Blue light-emitting antibacterial carbon dots as well as preparation method and application thereof
A carbon dot, blue technology, applied in the field of blue luminescent antibacterial carbon dots and its preparation, can solve the problems of toxicity, reduced stability, complicated preparation process, etc., and achieves simple preparation method, low cytotoxicity, and blood compatibility. Good results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0026] Some embodiments of the present invention provide a preparation method of blue-emitting antibacterial carbon dots, which includes: preparing carbon dots by heating a carbon source, wherein the carbon source is protamine sulfate.
[0027] Most methods in the prior art are to couple carbon dots with substances with antibacterial functions (such as antibiotics, silicon dioxide, nano-silver, etc.) to achieve bacterial imaging and inhibition, but the preparation process is cumbersome, the stability is reduced, and potential Biological toxicity and induction of drug resistance and other issues. In view of these problems, the inventor creatively proposed to prepare carbon dots by specifically selecting protamine sulfate as a carbon source and heating through a lot of research and practice. The preparation method is simple, the raw materials are easy to obtain, and the operation is green and environmentally friendly. The chromoluminescent carbon dots have good water solubility,...
Embodiment 1
[0046] (1) Weigh 0.5 g of protamine sulfate and disperse in 10 mL of ultrapure water, and then sonicate under an ultrasonic instrument to obtain a uniformly dispersed and transparent solution.
