Force-induced response drug controlled-release multifunctional wound dressing and preparation method and application thereof
A wound dressing, multi-functional technology, applied in medical science, bandages, etc., can solve the problems of difficult to control internal drug release, stimulate and regulate active drug release, poor ductility, etc., achieve good sterilization and anti-protein adsorption, clever concept , the effect of simple preparation method steps
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
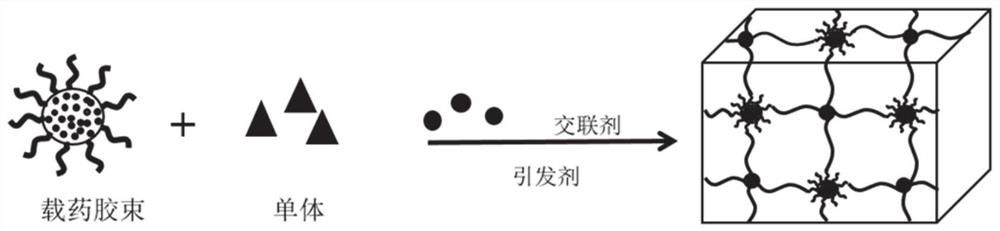
[0061] Step 1: Add 0.006 mol / L acrylylated Pluronic F127 (F127DA) and 0.0015 mol / L rifampicin to 5 mL of dichloromethane (DCM), fully dissolve, and dry in a vacuum oven after the DCM has evaporated. Add 2.5 mL of deionized water, shake in a constant temperature shaking box until the solution is clear and transparent, and a stable micellar solution is obtained.
[0062] Step 2: Add 4mol / L [2-(methacryloyloxy)ethyl]dimethyl-(3-sulfopropyl)ammonium hydroxide (SBMA) to the solution in step 1, stir until fully dissolved .
[0063] Step 3: Add 0.003mol / L N,N'-methylenebisacrylamide, stir to dissolve, add 0.005mol / L ammonium persulfate, add 2 drops of tetramethylethylenediamine after fully dissolved, mix well and trigger free radicals Polymerize and stand overnight at room temperature to obtain a hydrogel.
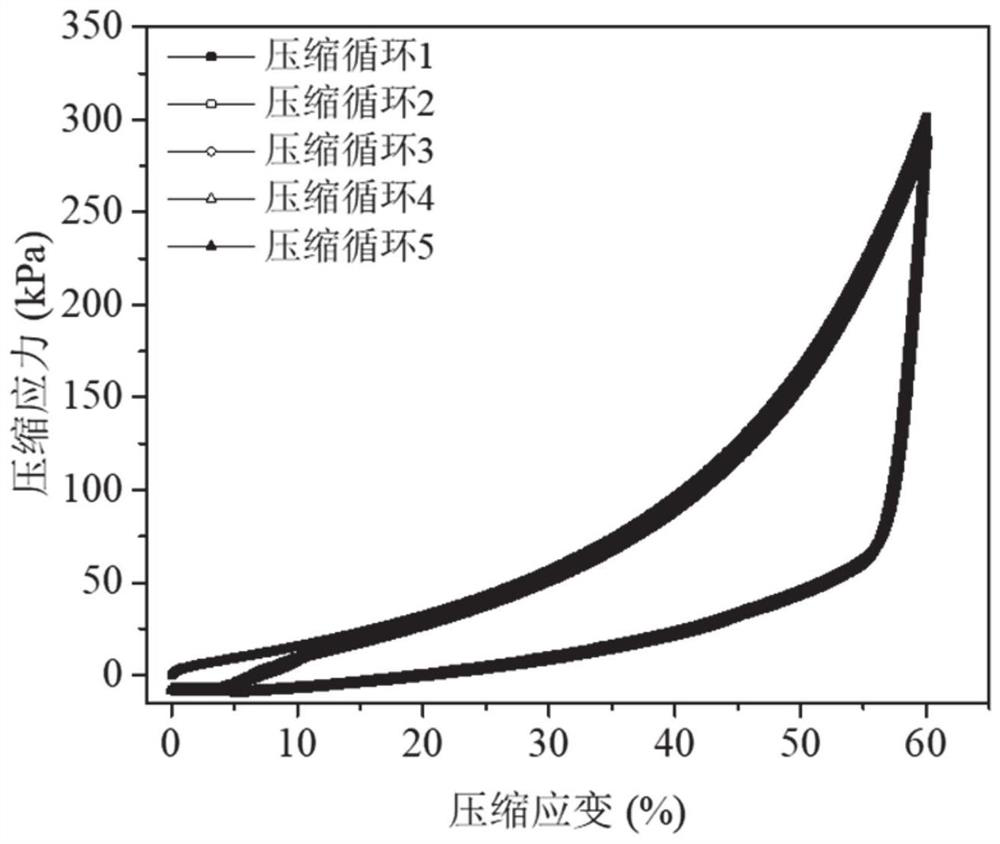
[0064] According to the mechanical property test, the elongation at break of the prepared hydrogel can reach 1,420%, and the break stress is 112kPa. The stress of the hydrogel...
