causes a significant flow of dialysate through the high flux venous membrane directly into the patient's blood. That backfiltered solution is subsequently ultrafiltered from the patient from the arterial dialyzer. The diffusion of dialysate into the venous filter and removal of dialysate from the arterial dialyzer causes a convective transport of toxins from the patient. Additionally, the dialysate that does not diffuse directly into the patient but instead flows across the membranes of both dialyzers provides a diffusive clearance of waste products.
Owner:BAXTER HEALTHCARE SA +1
Cartridges useful in cleaning dialysis solutions
InactiveUS20020112609A1Avoid a lotSolve the blockageIsotope separationLoose filtering material filtersHemodialysis membraneChemistry
Owner:RENAL SOLUTIONS
Cartridges useful in cleaning dialysis solutions
InactiveUS7033498B2Avoid a lotSolve the blockageZirconium compoundsLoose filtering material filtersMedicineHemodialysis membrane
Owner:RENAL SOLUTIONS
Dialysis solution for peritoneal dialysis
InactiveUS6284140B1Easy to degradeDwell timeBiocideSolvent extractionHydroxyethyl starchUltrafiltration
The present invention relates to dialysis solutions for peritoneal dialysis, containing hydroxyethyl starch as the osmotically-active substance, electrolytes and, optionally, conventional additives, where the hydroxyethyl starch has a molecular weight Mw in the range from 10,000 to 150,000, a substitution MS in the range from 0.10 to 0.40, a substitution DS in the range from 0.09 to 0.35 and a substitution ratio C2 / C6>=8. With this peritoneal dialysis solution it is possible, with an outstanding ultrafiltration, to maintain a longer dwell time, for example the dialysis solution can be utilized for a period of 12 hours in the CAPD without replacement. In addition, the inventive dialysis solution is also particularly advantageous for patients with residual kidney function. The resorption of the osmotically active substance is clearly diminished and even after a dwell time of 12 hours it amounts to a maximum of 60-70%.