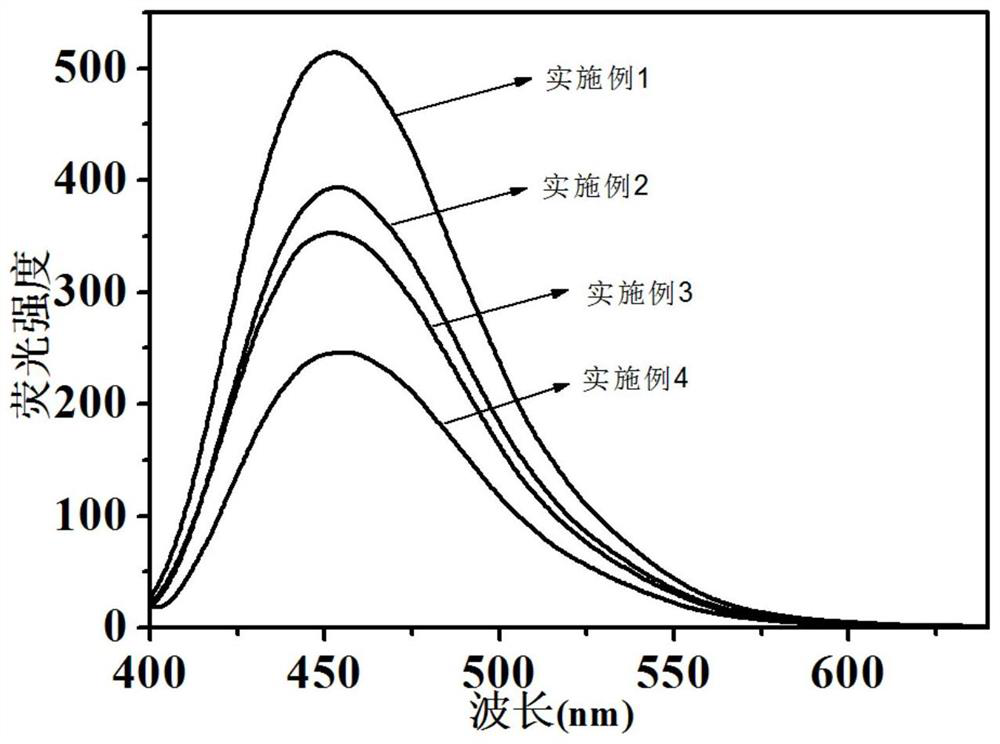
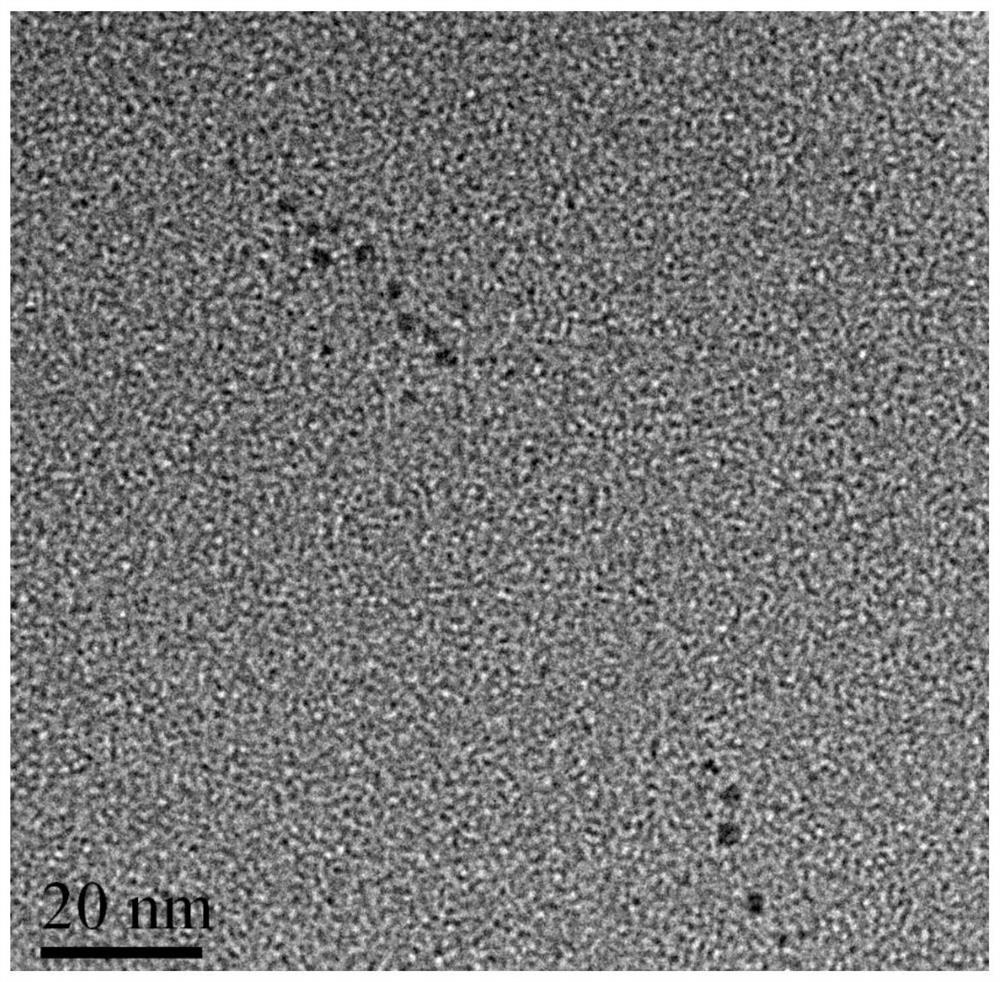
[0047] (2) Transfer the transparent solution obtained in step (1) to a microwave reactor, and react at 200°C for 60 minutes to obtain a carbon dot solution, whose fluorescence spectrum is as follows: figure 2 As shown, the fluorescence intensity is strong, and the particle size characterization results are shown in image 3 .
[0048] (3) Put the carbon dot solution obtained in step (2) directly into a 500D dialysis bag for 24 hours of dialysis and then dry to obtain blue luminescent antibacterial carbon dots.
[0049] To dissolve in 0.1mol / LH 2 SO 4 Quinoline sulfate in solution (refractive index (η) 1.33) was used as reference (quantum yield=54%). The quantum yield of carbon dots was calculated by comparing the ratio of fluorescence area (Ex=360nm) to absorbance. All samples ar...
Embodiment 2
[0054] (1) Weigh 0.1 g of protamine sulfate and disperse in 10 mL of ultrapure water, and then sonicate under an ultrasonic instrument to obtain a uniformly dispersed and transparent solution.
[0055] (2) Transfer the transparent solution obtained in step (1) to a microwave reactor, and react at 180°C for 50 minutes to obtain a carbon dot solution, whose fluorescence spectrum is as follows: figure 2 As shown, the fluorescence intensity is weaker than that of Example 1.
[0056] (3) Put the carbon dot solution obtained in step (2) directly into a 500D dialysis bag for 24 hours of dialysis and then dry to obtain blue luminescent antibacterial carbon dots.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Mic value | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com