Method for removing isonaringin from natural product hesperidin
A technology for isonaringin and hesperidin, which is applied in the field of purification of natural extraction product hesperidin, can solve the problems of difficulty in finding and dissolving hesperidin, impurity removal, solvent residue and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment example 1
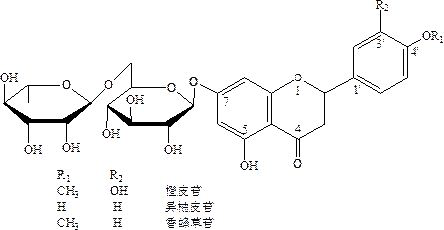
[0026] Take a 500mL three-neck flask, respectively install a syringe with a needle (put it into the rubber stopper first), an electric stirrer, and a thermometer, and place it in a fume hood. Measure 150mL of pure water and add it to a three-necked flask. Add 3.0 g of solid NaOH and stir to dissolve. Then slowly add 20.0g hesperidin 1, stir, and dissolve completely. Put a lot of solid ice cubes directly into the three-necked flask, and the temperature dropped to 8°C. Slowly push 0.3mL of dimethyl sulfate into the syringe, and the dropwise addition is completed within 5 minutes. The temperature of the solution in the flask is between 8-10°C, and the volume is about 300mL. After the dropwise addition was completed overnight, the temperature of the solution was slowly returned to normal temperature, and the reaction was stirred for 10 hours.
[0027] The next morning, add 9.5 g of activated carbon and stir at 30°C for 2 hours to decolorize. Filter and clean the activated char...
Embodiment example 2
[0029] Pour 150 mL of pure water into the three-necked flask, add 3.5 g of solid NaOH, 20.0 g of hesperidin 1, and stir until completely dissolved. Ice cubes were put into the flask to cool down to 0°C, and 0.2 mL of dimethyl sulfate was slowly added dropwise, and the addition was completed within 3 minutes. After the dropwise addition was completed, wait for the solution to return to normal temperature slowly, and heat to 30° C. to react for 4 hours.
[0030] It was acidified to neutral with dilute hydrochloric acid, and a large amount of yellow precipitates precipitated out of the solution immediately. Let stand for 2 hours, and filter with suction. Dry at 60° to get 18.6g hesperidin. The isonaringin was reduced from 2.8% to 0.8%, and the yield was 93.0%.
Embodiment example 3
[0032] Pour 150mL of pure water and 4.0g of solid NaOH into the three-necked flask, and slowly add 20.0g of hesperidin 1 after dissolution, and stir until completely dissolved. Cool down to -8°C with ice cubes, slowly push in 0.4 mL of dimethyl sulfate with a syringe, and complete the addition within 7 minutes. The temperature in the flask rises slowly to about 0°C, and the volume of the solution is 350 mL. After the temperature of the solution returned to normal temperature slowly, the reaction was heated at 40°C for 3 hours. At the same time, weigh 200g of resin AB-8 and pack it into a column, and treat it with ethanol, dilute hydrochloric acid, and dilute NaOH respectively for use.
[0033] After the reaction is completed, the solution is passed through the pretreated AB-8 macroporous adsorption column. The passing solution was acidified to neutral with dilute hydrochloric acid, and a large amount of precipitates appeared in the solution immediately, which was allowed to sta...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com