Owner:FRESENIUS AG
Automated solution injection-discharge system and automated peritoneal dialysis system
InactiveUS6491658B1Easy to controlOperational securityPeritoneal dialysisIntensive care medicineDialysis fluid
The automated solution injection-discharge system is used as an APDS system to supply and discharge a dialysate and a patient's drain. And an automated solution injection-discharge system provides free of contamination and operation mistakes, and can accurately control the injected dialysate volume and the discharged dwell solution volume even when a patient does not maintain a fixed posture while replacing the solution.
Owner:JMS CO LTD
Drain and fill logic for automated peritoneal dialysis
ActiveUS20100191181A1Limit low drain alarmLimitMedical devicesDialysisContinuous cycling peritoneal dialysisDraining tube
A system and method for automatically adjusting a Continuous Cycling Peritoneal Dialysis (“CCPD”) therapy to minimize the potential for excess intra-peritoneal volume. The adjustments are made at the end of the drain, just prior to the next fill. The adjustments short the next fill, if necessary, to limit the intra-peritoneal volume, add a cycle, if necessary, to use all of the available dialysis solution and will average the remaining dwell time to maximize the therapeutic benefit of the therapy in the allotted time. In another embodiment, a tidal therapy using trended patient UF data is provided.
Owner:BAXTER HEALTHCARE SA +1
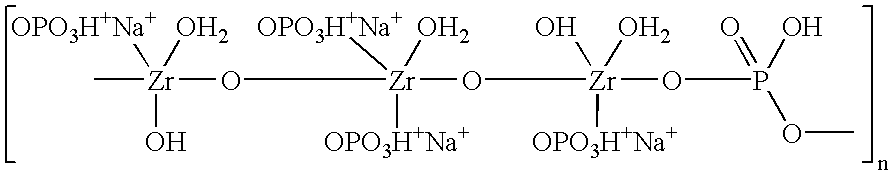
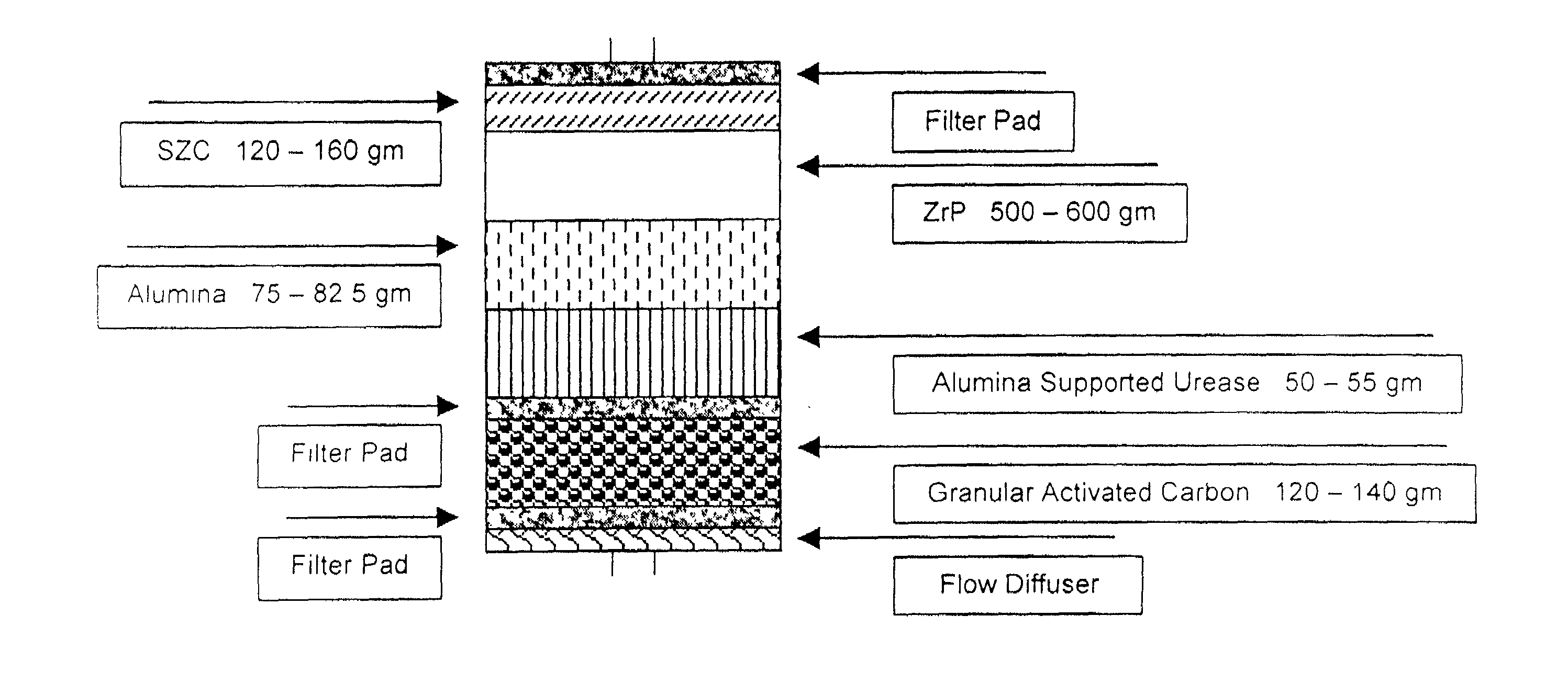
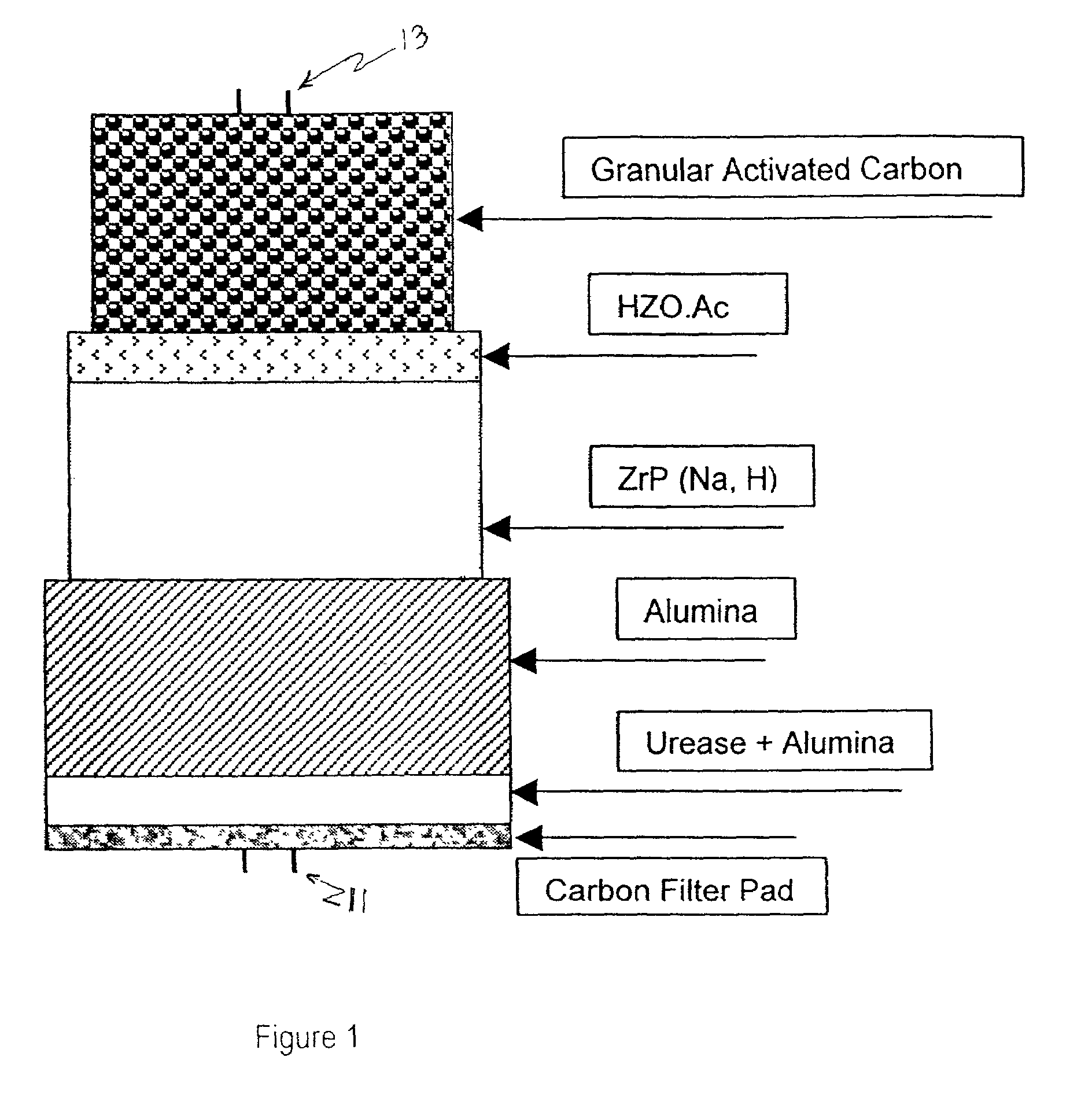
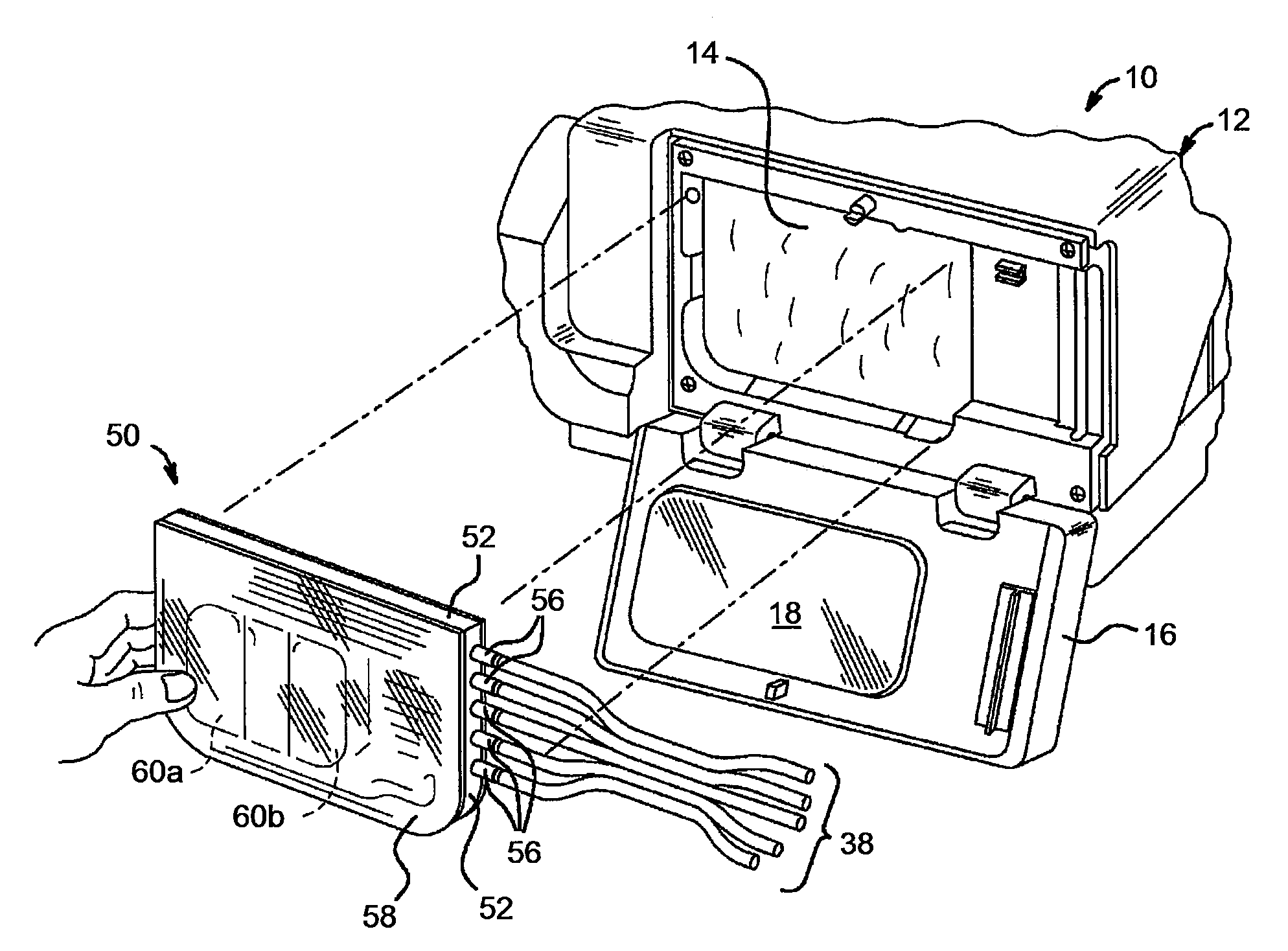
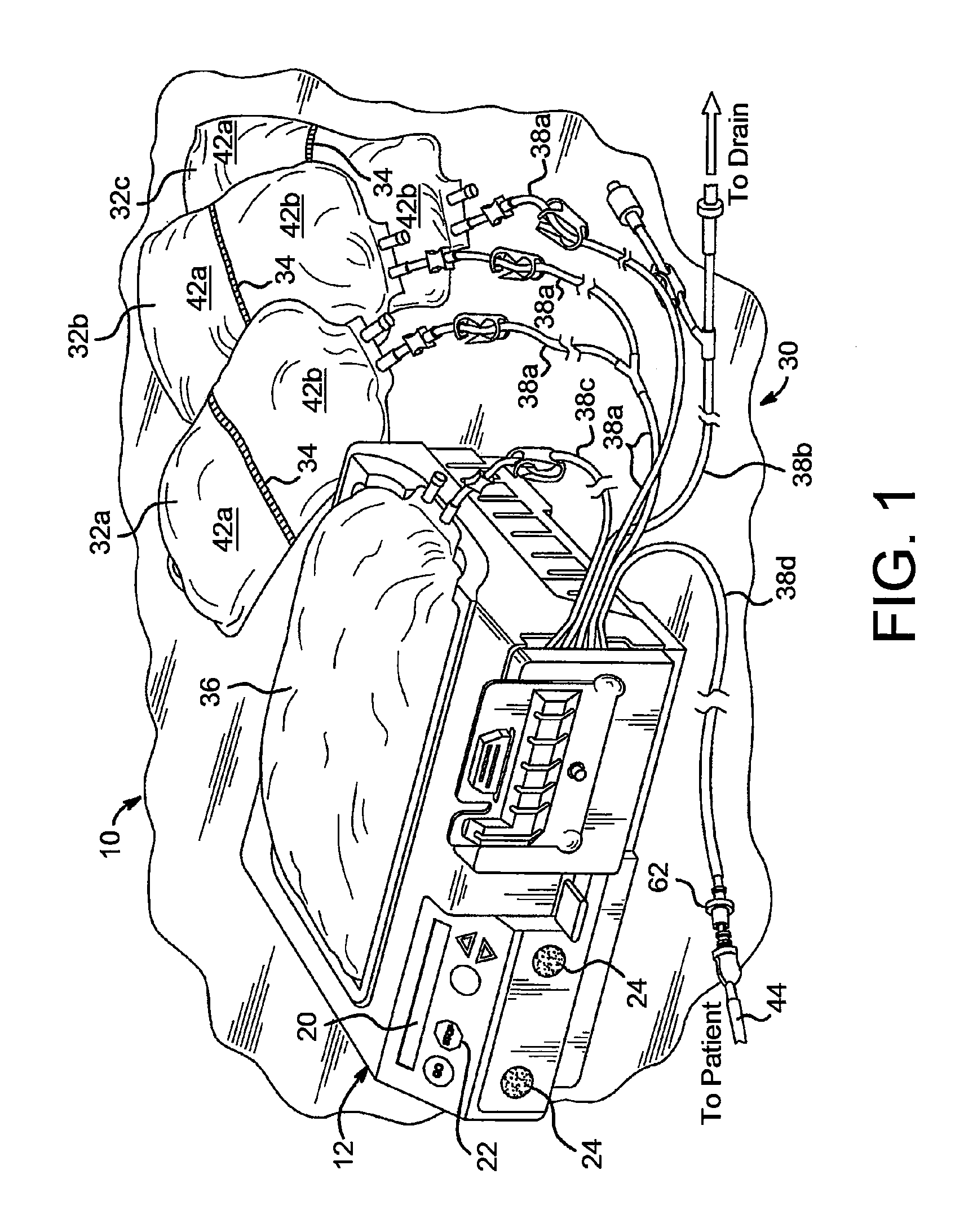
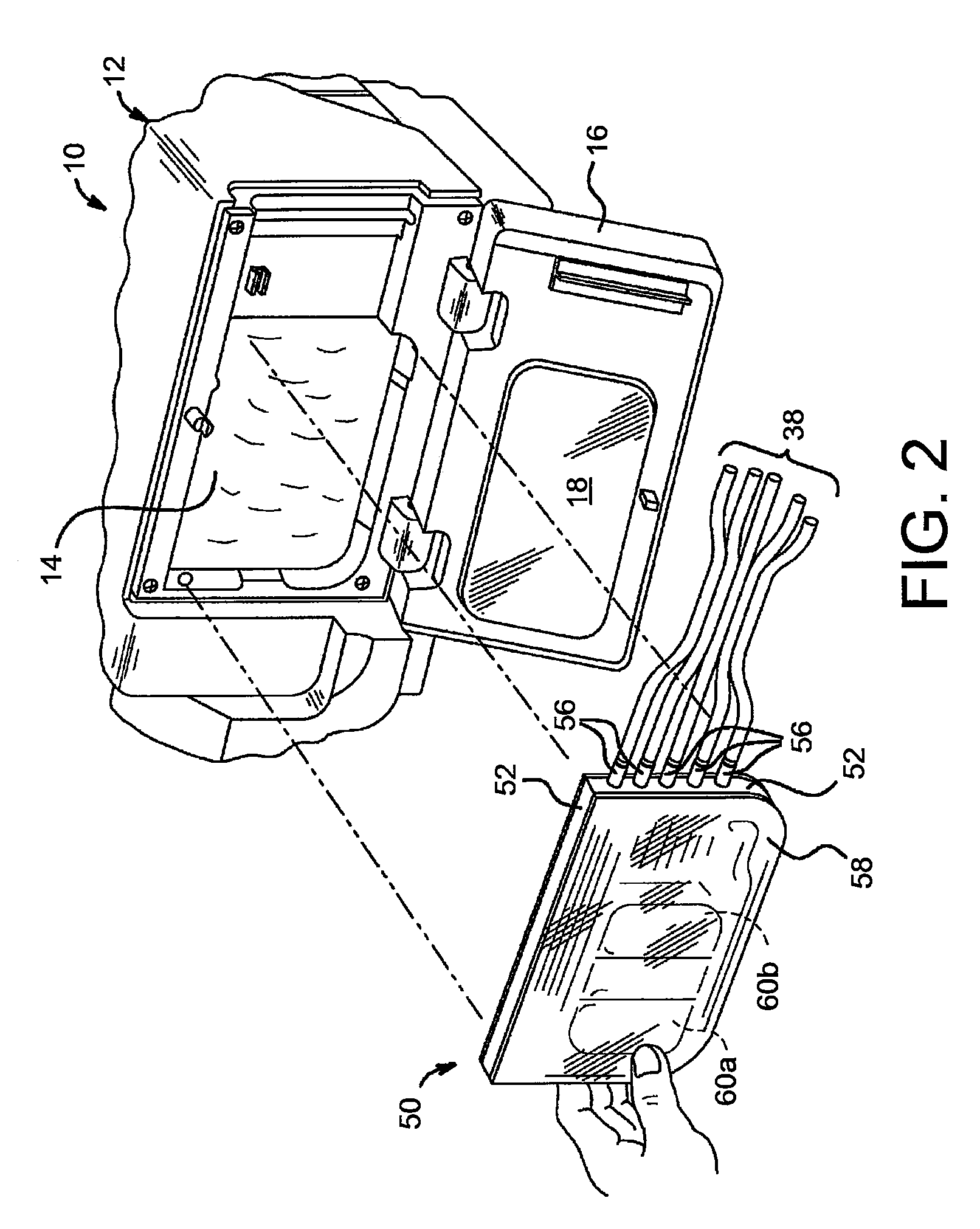
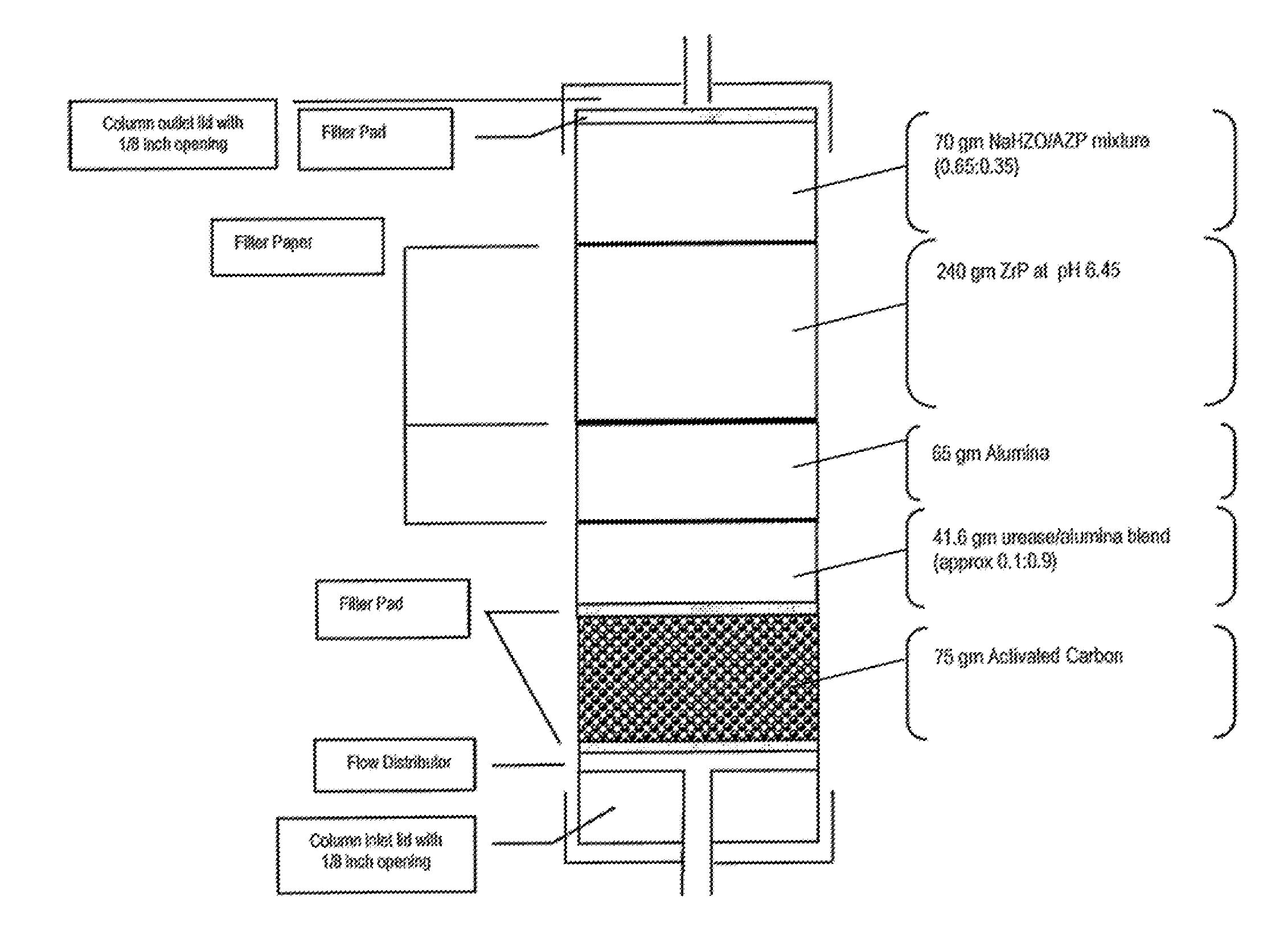
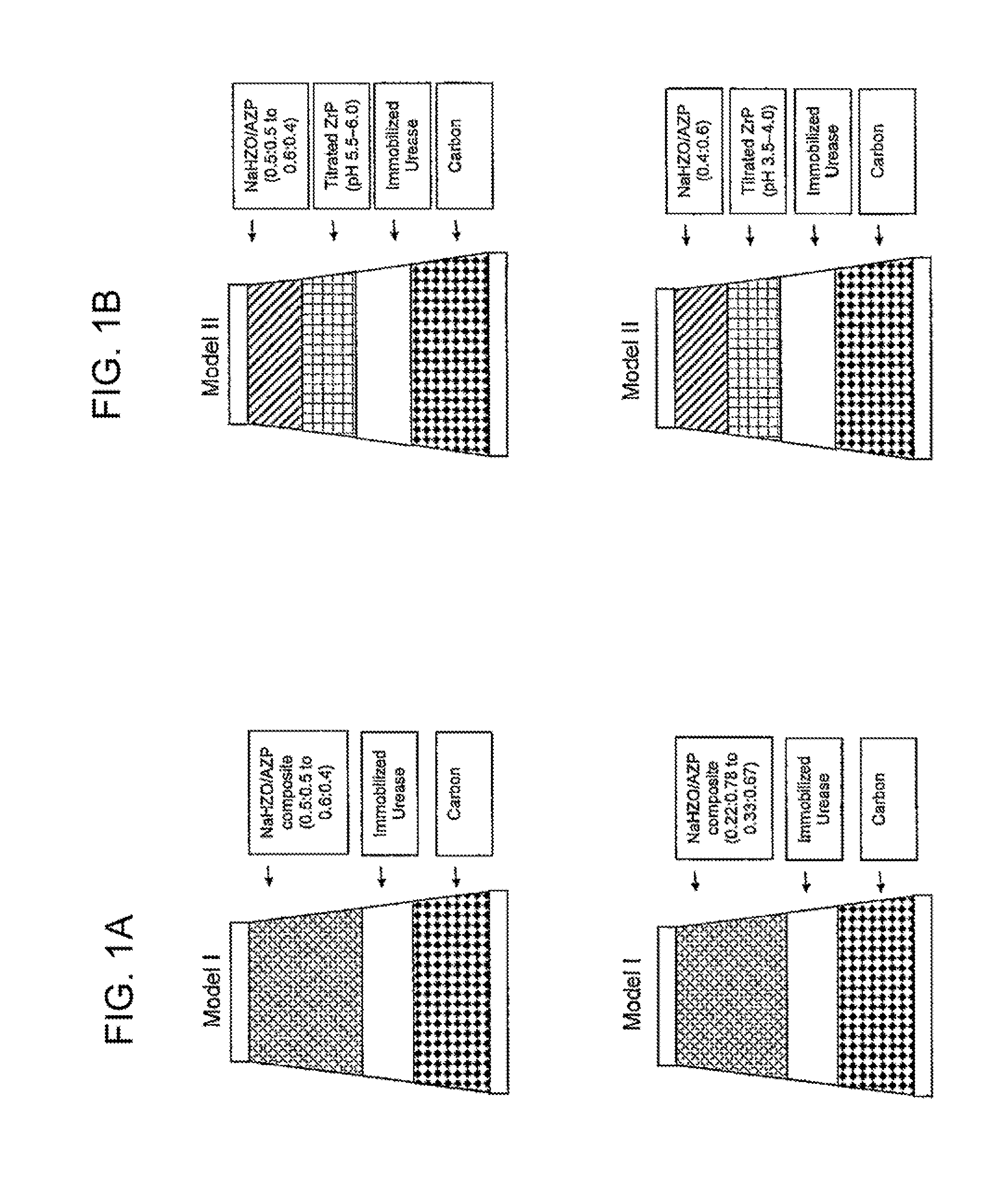
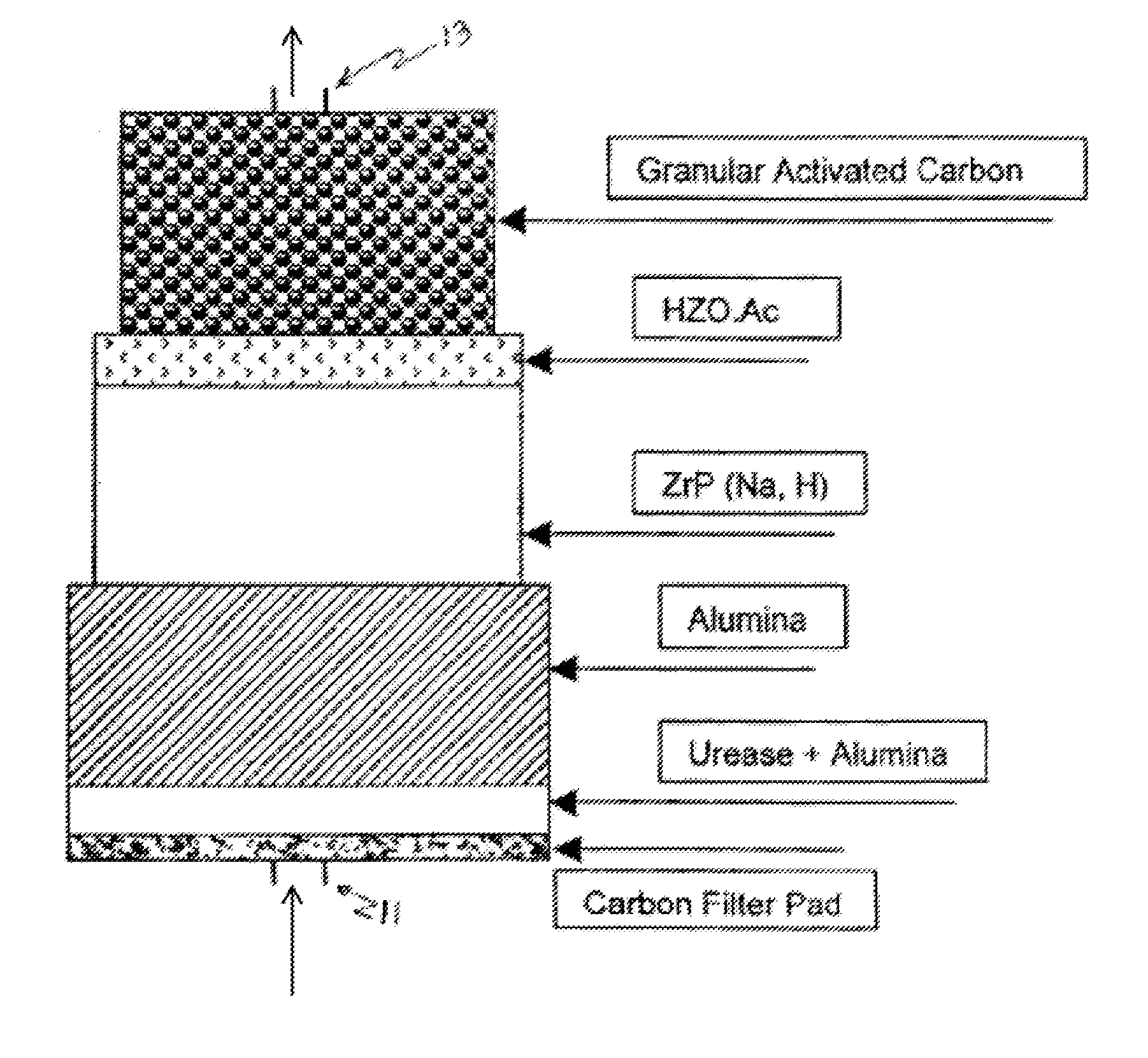
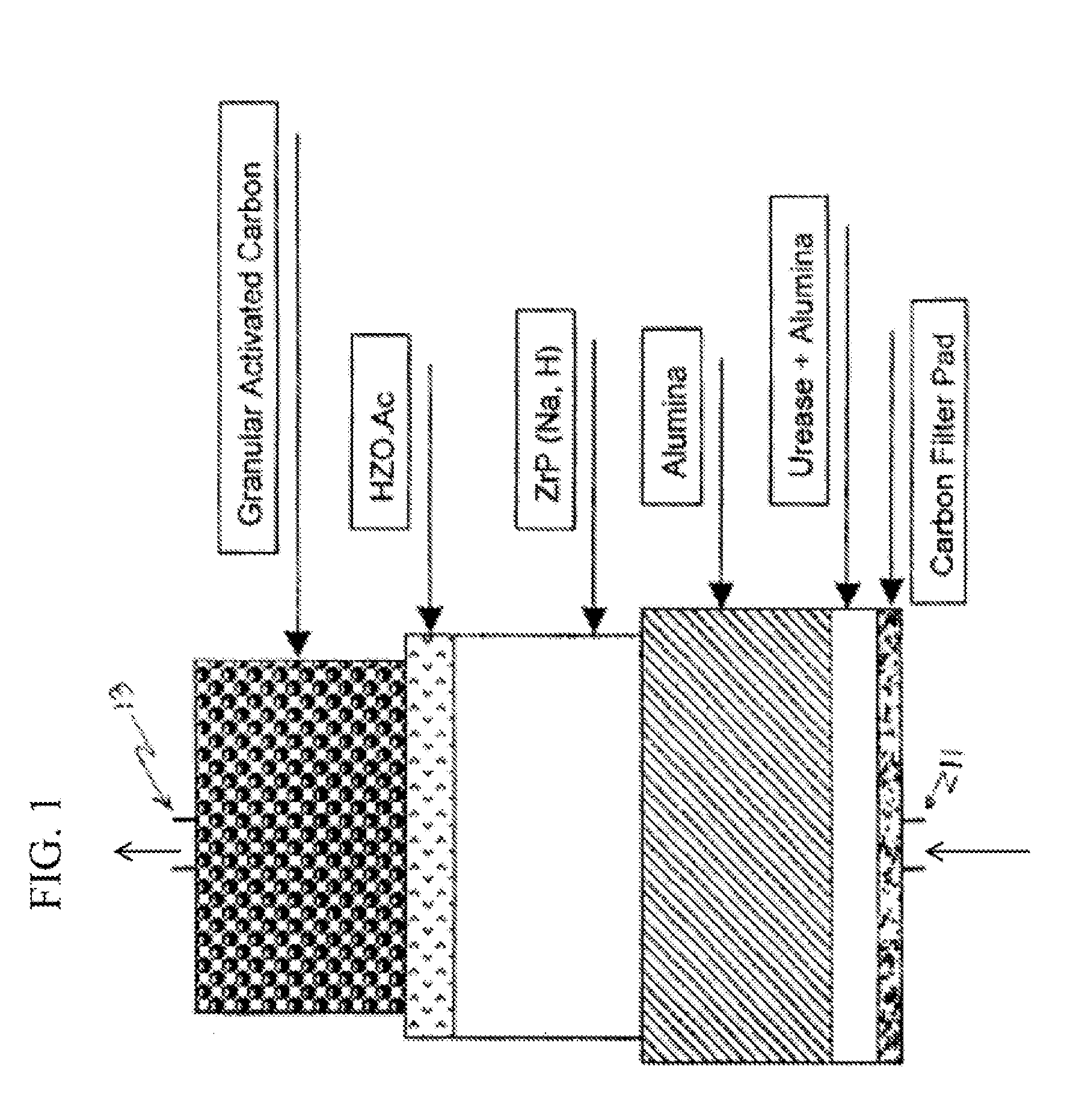
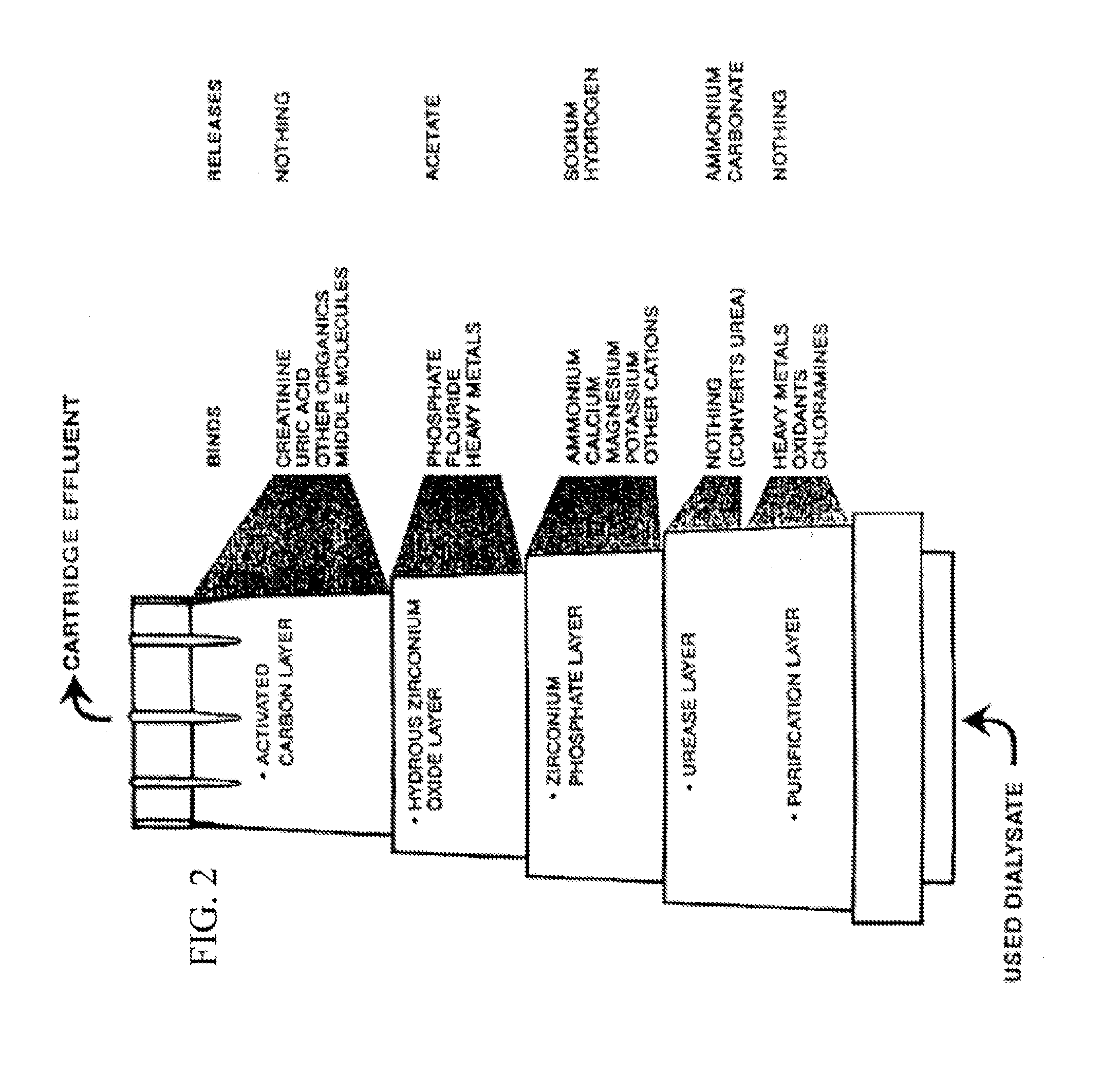
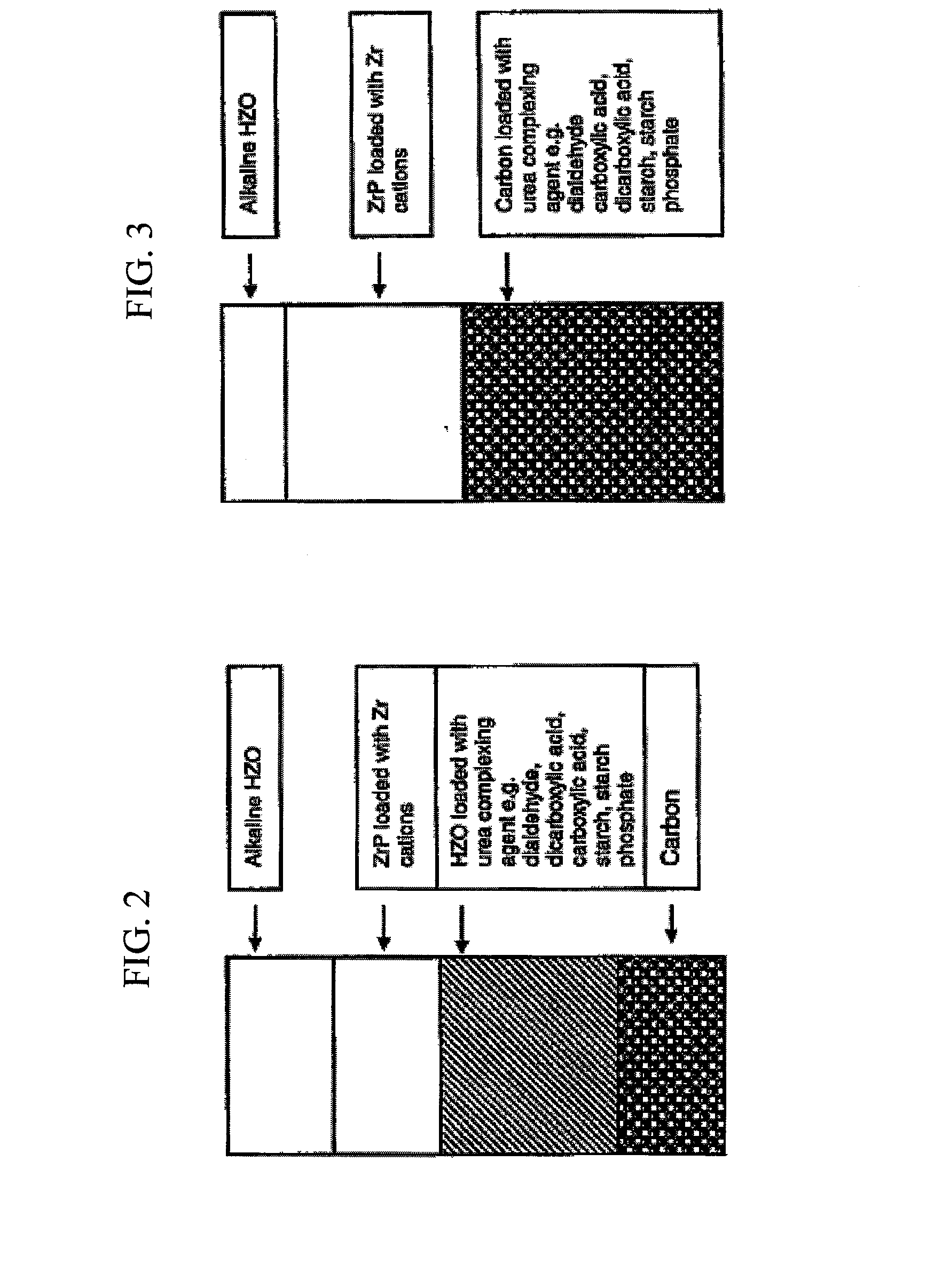
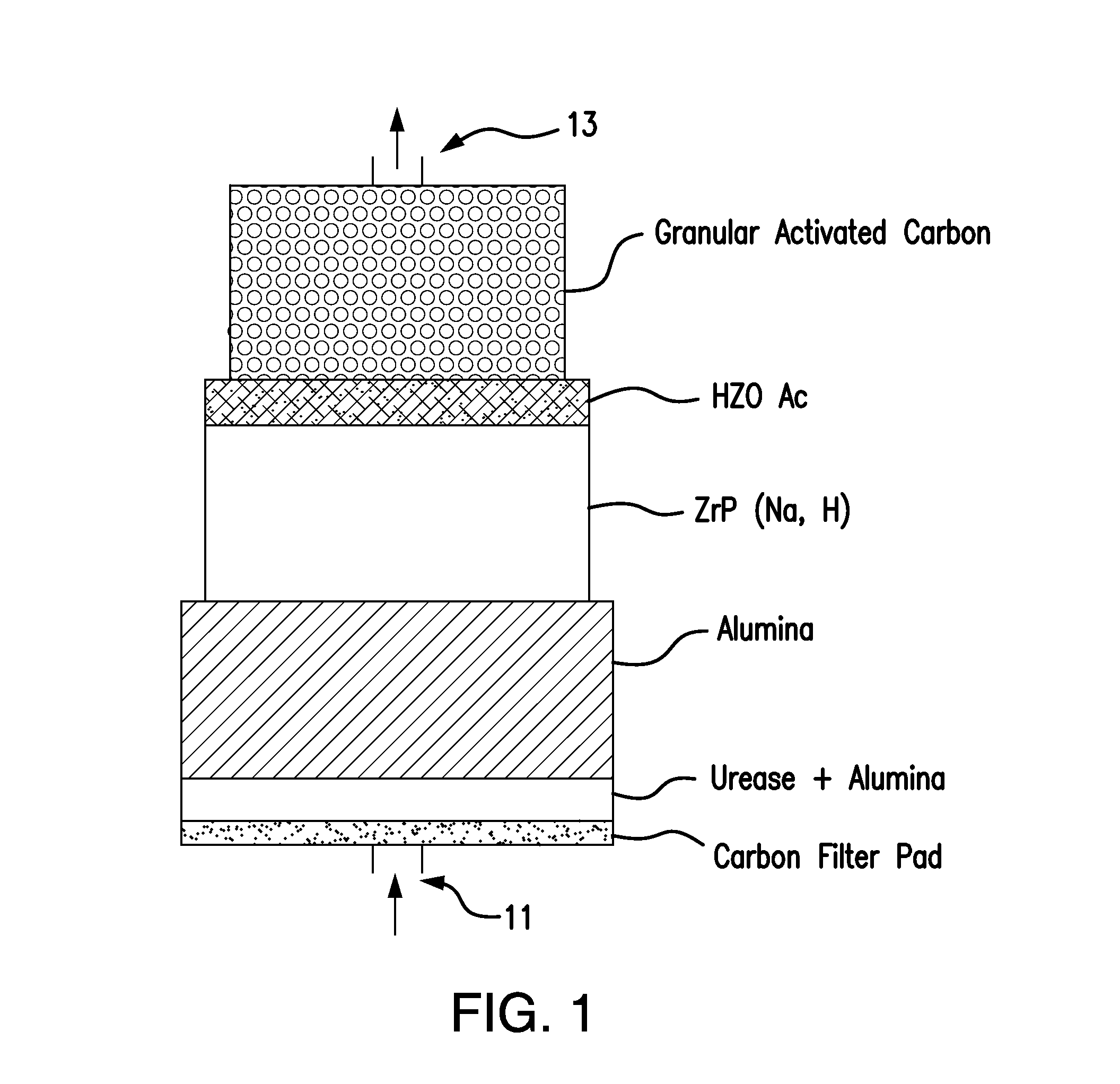