Embodiment 2
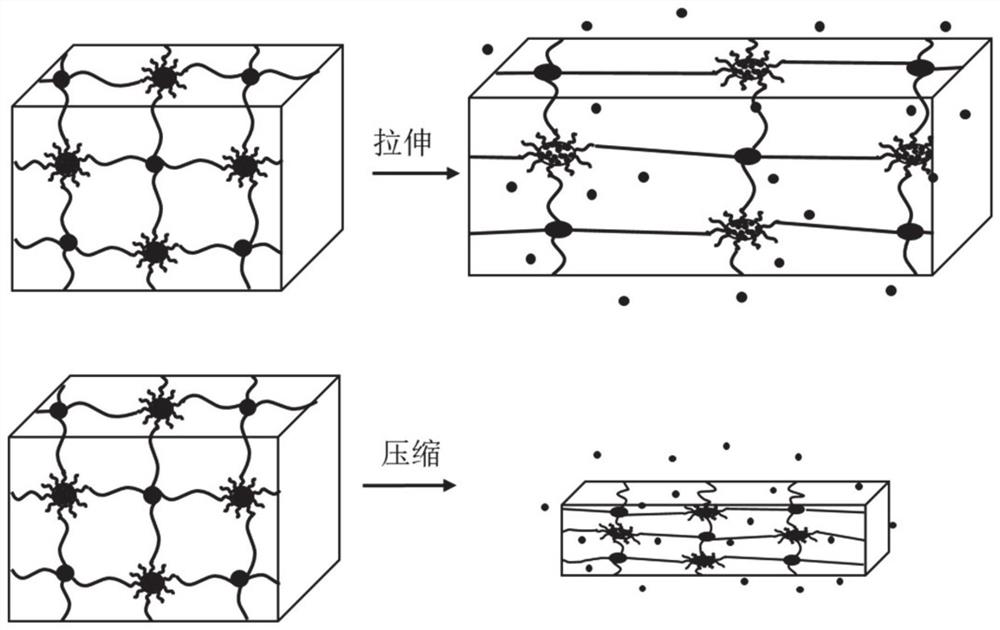
[0068] Compression release experiment: take the hydrogel prepared in Example 1 to make a disk-shaped sample with a diameter of 15 mm and a thickness of 2 mm. Put into a container containing 6mL deionized water (6.3×3.7×1.2cm 3 ), so that the hydrogel is completely submerged. The hydrogel was cyclically compressed at a constant speed of 6 s / cycle at 40%, 50%, and 60% compressive strain. In the control group, the hydrogel was placed in the same volume of deionized water without compression. At intervals of every 40 compression cycles (or 240s), take 4mL of the solution to be tested for drug concentration, and at the same time replenish the container with the same volume of deionized water. The drug concentration in the solution was measured by a UV-vis spectrophotometer, and the cumulative release rate of the drug was calculated. The antibacterial properties of the drug-releasing solutions were determined by the zone of inhibition method.
[0069] The release rate of the dru...
Embodiment 3
[0071] Tensile release test: the hydrogel prepared in Example 1 was taken to make an effective release volume of a cuboid sample with a length of 20 mm, a width of 25 mm, and a thickness of 2 mm, and was immersed in a container with 10 mL of deionized water (10 × 3.7 × 1cm 3 ). The hydrogel was cyclically stretched at a constant speed of 6 s / cycle at 60%, 80% tensile strain. In the control group, the hydrogel was placed in the same volume of deionized water without stretching. At intervals of every 50 compression cycles (or 300s), take 4mL of the solution to be tested for drug concentration, and at the same time add the same volume of deionized water to the container. The drug concentration in the solution was measured by a UV-vis spectrophotometer, and the cumulative release rate of the drug was calculated. The antibacterial properties of the drug-releasing solutions were determined by the zone of inhibition method.
[0072] The release rate of the drug in the hydrogel un...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fracture stress | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Stress | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fracture stress | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com