Phase-change foamied insulation board based on phenolic foam waste, and preparation method thereof
A foam insulation board and phenolic foam technology, applied in the field of building materials, can solve the problems of less storage capacity of phase change materials, shorten the service life of building materials, and low mechanical strength of building materials, so as to improve indoor comfort and thermal insulation performance , Solve the effect of liquid phase leakage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
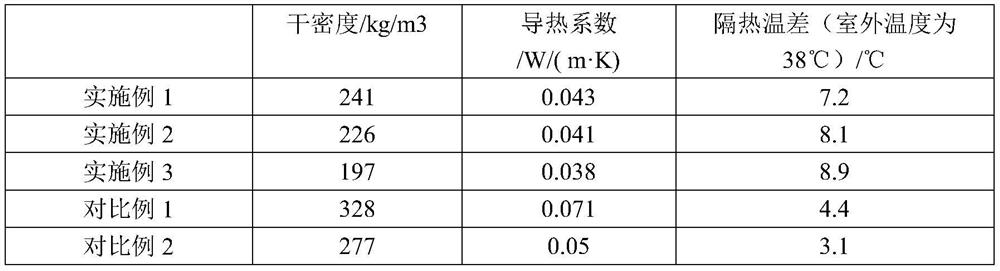
Embodiment 1
[0025] A preparation method of a phase-change foam insulation board based on phenolic foam waste, comprising the following steps:
[0026] S1: Preparation of organic phase-change thermal insulation material: in parts by mass, heat and melt 10 parts of capric acid, 0.8 parts of myristic acid, and 6 parts of myristyl alcohol at 65°C, add an emulsifier, stir evenly, and then add 100 parts of porous polymer Styrene microspheres, in an environment with a vacuum degree of 0.03MPa and a temperature of 40°C, stirred and adsorbed for 1h, then cooled and crystallized at 15°C for 2h, stirred continuously during the crystallization process, and then added 30 parts of silicone styrene-acrylic emulsion. Under the irradiation of a 100W ultraviolet lamp, after curing at 25°C to form a film, an organic phase change thermal insulation material is obtained;
[0027] S2: Prepare an alkali activator: mix sodium hydroxide, trisodium phosphate, and sodium citrate evenly in a mass ratio of 1:1:0.5; ...
Embodiment 2
[0037] A preparation method of a phase-change foam insulation board based on phenolic foam waste, comprising the following steps:
[0038] S1: Preparation of organic phase-change thermal insulation material: in parts by mass, heat and melt 12.5 parts of capric acid, 1.5 parts of myristic acid, and 7 parts of myristyl alcohol at 70°C, add an emulsifier, stir evenly, and then add 100 parts of porous polymer Styrene microspheres, under the environment of vacuum degree of 0.05MPa and temperature of 45°C, stirred and adsorbed for 1.5h, then cooled and crystallized at 15°C for 4h, stirred continuously during the crystallization process, and then added 35 parts of silicone styrene-acrylic emulsion, in Under the irradiation of a UV lamp with a power of 100W, after curing at 25°C to form a film, an organic phase change thermal insulation material is obtained;
[0039] S2: Prepare an alkali activator: mix sodium hydroxide, trisodium phosphate, and sodium citrate evenly according to a ma...
Embodiment 3
[0049] A preparation method of a phase-change foam insulation board based on phenolic foam waste, comprising the following steps:
[0050] S1: Preparation of organic phase-change thermal insulation material: in parts by mass, heat and melt 15 parts of capric acid, 2 parts of myristic acid, and 8 parts of myristyl alcohol at 70°C, add an emulsifier, stir evenly, and then add 100 parts of porous polymer Styrene microspheres, in an environment with a vacuum degree of 0.07MPa and a temperature of 50°C, stirred and adsorbed for 2 hours, then cooled and crystallized at 20°C for 6 hours, stirred continuously during the crystallization process, and then added 40 parts of silicone styrene-acrylic emulsion. Under the irradiation of a 100W ultraviolet lamp, after curing at 25°C to form a film, an organic phase change thermal insulation material is obtained;
[0051] S2: Prepare the alkali activator: mix sodium hydroxide, trisodium phosphate, and sodium citrate evenly according to the mas...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com