Acid zirconium phosphate and alkaline hydrous zirconium oxide materials for sorbent dialysis
ActiveUS8409444B2Avoid disadvantagesRestore balanceCation exchanger materialsSolvent extractionIon exchangeDialysis fluid
Owner:FRESENIUS MEDICAL CARE HLDG INC
Haemodialfiltration method and apparatus
InactiveUS20100187176A1Extended service lifeAvoid performance degradationSolvent extractionMixing methodsBlood pumpToxic material
Device for haemodiafiltration, which comprises a first circuit for a dialysis solution and a second circuit for blood, so that the toxic substances from the blood flow pass into the dialysis liquid within a haemofilter (11), a liquid pump (20) located upstream of the haemofilter (11) in the first dialysis liquid circuit, is adapted for injecting replacement liquid into the dialysis solution flow after a blood pump (15) finishes pumping blood to the interior of the haemofilter (11).
Owner:FUNDACION PARA LA INVESTIGACION BIOMEDICA DEL HOSPITAL GREGORIO MARANON
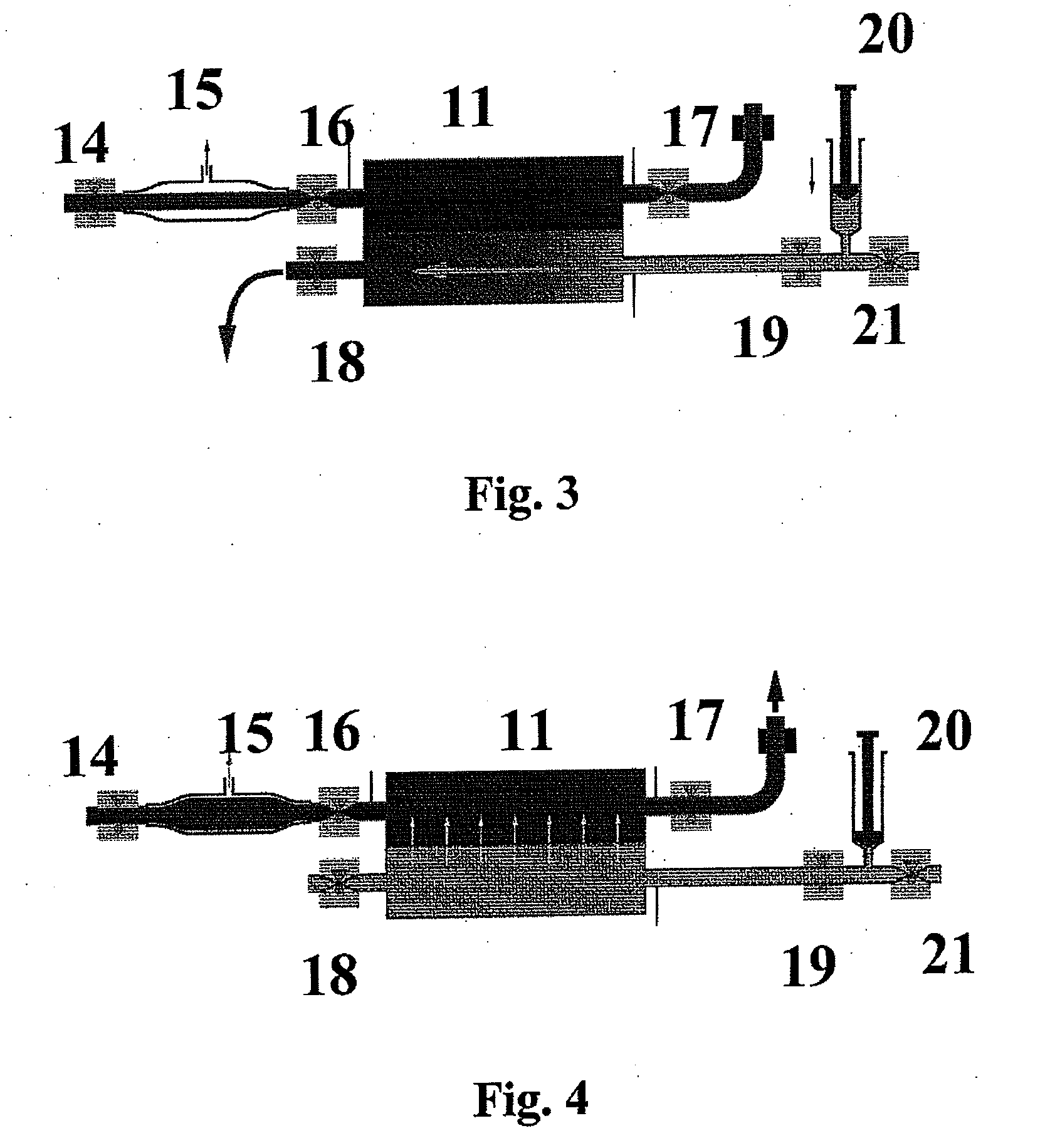
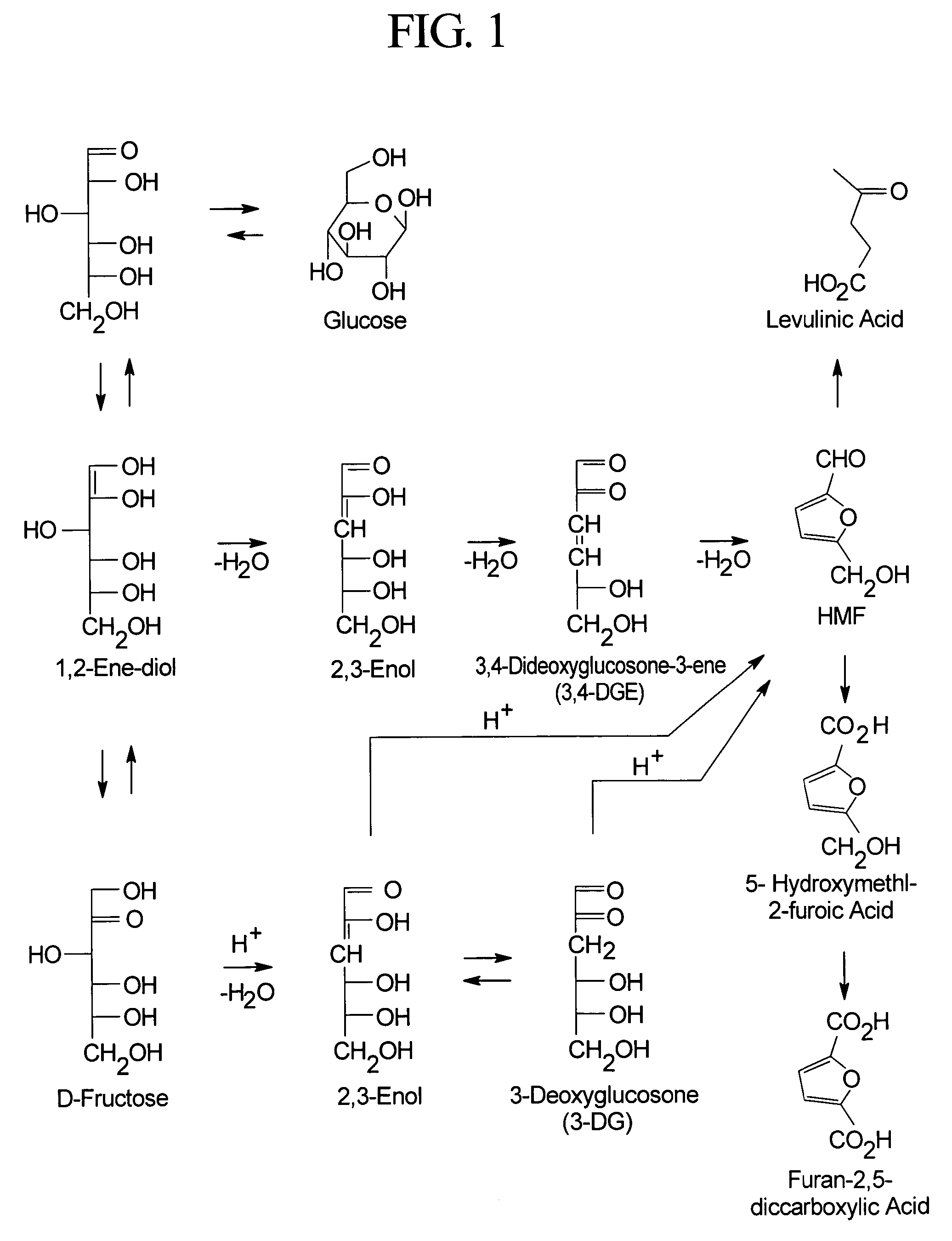
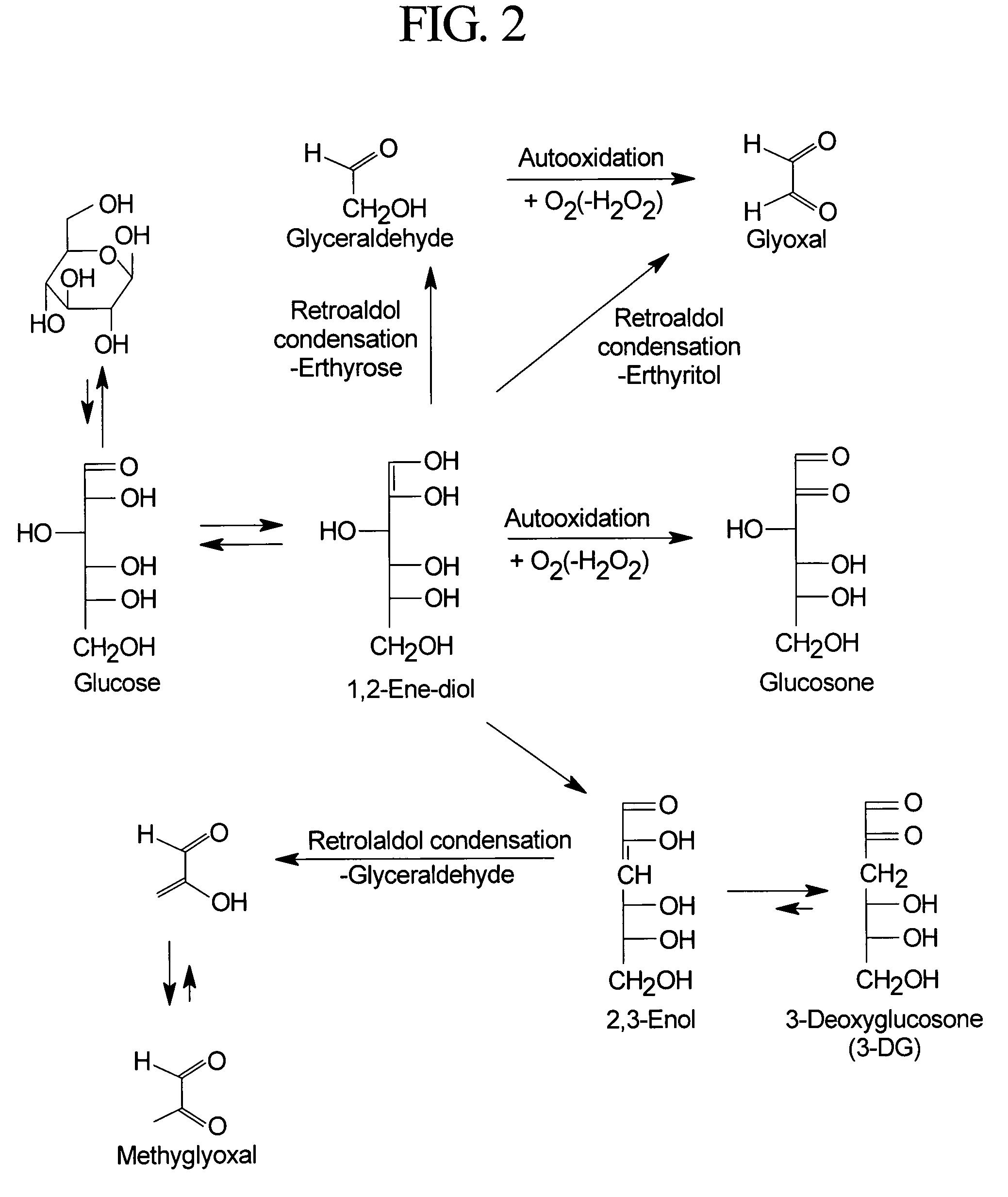
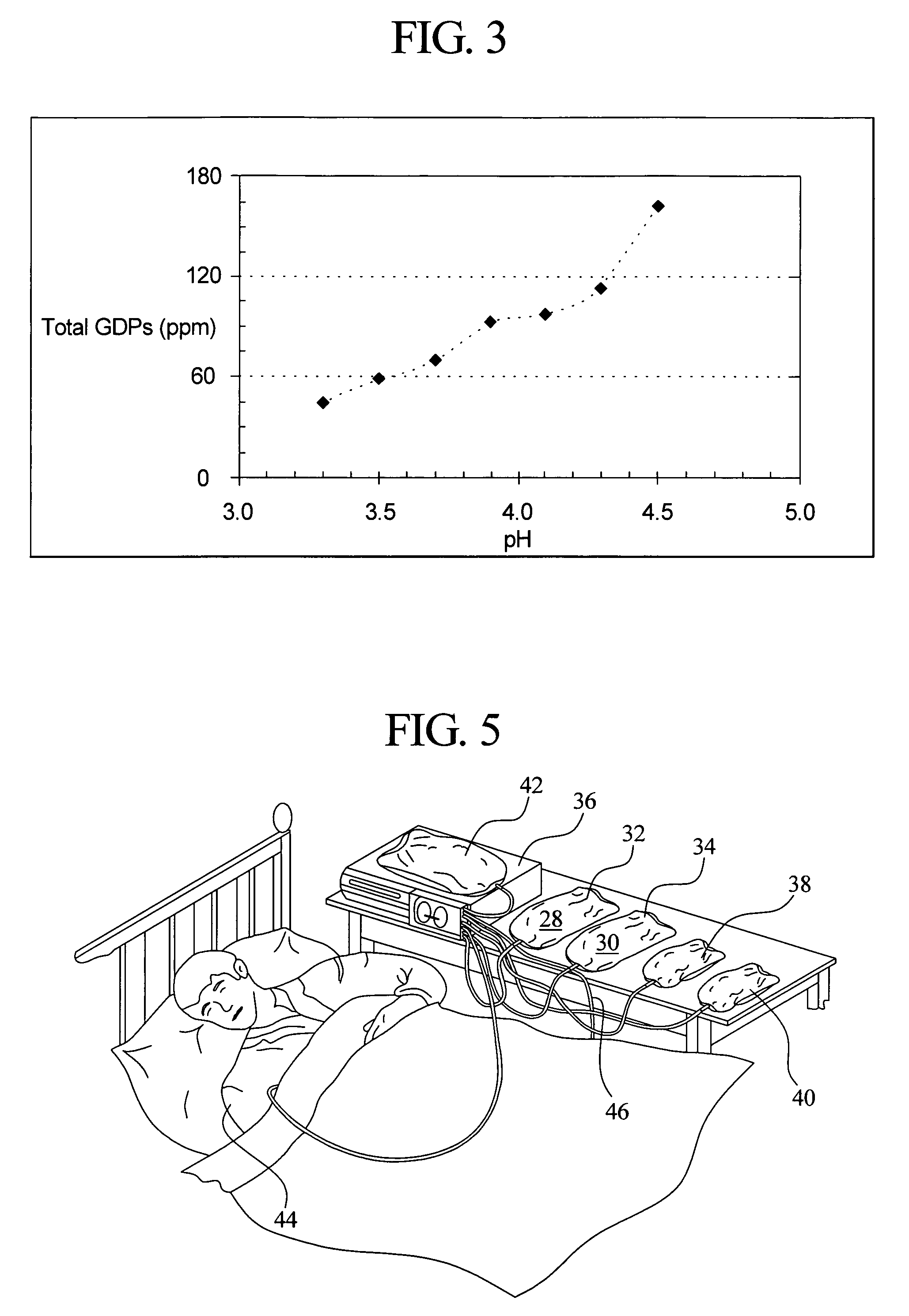
Dialysis solutions with reduced levels of glucose degradation products
InactiveUS7053059B2Improve featuresDecrease in levelBiocidePharmaceutical delivery mechanismMedicineBiocompatibility Testing
Dialysis solutions with enhanced biocompatibility are provided. The dialysis solutions include a first acidic solution and a second acidic solution that are admixed to form a ready-to-use dialysis solution with reduced levels of glucose degradation products prior to use. The first acidic solution includes a dextrose concentrate, and the second acidic solution includes a buffer concentrate, such as a lactate-based buffer. The first and second acid solutions are separately sterilized prior to mixing to form the ready-to-use dialysis solutions. The dialysis solutions can be used in a variety of different applications, such as infusion into a patient during peritoneal dialysis.
Owner:BAXTER INT INC +1
Cartridges Useful In Cleaning Dialysis Solutions
ActiveUS20150258266A1Reduce and eliminate contentReduce and eliminate and releaseDialysis systemsMedical devicesDialysis methodChemistry
Owner:FRESENIUS MEDICAL CARE HLDG INC
Hyperthermia, system, method and components
ActiveUS7819835B2Effective and safe for patientElectrotherapyInfusion devicesIntensive care medicineHigh body temperature
An IV pole mountable, therapeutic infusate processing device is incorporated into a hypothermia system to receive therapeutic fluid(s), such as normal saline, peritioneal dialysis solution, or other crystalloid solution, to heat such therapeutic fluid(s) a few degrees centigrade above normal body temperature and to direct the resulting heated infusate to and through a selected anatomical portion of a patients body to raise the temperature of that body portion so as to affect any cancerous or other tumors that may be located therein. The processing device is provided with touch screen controls and visual indicators to facilitate its proper use; while the system further includes temperature and pressure sensors to monitor the hyperthermia processing to insure patient safety.
Owner:BELMONT INSTR LLC
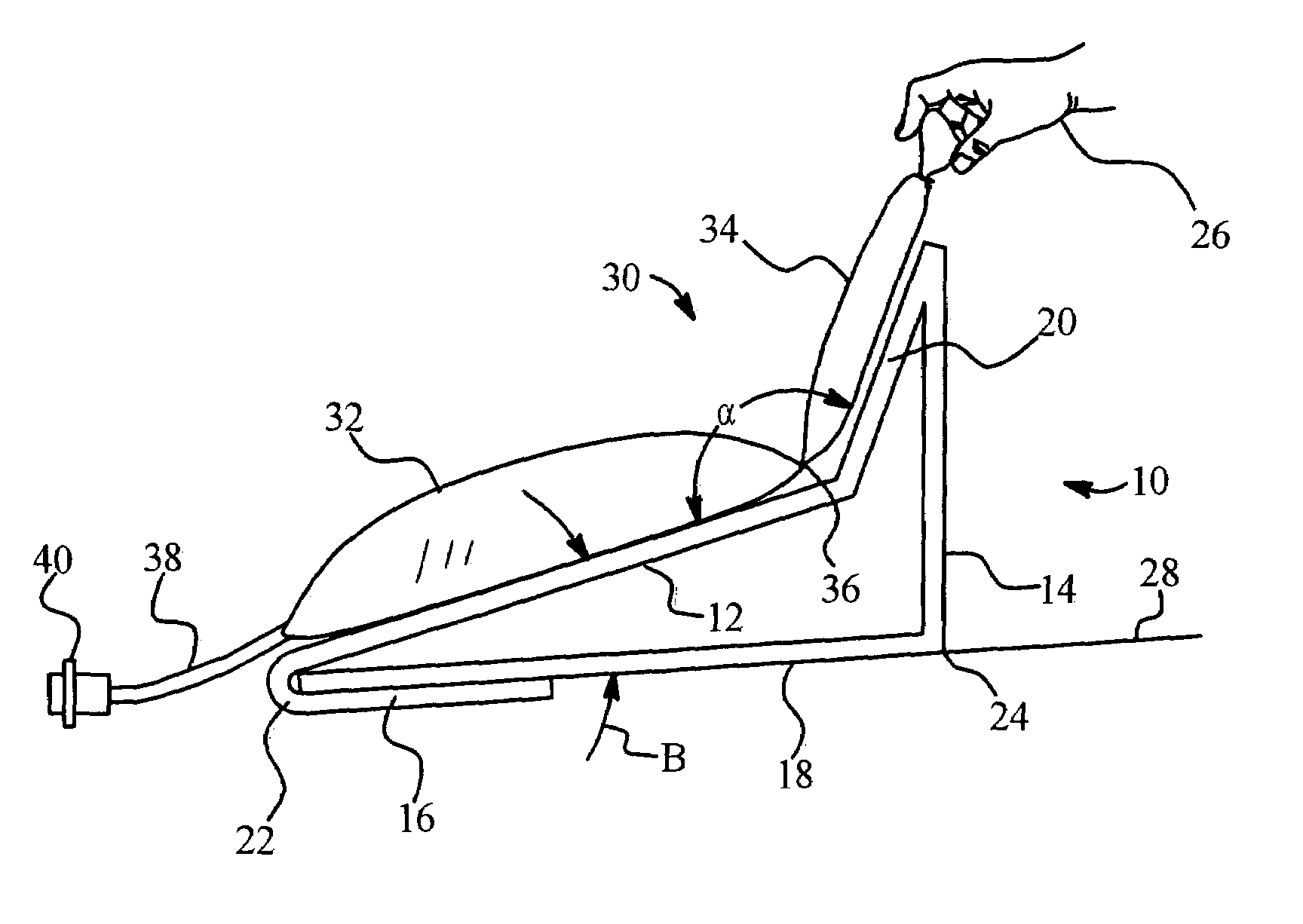
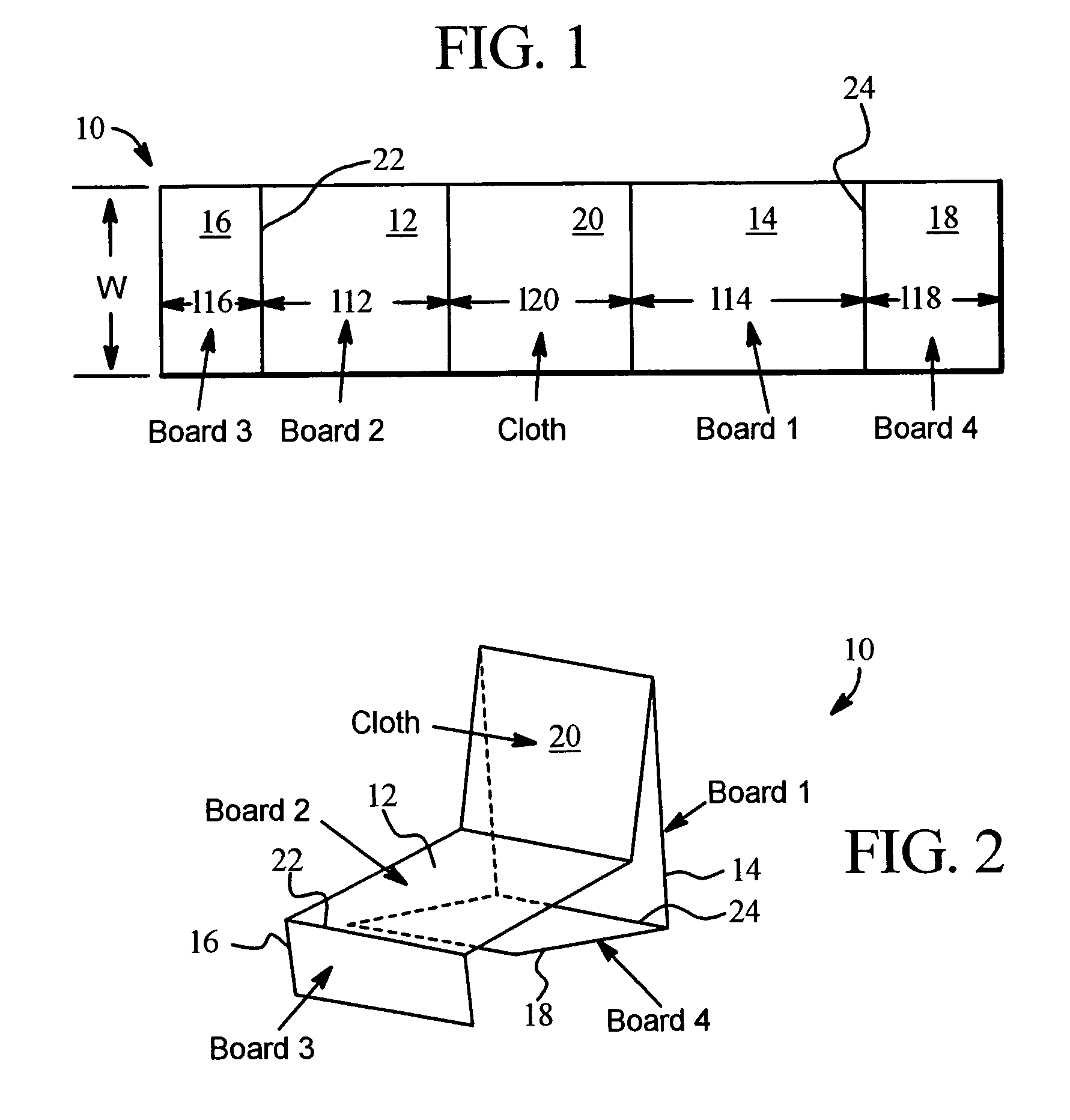
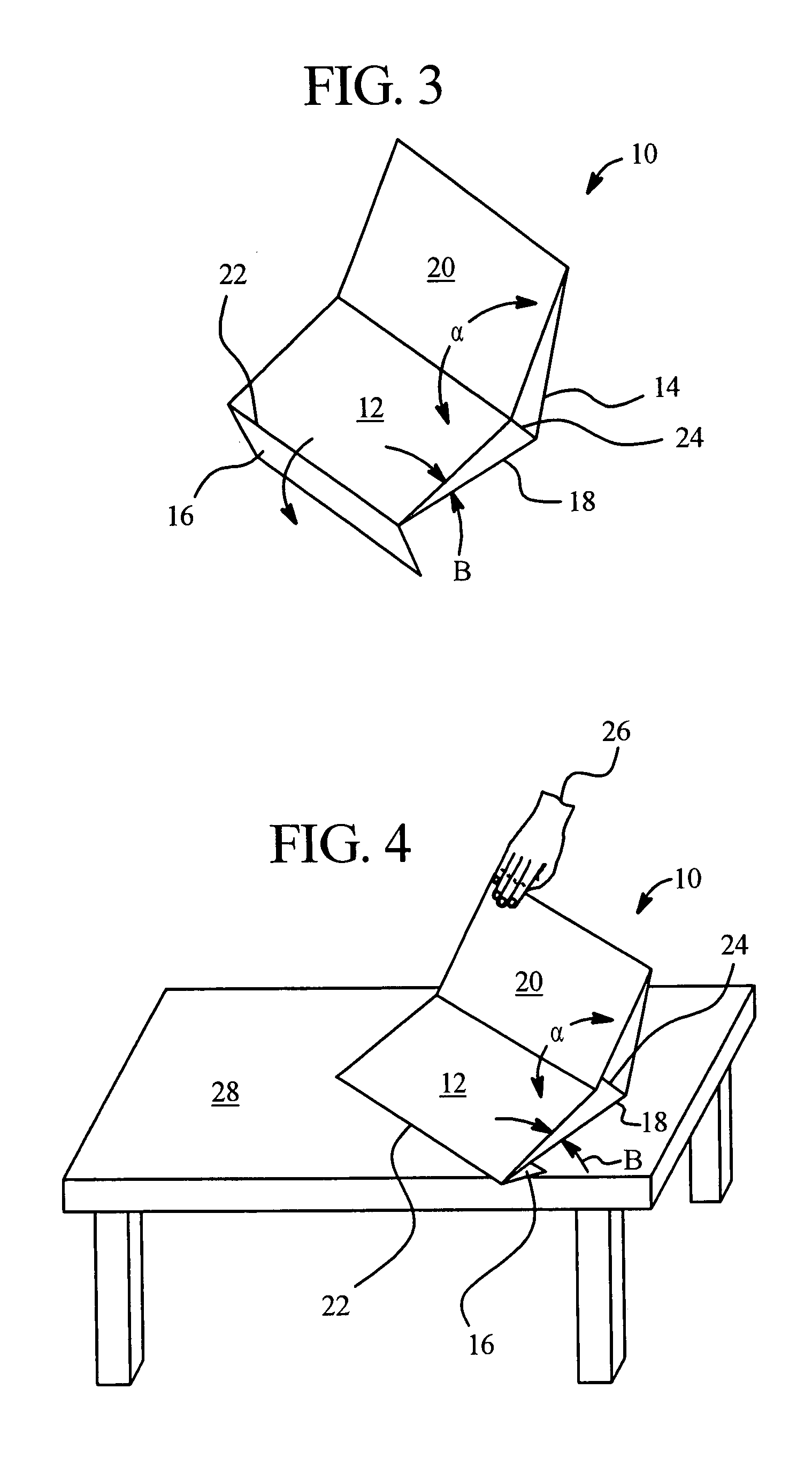
Dialysis solution bag stand
InactiveUS7243893B2Accurate flowTherapy failurePharmaceutical containersMedical devicesVisual perceptionMedical treatment
A stand for a medical fluid treatment, a system for supporting multi-chamber medical fluid bags and a method for testing whether the multi-chamber bags have been preset properly for therapy are provided. In one embodiment a multi-section stand is provided that is folded in a number of places to produce a structure upon which fluid from a properly preset solution bag flows readily to a patient, but upon which a dual-chamber bag that has not been modified properly for treatment collapses, folds or falls to a position providing visual indication that the chamber seal needs to be released or opened.
Owner:BAXTER INT INC +1
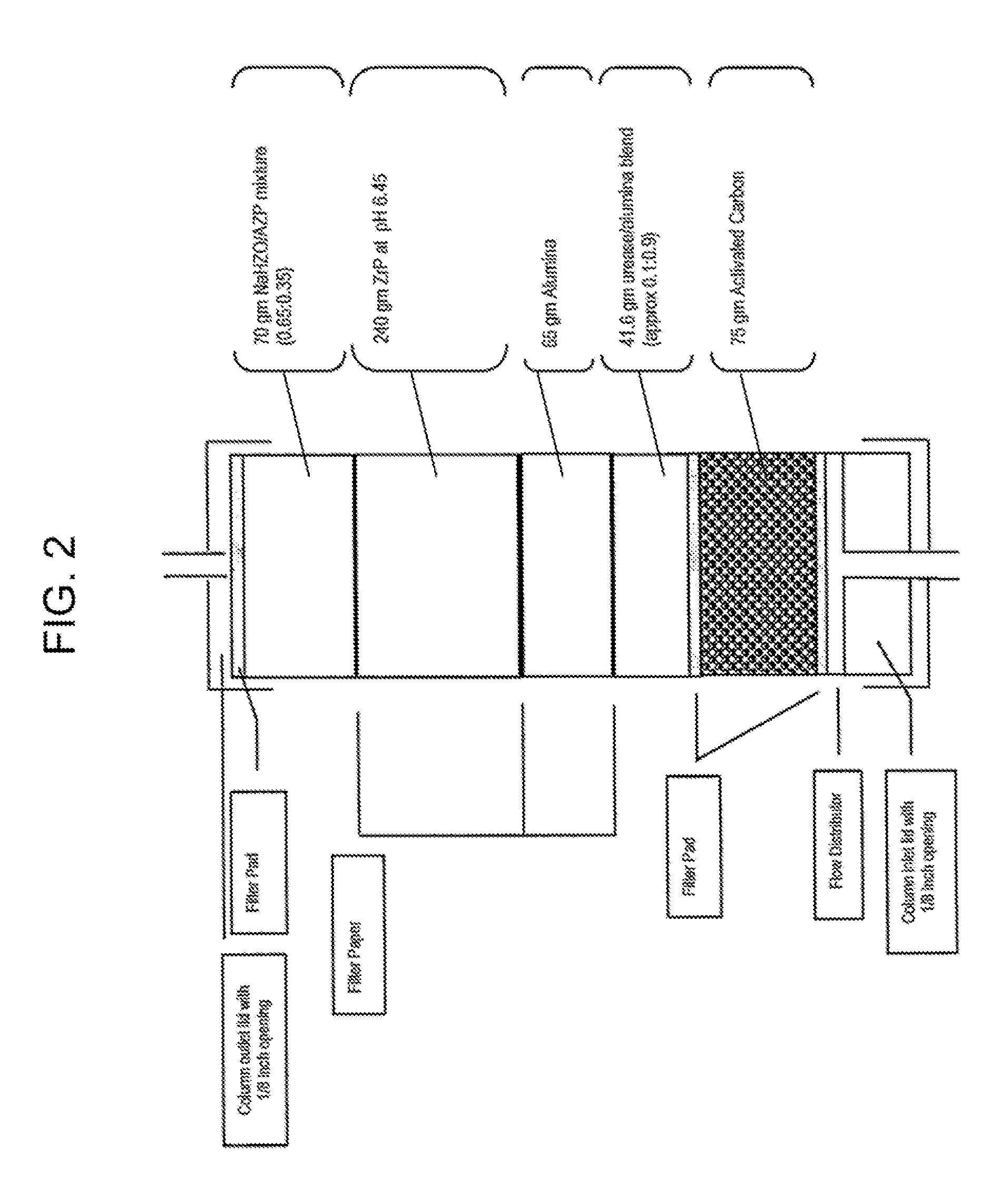
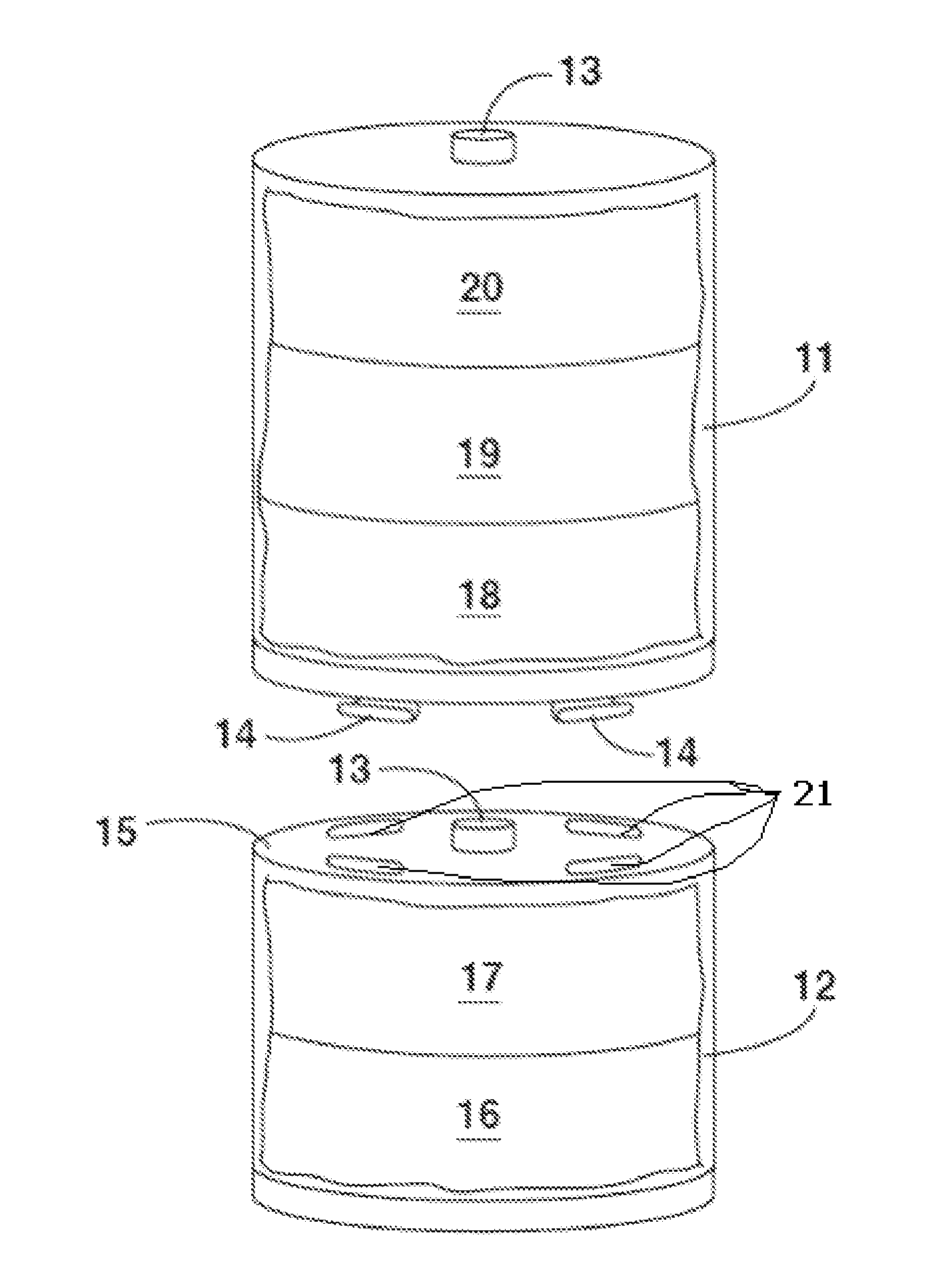
Reserve zirconium phosphate module for use in sorbent dialysis
A reserve zirconium phosphate module for continuing dialysis in the event the capacity of the original zirconium phosphate module is exceeded. The sorbent cartridge can have a sensor for detecting when the capacity of the zirconium phosphate material has been exceeded, and a valve assembly for diverting the flow of spent dialysate into the reserve module when needed. Any of the modules of the sorbent cartridge can be reusable and the sorbent materials therein recharged.
Owner:MOZARC MEDICAL US LLC
Replenisihing urease in dialysis systems using a urease introducer
An apparatus and method for replenishing urease in a sorbent cartridge for use in sorbent dialysis. The sorbent cartridge is configured to allow an amount of urease to be added to the sorbent cartridge. A urease solution can be injected into the sorbent cartridge to replenish the urease containing module, or solid urease can be added to the sorbent cartridge. The sorbent module can also comprise other, rechargeable, sorbent materials for removing toxins other than urea from spent dialysate.
Owner:MOZARC MEDICAL US LLC
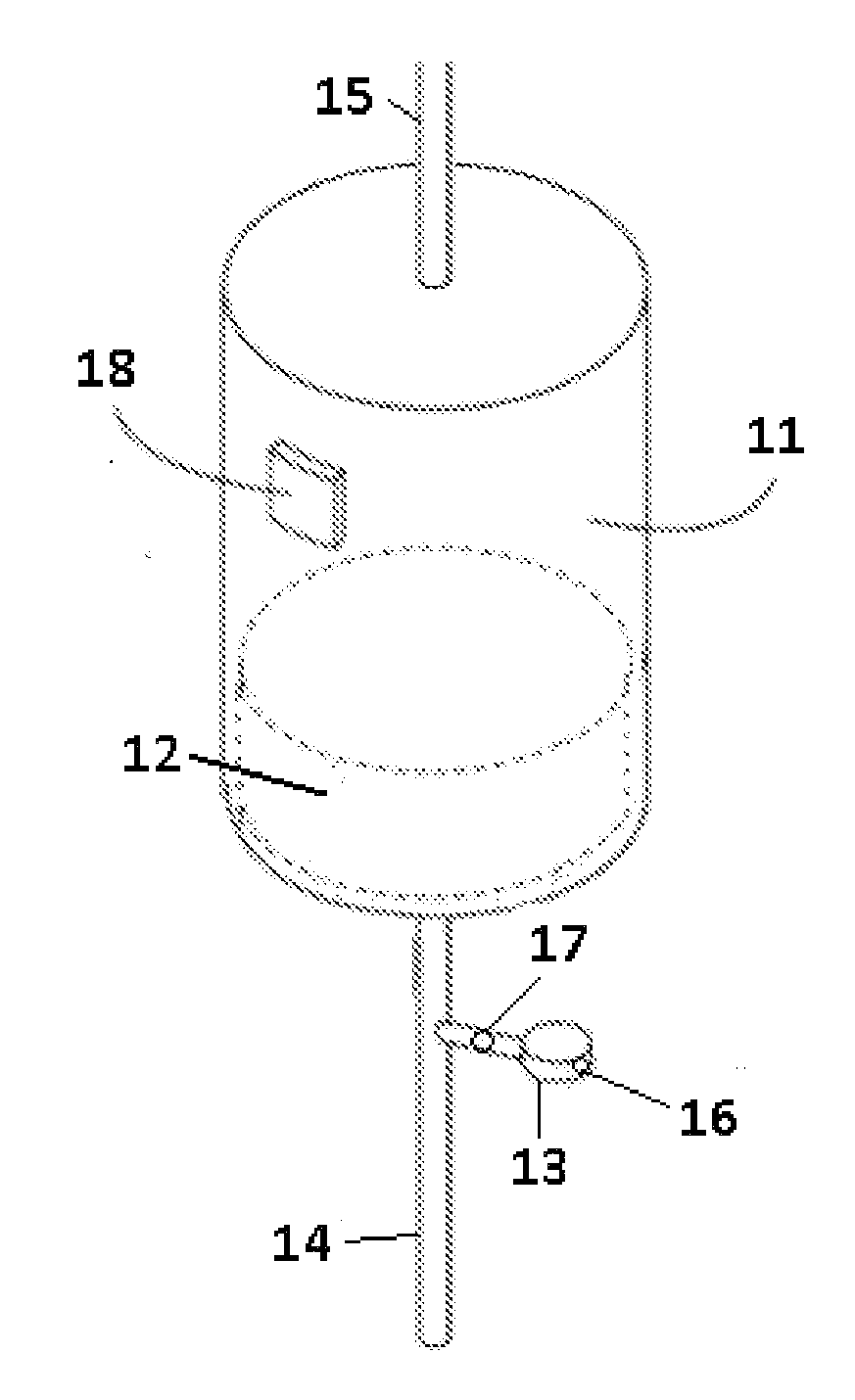
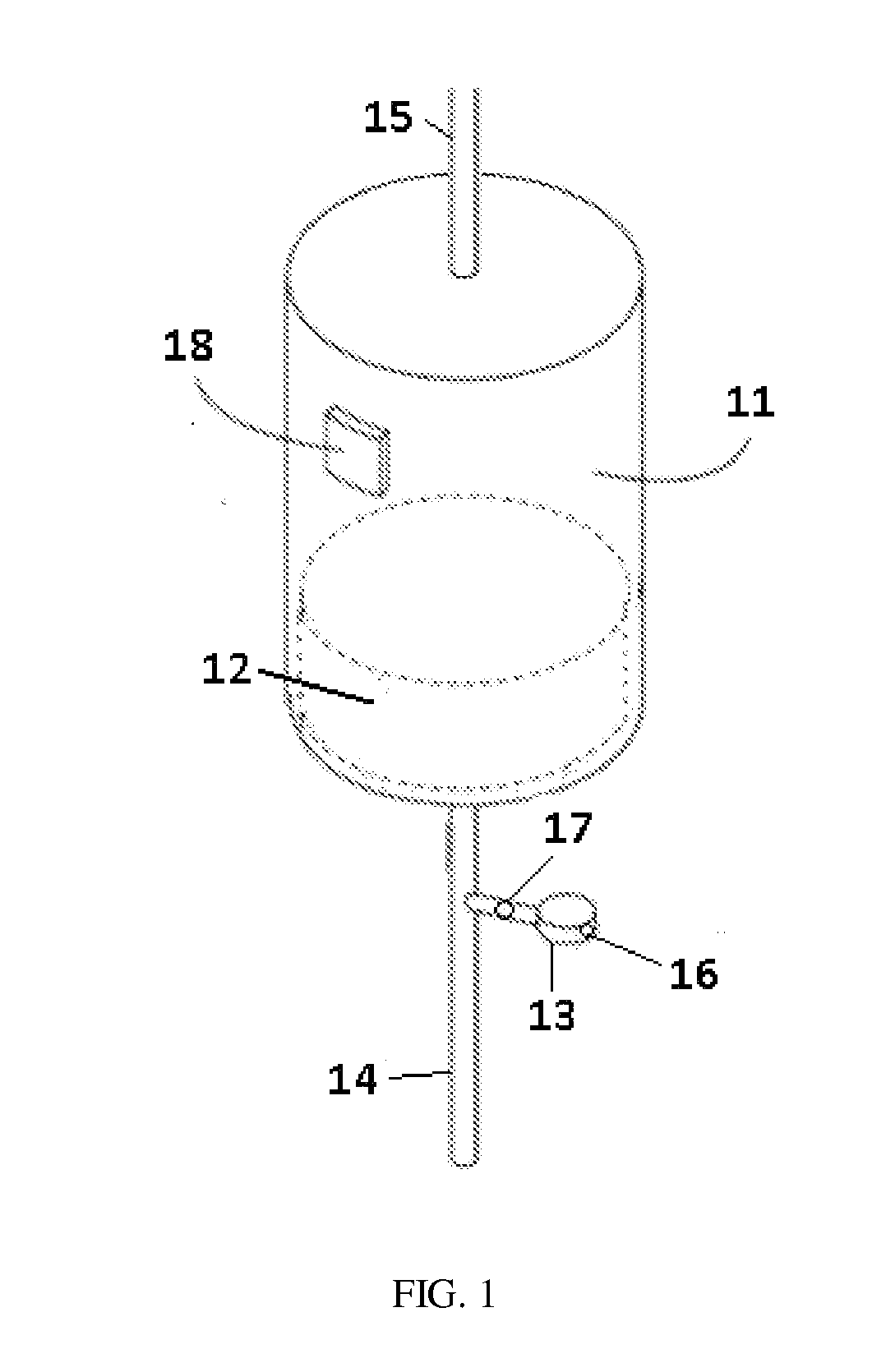
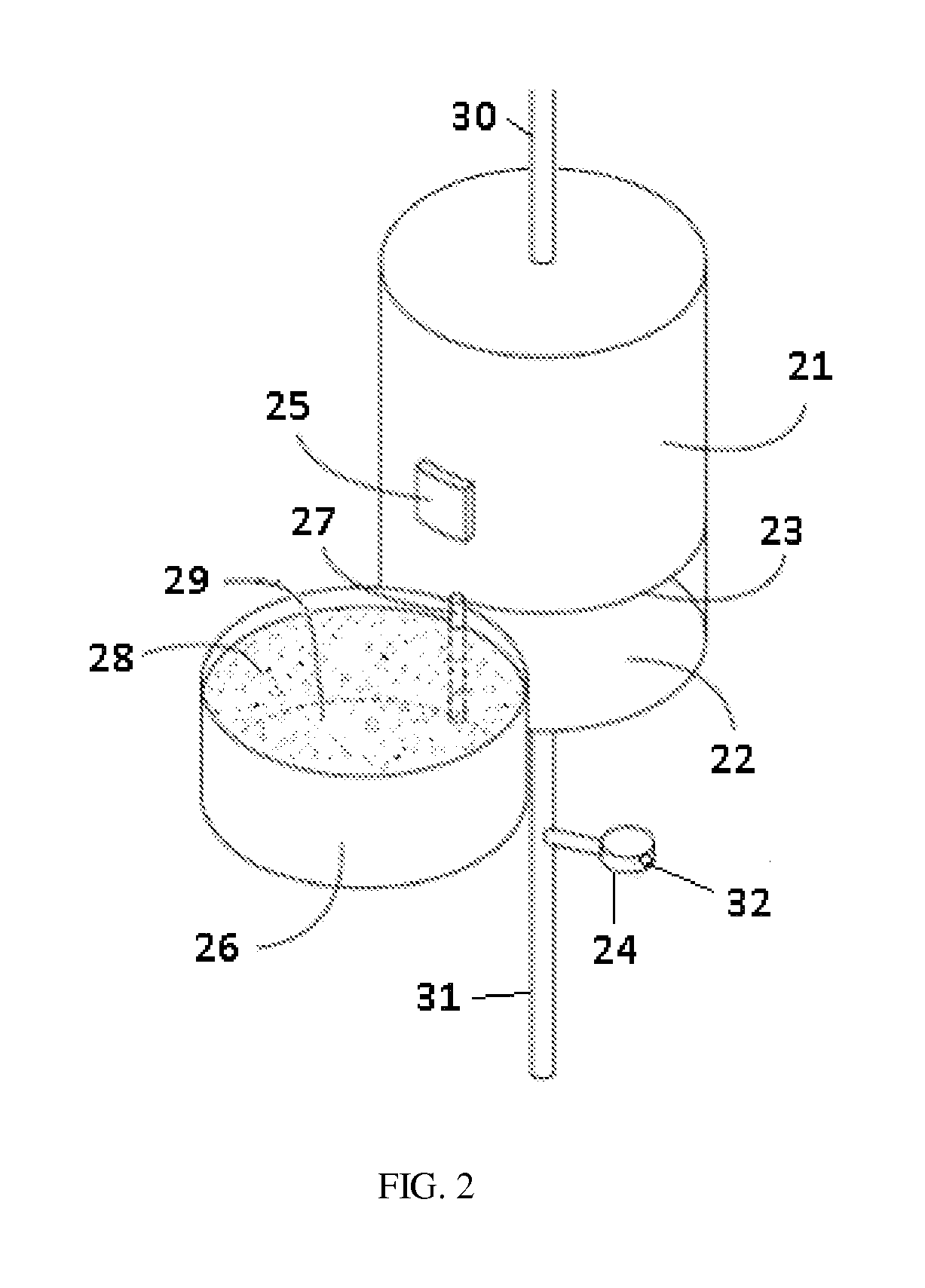
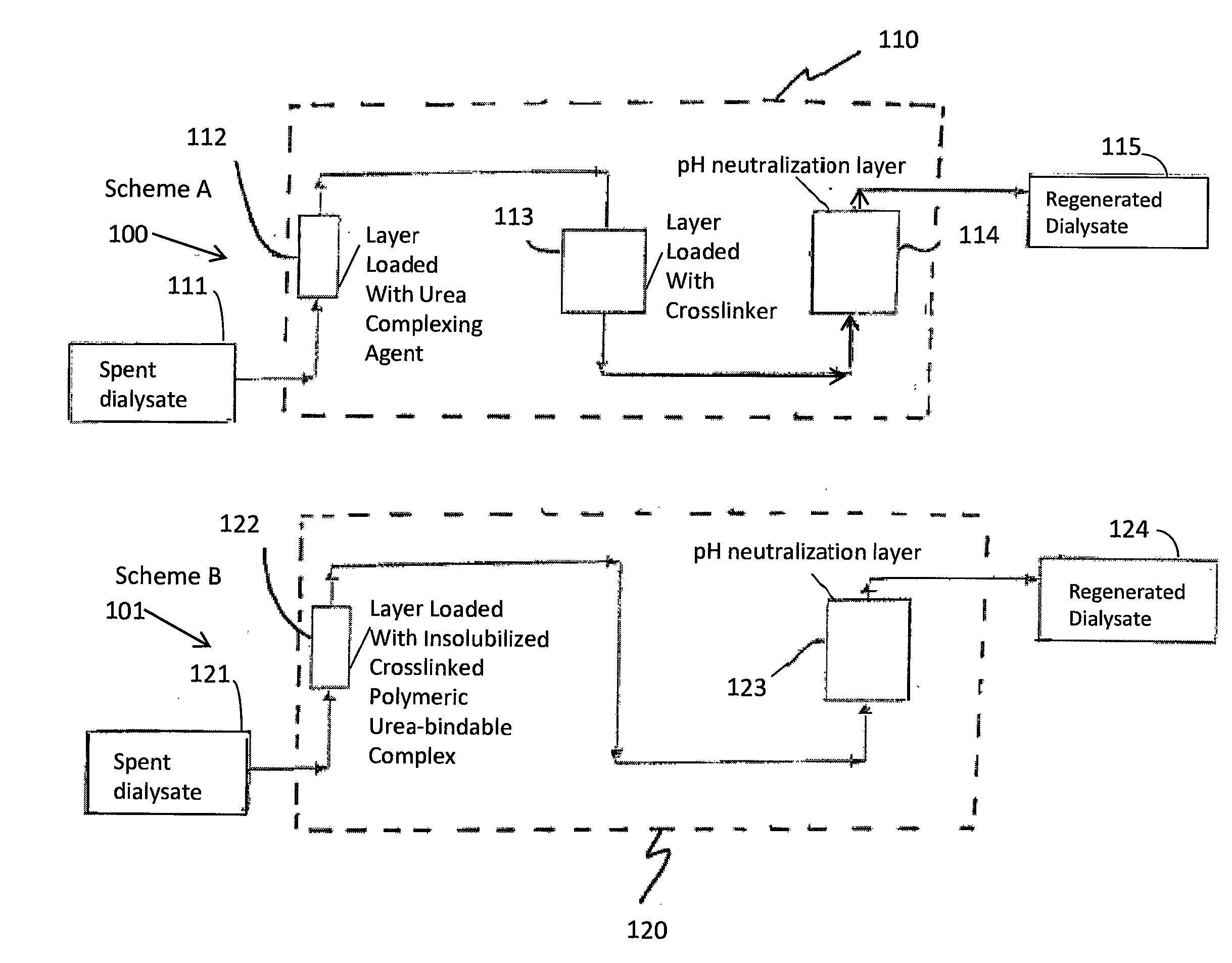
Materials For Removal Of Toxins In Sorbent Dialysis And Methods And Systems Using Same
ActiveUS20140336568A1Size reduction requirementsSemi-permeable membranesOther chemical processesUrocaninaseCross linker
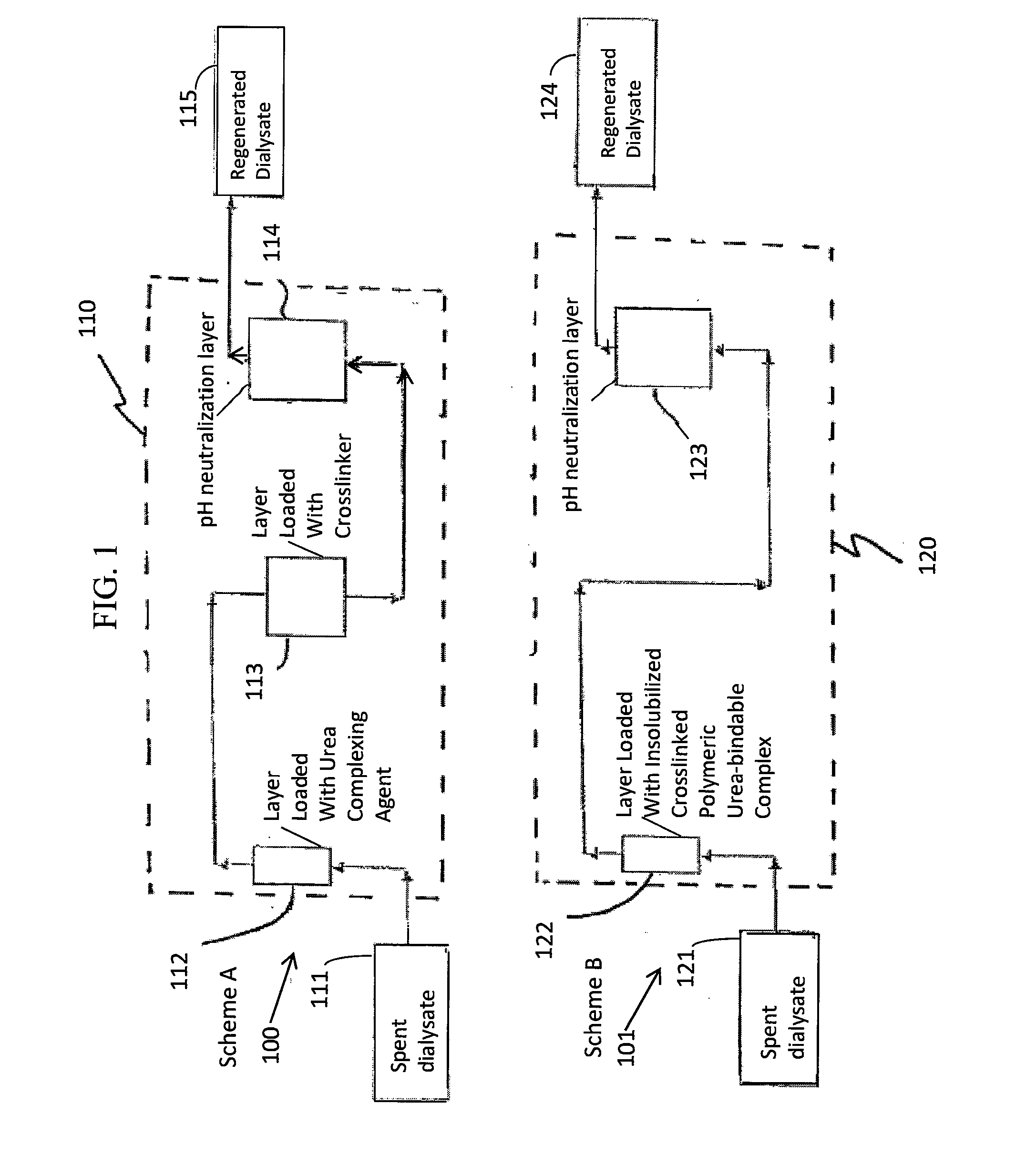
A sorbent dialysis cartridge is provided for removal of uremic toxins from dialysate wherein the sorbent cartridges can use non-enzymatic urea-binding materials in place of urease. The cartridge can have a first sorbent layer loaded with a polymerizable urea complexing agent and a second sorbent layer loaded with a crosslinker. The crosslinker can be crosslinkable with a soluble urea complex reaction product of the polymerizable urea complexing agent and urea when passing through the first sorbent layer to form a crosslinked polymeric urea complex which is attachable to the second sorbent layer. In another option, a sorbent layer can be used which has an insolubilized crosslinked polymeric urea-bindable complex attached thereto, wherein the crosslinked polymeric urea-bindable complex can be a reaction product of a crosslinker and polymerizable urea complexing agent. Methods and sorbent dialysis systems using the cartridge, and methods of making the sorbent material, are provided.
Owner:FRESENIUS MEDICAL CARE HLDG INC
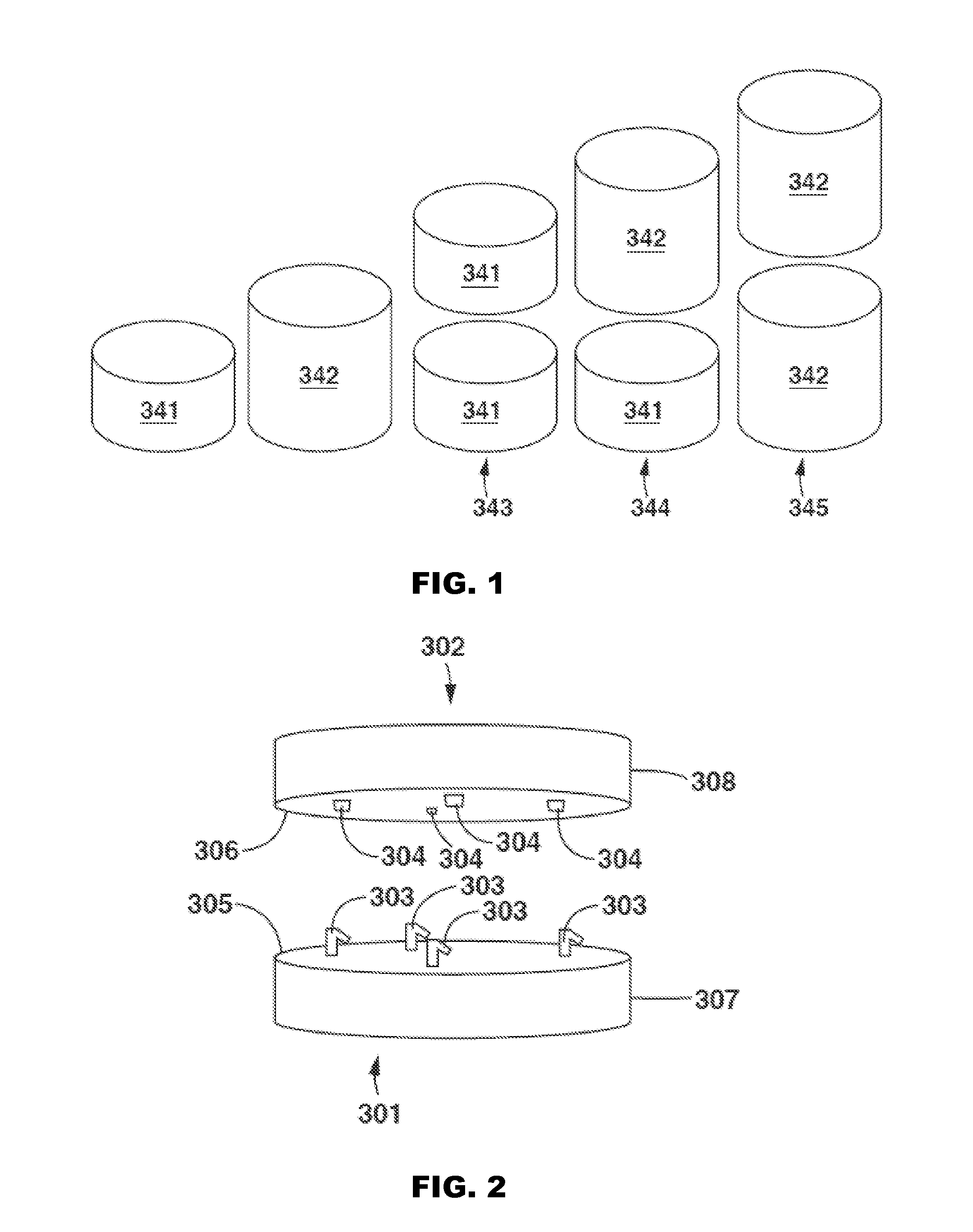
Modular dialysate regeneration assembly
ActiveUS20150367056A1Ion-exchange process apparatusIon-exchanger regenerationIntensive care medicineBiomedical engineering
A customizable modular dialysate regeneration assembly with connectable sorbent packaging systems. The dialysate regeneration assembly can be customized based on patient parameters or dialysis session parameters. A processor can be included that can determine the correct amount of each sorbent material necessary for a given patient and a given dialysis session.
Owner:MOZARC MEDICAL US LLC
Replenishing urease in dialysis systems using urease pouches
InactiveUS20150367060A1Simple designReduce cost per sessionOther blood circulation devicesIon-exchanger regenerationUrease enzymeUrocaninase
An apparatus and method for replenishing urease in a sorbent cartridge for use in sorbent dialysis using urease pouches. The sorbent cartridge is configured to allow insertion of a urease pouch or injection of a urease solution into the sorbent cartridge containing a urease pouch. The sorbent module can also comprise other, rechargeable, sorbent materials for removing toxins other than urea from spent dialysate.
Owner:MOZARC MEDICAL US LLC
Urease introduction system for replenishing urease in a sorbent cartridge
An apparatus and method for replenishing urease in a sorbent cartridge for use in sorbent dialysis. The system is configured to allow insertion of a urease pouch, injection of a urease solution, or addition of a urease cartridge, into a dialysis cabinet containing a dialysis flow loop. The urease can be dissolved and the resulting urease solution added to the sorbent cartridge in the flow loop to replenish the urease within the sorbent cartridge. The sorbent cartridge can also comprise other, rechargeable, sorbent materials for removing toxins other than urea from spent dialysate.
Owner:MOZARC MEDICAL US LLC
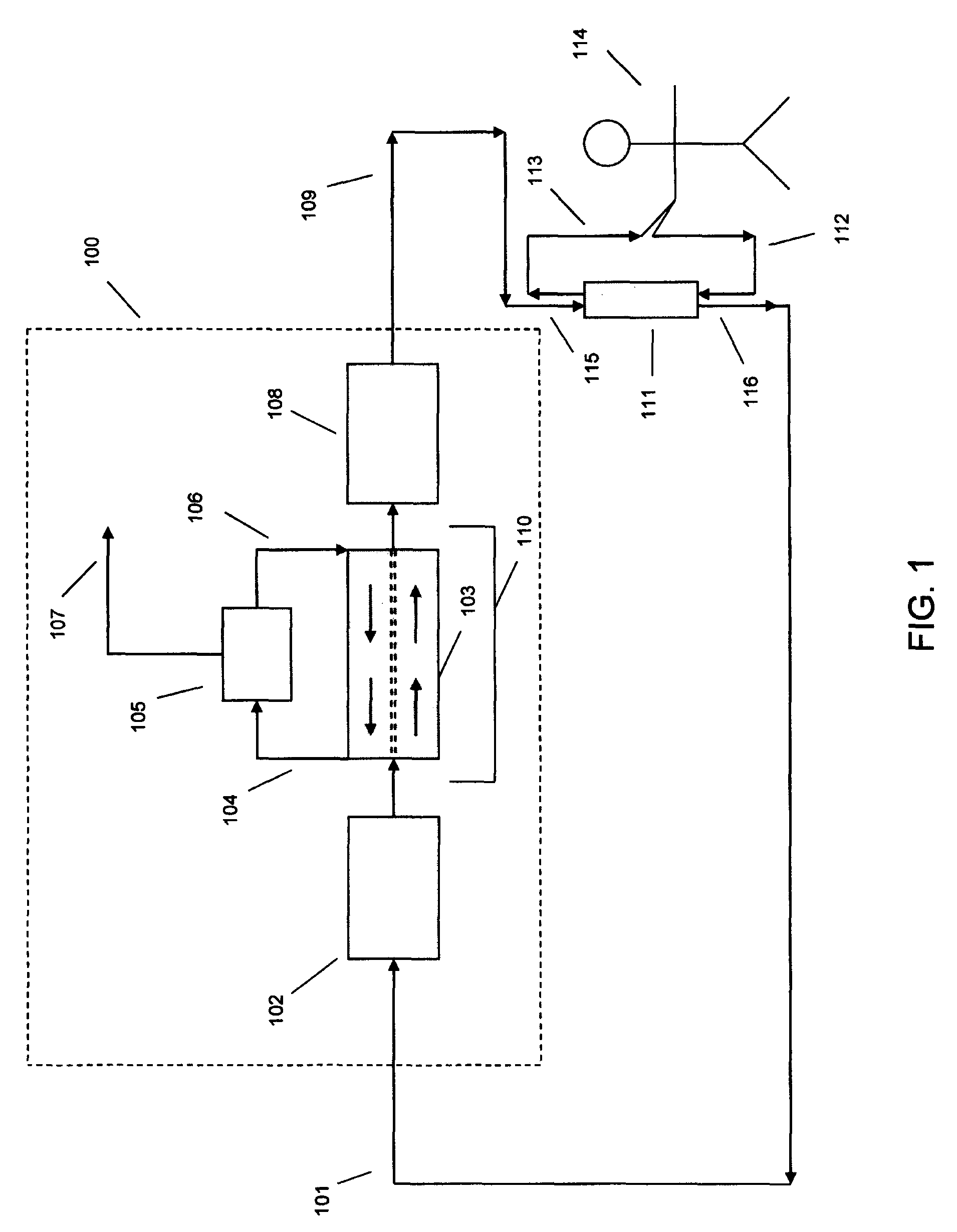
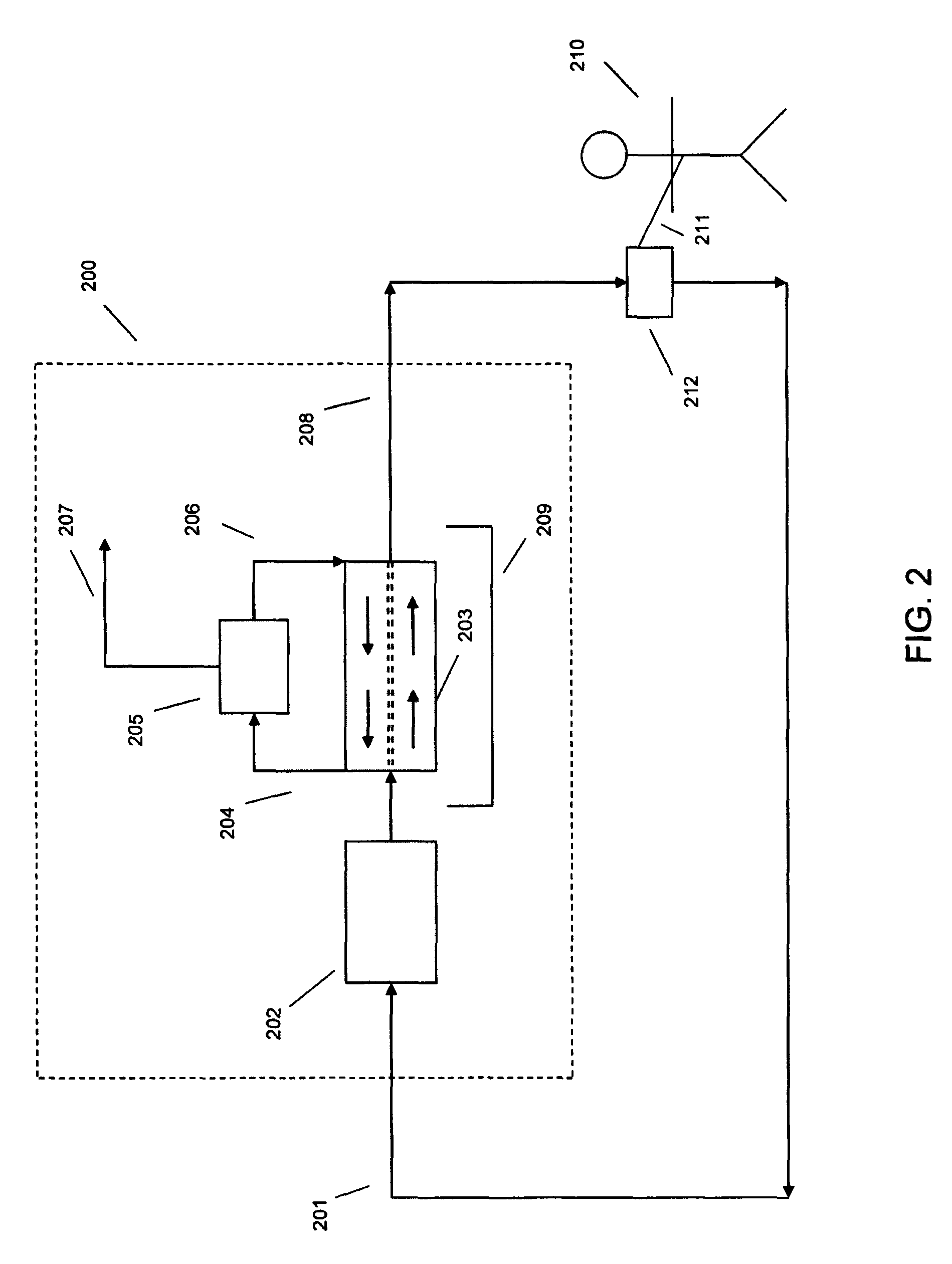
Apparatus and method for preparation of a peritoneal dialysis solution
InactiveUS6986872B2Minimize the possibilityEasy to separateGeneral water supply conservationDiagnosticsPeritoneal dialysateMagnesium salt
The invention provides an apparatus and method for storing and transporting peritoneal dialysate in dry or lyophilized form, and for forming a deliverable peritoneal dialysis solution therefrom. In one embodiment, a dry reagent bed, including reagents sufficient to produce a dialysis solution, is suspended in a diluent flow path through the apparatus housing. Continuous pressure on the reagent bed causes the bed to compact as it erodes when purified water is passed through the housing. The pressure ensures complete and even dissolution of the reagents. Through dry storage and simple dissolution, even in a home, the invention enables a wider variety of solution constituents, including reduced acid content and the use of bicarbonate as a stable buffer component. The latter is illustrated in a double-bed embodiment, where bicarbonate is stored separately from calcium or magnesium salts within a single housing.
Owner:PRISMEDICAL CORP
Hyperthermia, system, method and components
ActiveUS20090043256A1Effective and safe for patientInfusion devicesMedical devicesIntensive care medicineHigh body temperature
An IV pole mountable, therapeutic infusate processing device is incorporated into a hypothermia system to receive therapeutic fluid(s), such as normal saline, peritioneal dialysis solution, or other crystalloid solution, to heat such therapeutic fluid(s) a few degrees centigrade above normal body temperature and to direct the resulting heated infusate to and through a selected anatomical portion of a patients body to raise the temperature of that body portion so as to affect any cancerous or other tumors that may be located therein. The processing device is provided with touch screen controls and visual indicators to facilitate its proper use; while the system further includes temperature and pressure sensors to monitor the hyperthermia processing to insure patient safety.
Owner:BELMONT INSTR LLC
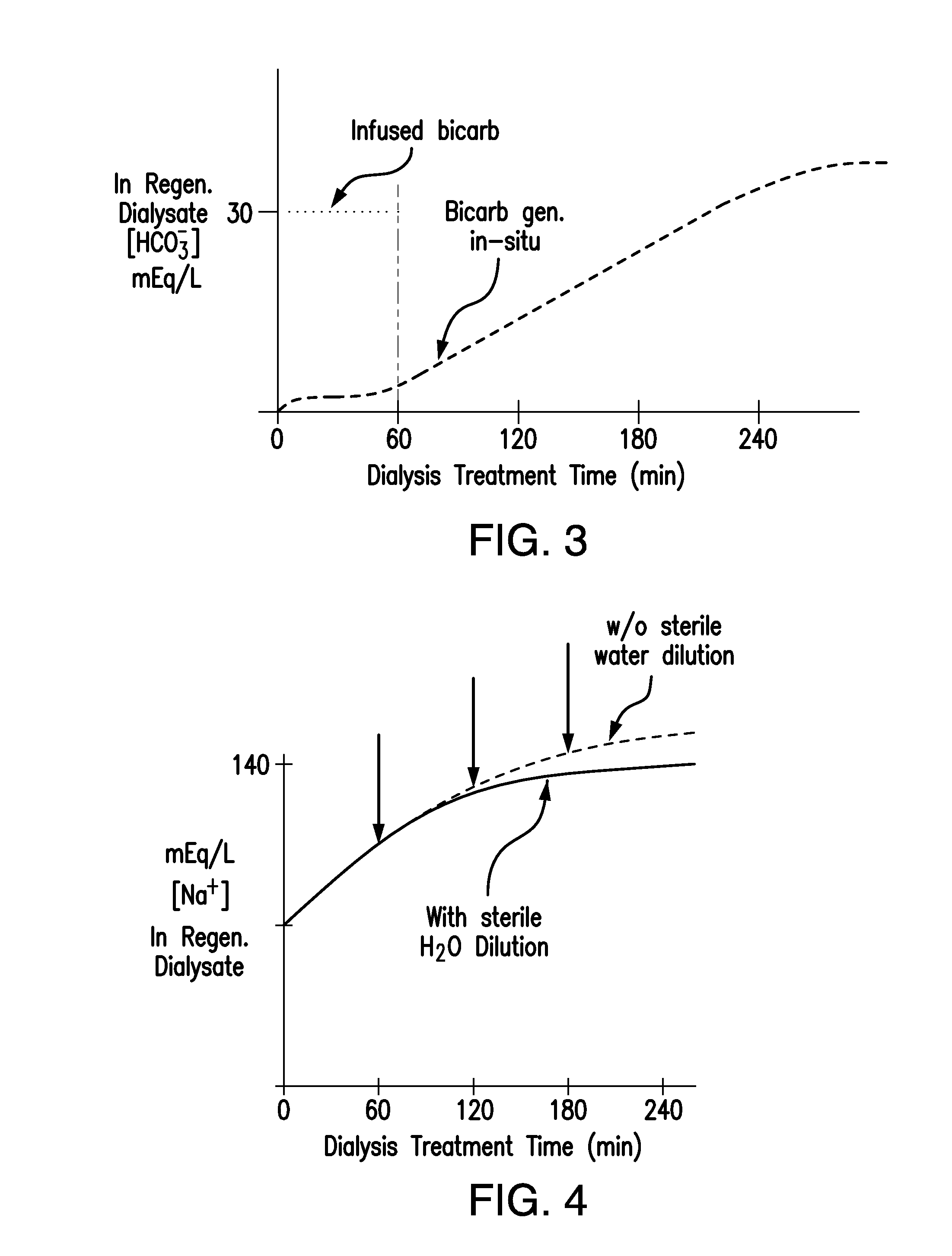
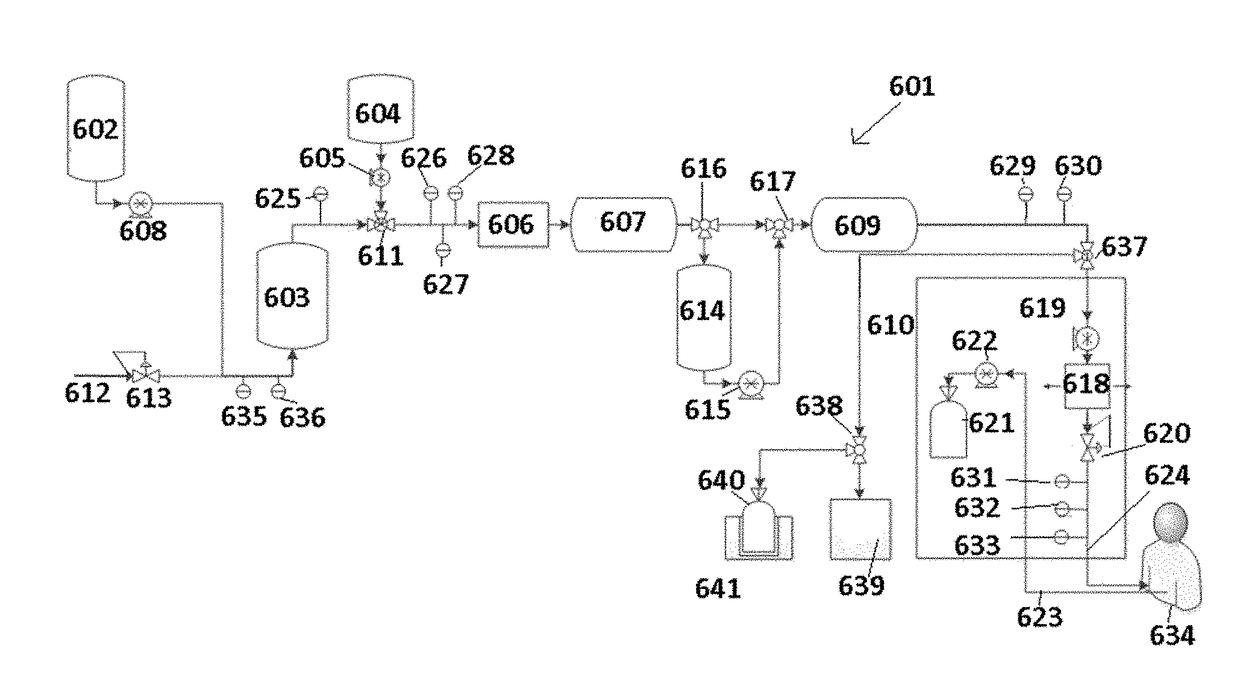
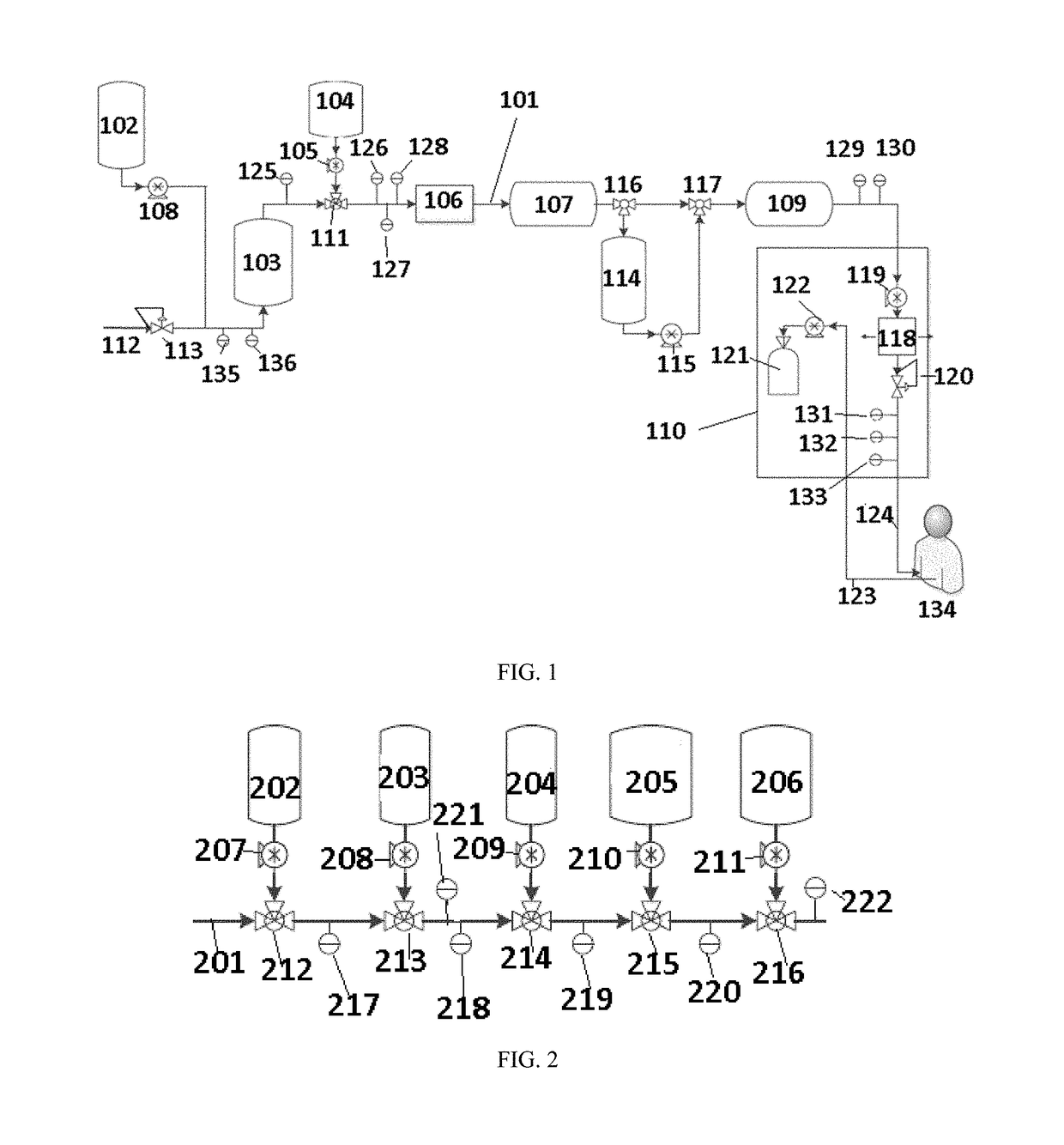
Method For Treating Dialysate, Dialysis System, And Method For Pre-Evaluating Dialysis Patients For Treatment With Same
ActiveUS20150343126A1Eliminate needReduce sodiumDialysis systemsSolid sorbent liquid separationSorbentDialysis fluid
A method for treating dialysate solutions used in dialysis wherein dialysate is treated in an early part of a dialysis treatment session by external infusion of bicarbonate solution into the dialysate circuit to eliminate the need for bicarbonate requirements in concentrates used for preparation of precursor dialysate (priming) solutions and / or for a solid bicarbonate layer in a sorbent cartridge. Dialysate is treated in a latter part of a dialysis treatment session by introduction of sterile dilution water to reduce sodium concentration in the dialysate. The method provides a more efficient and reduced use of dialysate fluids, electrolytes, sorbent cartridge materials, equipment scale, or any combinations of these, while maintaining purity standards and applicable physiological ranges for bicarbonate, sodium, and other dialysate solution components over the course of a dialysis treatment session.
Owner:FRESENIUS MEDICAL CARE HLDG INC
Citrate-based dialysate chemical formulations
The present invention constitutes dialysate formulations that are suitable for use in preparing dialysate solutions for use in batch and / or proportioning systems and for improving dialysis efficiency by reducing or preventing clotting of the dialysis flow paths. The dialysate chemical formulations for one batch of dialysate comprise an acid concentrate stored in a first vessel, and a citrate-containing bicarbonate concentrate stored in a second vessel. The contents of the first and second vessels are emptied into a dialysate preparation tank and mixed with water to form a batch quantity of dialysate solution. Alternately, a dry acid and / or a dry citrate-containing base concentrates are dissolved separately in measured quantities of water to form liquid concentrates which are then used in conjunction with a proportioning machine to generate on-line a final dialysis solution stream.
Owner:HHD LLC A DELAWARE LLC +2
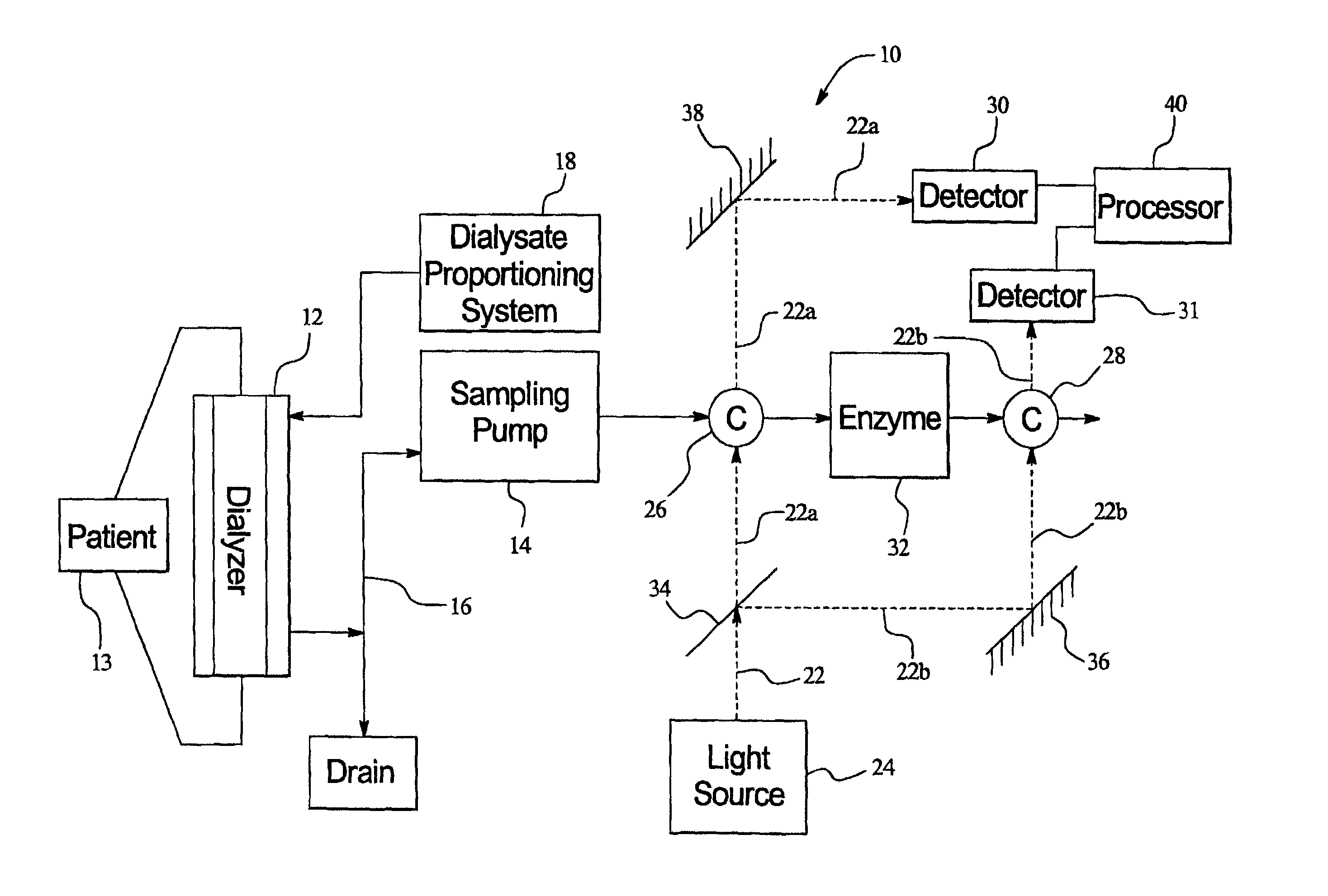
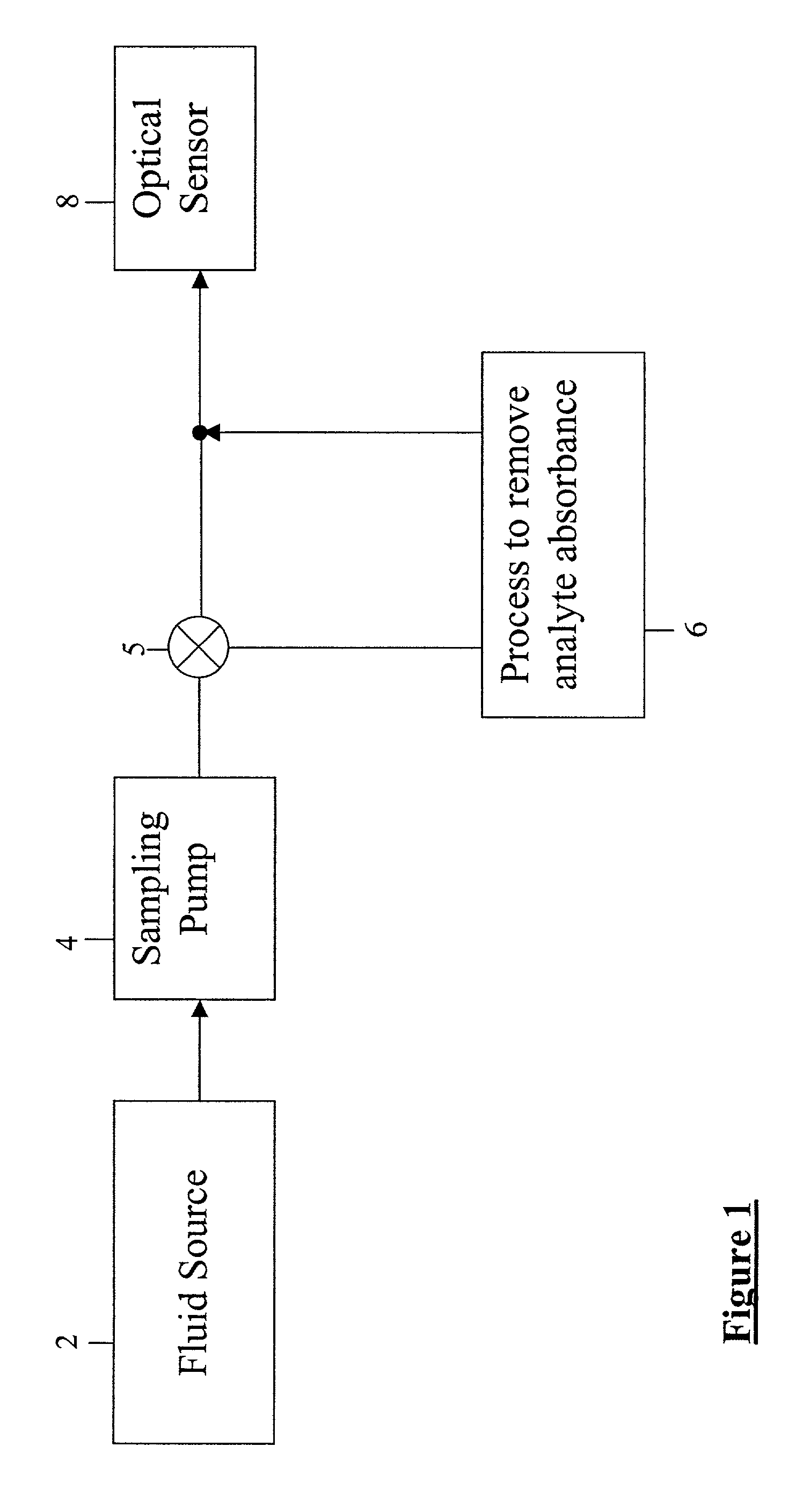
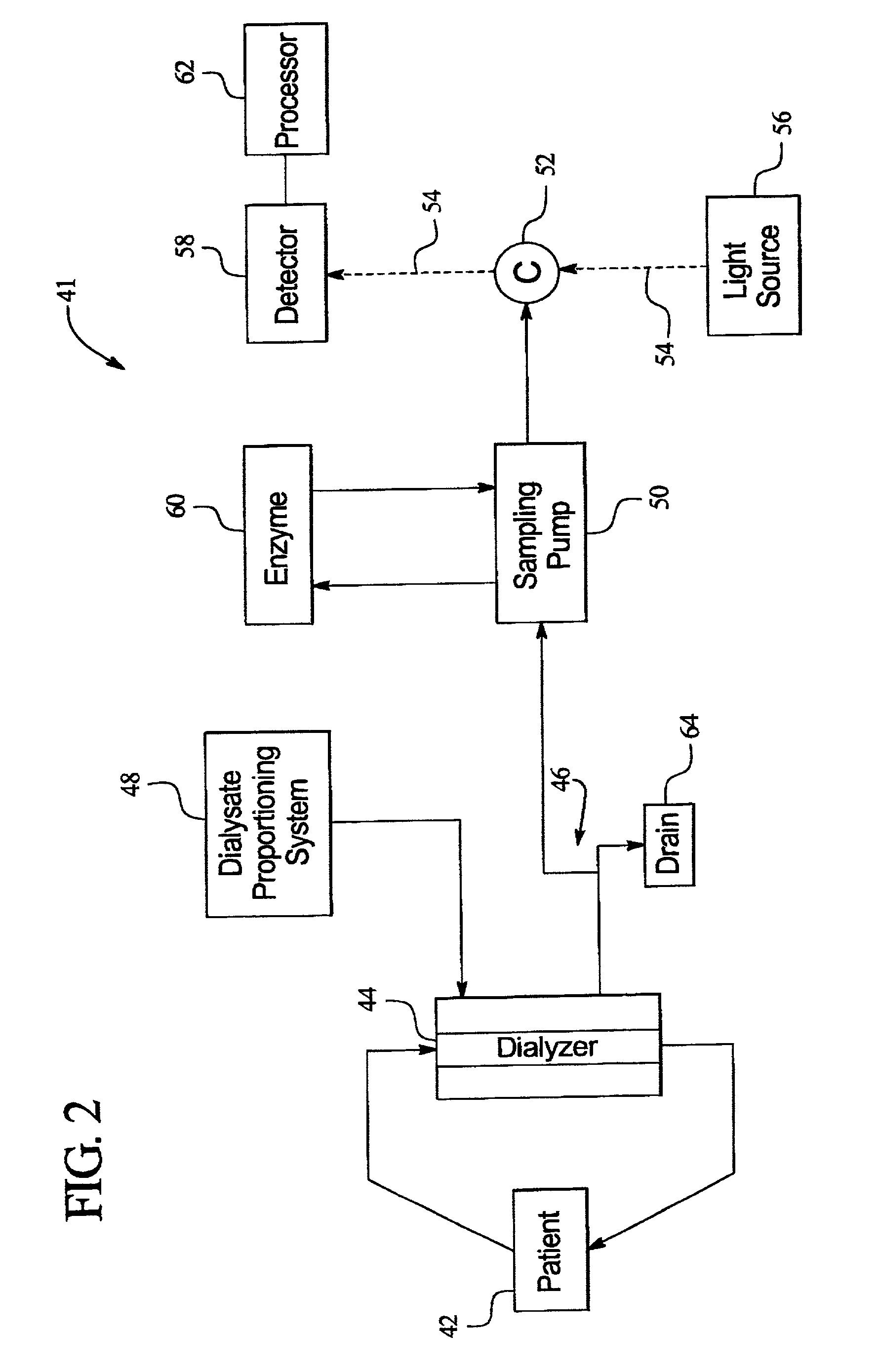
Optical sensor and method for measuring concentration of a chemical constituent using its intrinsic optical absorbance
InactiveUS7002670B2Microbiological testing/measurementInvestigating moving fluids/granular solidsCreatinine riseChemical composition
An improved optical sensor and method for measuring concentration of a chemical constituent where measurement interference from other chemical compounds is present in the solution is provided. More specifically, the invention relates to a system for measuring the amount of creatinine in effluent dialysate during, before, or following a kidney dialysis procedure and a method for using the same. Alternatively, the method may be used with blood and other body fluids or solutions that contact the patient. The system may use an enzyme or other chemical process to specifically remove or convert an analyte with an intrinsic optical absorbance. By measuring the absorbance before and after the chemical process the analyte can be measured with high accuracy and specificity. The method may be extended to multiple analyte measurements using cascaded chemical processes.
Owner:BAXTER INT INC +1
Method for modification of rice protein and oryzenin with protein glutaminase
ActiveCN101861909AOvercome hydrolysisOvercoming the problem of partial denaturation of proteinsVegetable proteins working-upFreeze-dryingReaction temperature
The invention relates to a method for modification of rice protein and oryzenin with protein glutaminase, which comprises the following steps: adding the rice protein or oryzenin into a constant-temperature enzyme reactor with phosphate buffer solution while stirring to obtain protein dispersion solution with a certain substrate concentration; adding protein glutaminase to obtain a system with a certain proportion of enzyme and substrate, wherein the temperature of enzymatic reaction is 36-38 DEG C, the time of the enzymatic reaction is 0.1-48 hour(s), and the pH value of the enzymatic reaction is maintained 7.0; adding dialysis solution, i.e. acetic acid solution of 0.10mol / L, wherein the dialysis time is about 8 hours; and carrying out vacuum freeze-drying, thereby obtaining the product. The invention can improve the protein solubility of the rice protein or the oryzenin, and can also enhance the emulsification, foaming performance, gelation and other functional properties of the rice protein or the oryzenin.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
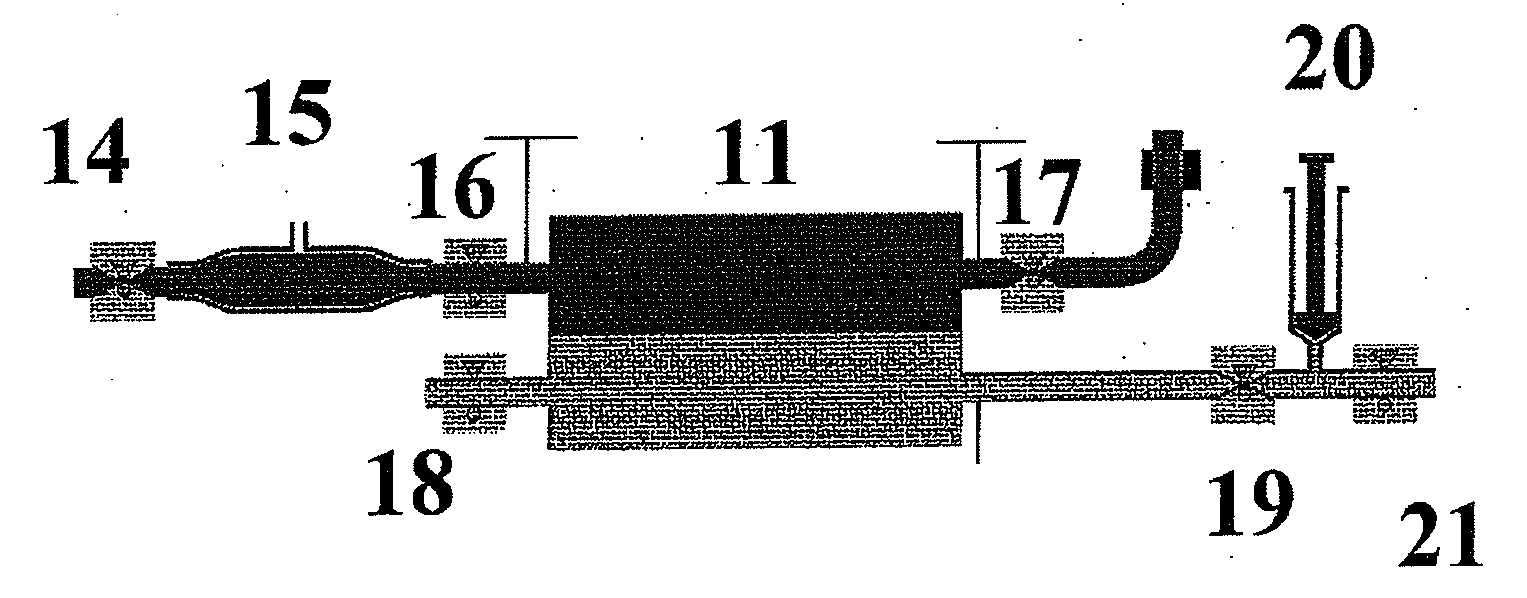
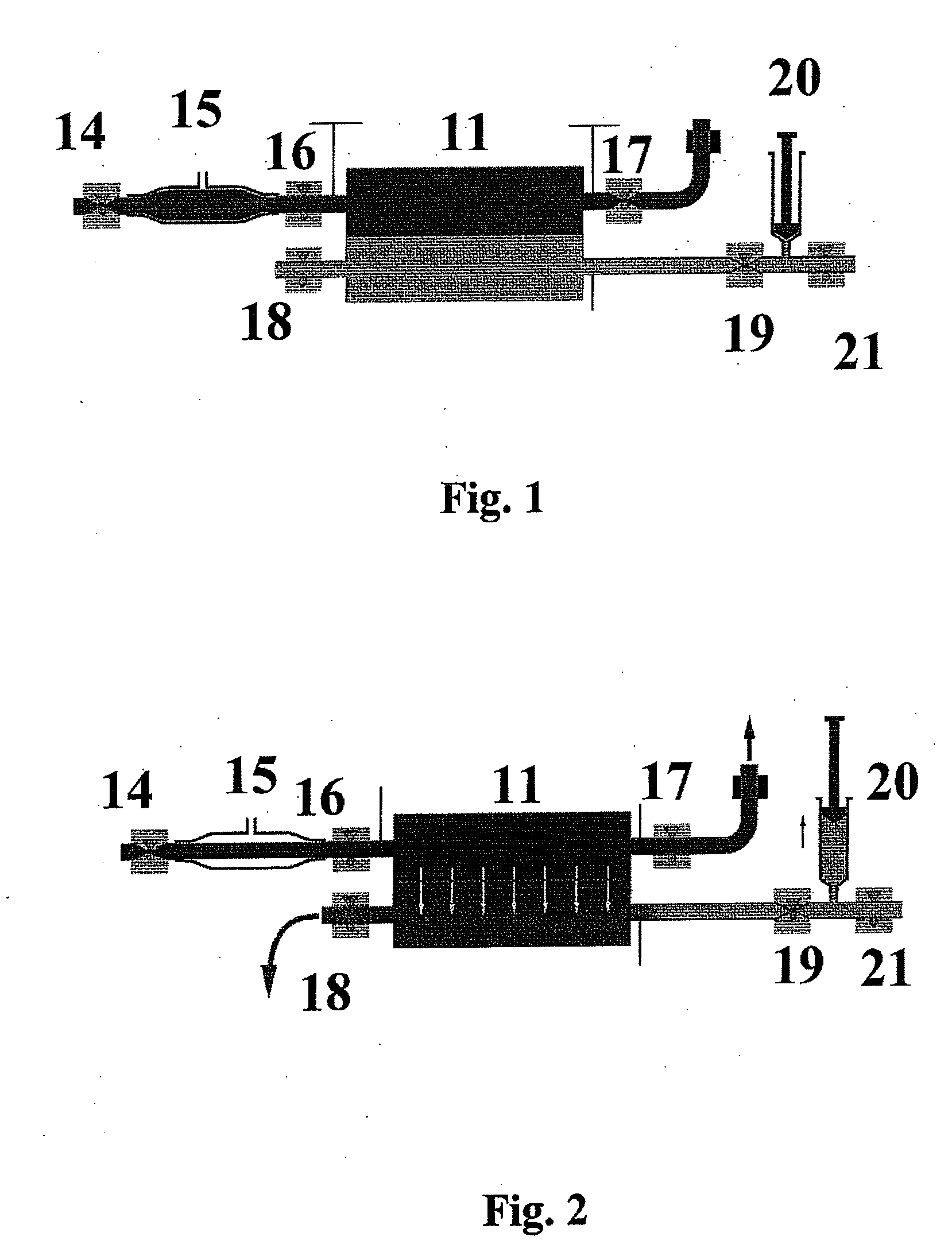
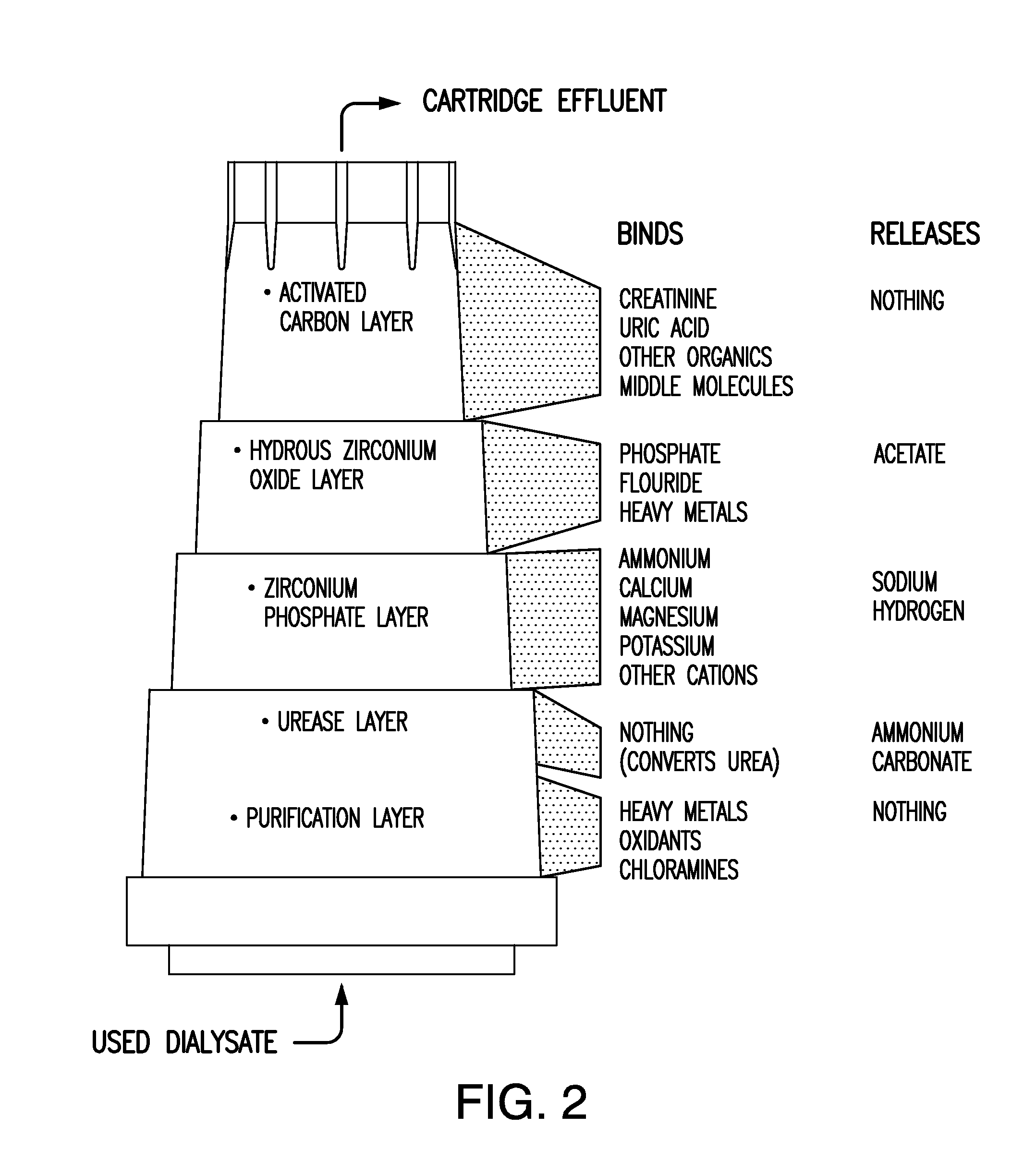
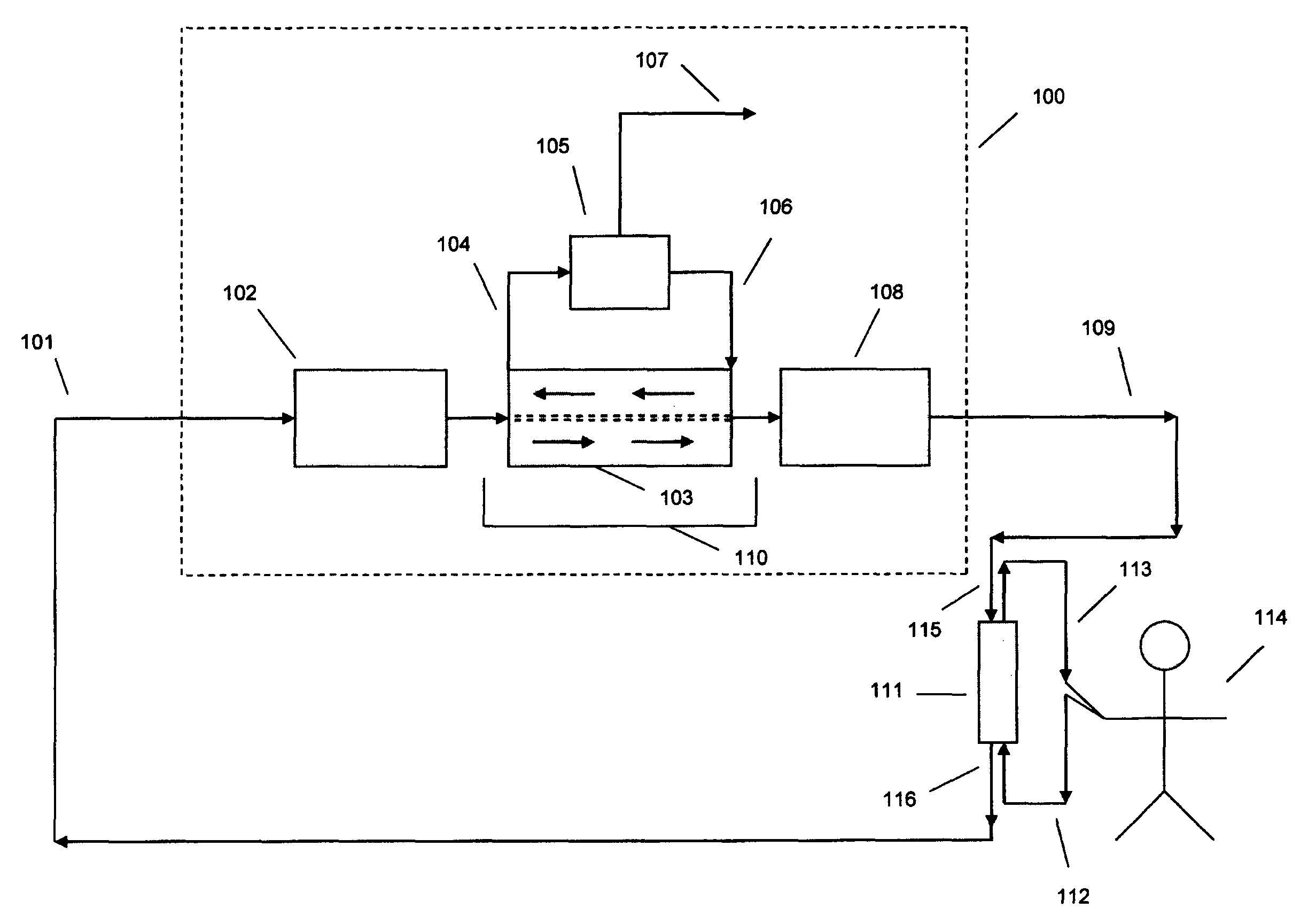
Sorbent and chemical regeneration of dialysate
The present invention generally relates to systems and methods for the regeneration of spent dialysis solutions. The present invention further relates to systems and methods for continuously regenerating spent dialysis solution during dialysis. The present invention further relates to systems and methods for conducting dialysis that further include using chemical and physical separators in conjunction with ion exchange cartridges and / or adsorption cartridges.
Owner:FRESENIUS MEDICAL CARE HLDG INC
Peritoneal dialysate preparation and sensor system
PendingUS20180021501A1Specific water treatment objectivesMedical devicesSensor systemPeritoneal dialysate
The invention relates to devices, systems, and methods for generating a peritoneal dialysate having specified concentrations of one or more solutes. The devices, systems and methods use conductivity sensors, flow meters, and composition sensors to control addition of osmotic agents and ion concentrates into a peritoneal dialysate generation flow path.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Regenerative peritoneal dialysis system
PendingUS20170281847A1Organic active ingredientsInorganic active ingredientsEngineeringMechanical engineering
Systems and methods of generating and regenerating peritoneal dialysate are provided. The systems and methods use a dialysate regeneration module, a sterilization module and concentrates to prepare peritoneal dialysate from used peritoneal dialysate or source water. An optional integrated cycler for direct infusion of the generated peritoneal dialysate is included. Optional dialysate storage containers are provided for storage of the peritoneal dialysate prior to use.
Owner:MOZARC MEDICAL US LLC
Hemodialysis apparatus and methods
InactiveUS7527737B2Semi-permeable membranesWater/sewage treatment by irradiationSide effectCardio vascular disease
A hemodialysis apparatus comprises dialyzer means, dialyzing solution supply means, blood circulation means, and blood irradiation means. Employing electromagnetic radiation in the red visible and near infrared spectrum as part of a hemodialysis apparatus prevents long-term side effects associated with the use of dialysis, including cardiovascular diseases and anemia, and protects and restores the remaining kidney function.
Owner:CHINA MEDICAL (SHENZHEN) TECH CO LTD
Method and apparatus for home dialysis
ActiveUS8034017B2Low dialysate consumptionPerformSemi-permeable membranesMedical devicesHome dialysisHaemodialysis machine
A system, process, and method for home hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis to be carried out by the patient or other non-professional users based upon re-circulation of dialysate from small dialysate containers which allows for very small dialysate consumption and easy portability. The system thereby also allow for long-duration dialysis without use of large volumes of dialysate. The invention may be implemented as a hemodialysis system, a process for administering dialysate, or as a method for performing dialysis.
Owner:DANISH MEDICAL RES APS
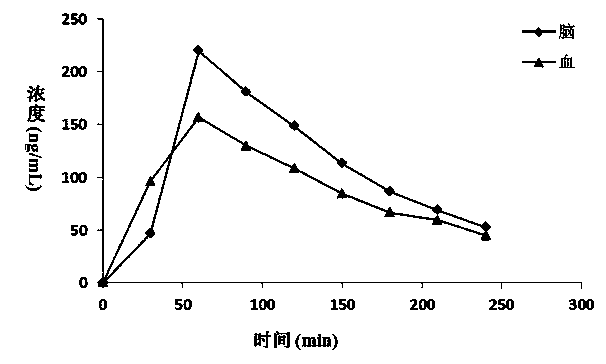
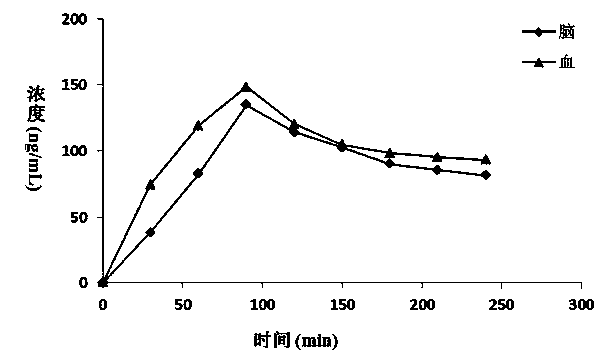
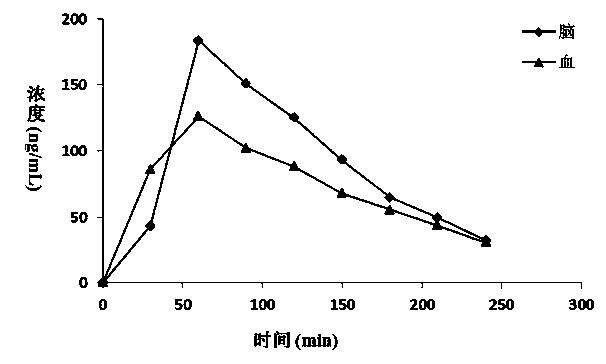
Synchronous analysis method for trace nicotine in blood-brain samples of animal and main metabolites thereof
InactiveCN104020241ADirectly and accurately measureEasy to operateComponent separationDialysate sampleAnimal science
The invention discloses a synchronous analysis method for trace nicotine in blood-brain samples of an animal and main metabolites thereof. The synchronous analysis method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: utilizing a microdialysis system to synchronously collect blood dialysate and brain tissue dialysate samples of an animal in lined pipes of different chromatographic sampling bottles, respectively adding NIC-d3 and COT-d3 to be mixed with internal labeled solution, and after mixing uniformly, directly analyzing and detecting the content of the nicotine and cotinine in a microdialysis sample by using UPLC-MS / MS. The synchronous analysis method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the pretreatment steps of protein precipitation and purification for the samples are not needed, the synchronous and accurate analysis of nicotine and metabolites in an animal body is realized; and compared with the prior art, the synchronous analysis method has the characteristics of simple operation, high sensitivity and reliable result and the like, and a new method for researching the metabolism of the nicotine in the animal body is provided.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU TOBACCO RES INST OF CNTC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com