Preparation method of photosensitive antibacterial material
A photosensitive antibacterial and photosensitizer technology, applied in botany equipment and methods, chemicals for biological control, animal repellants, etc., can solve the problems of limited antibacterial effect, achieve short diffusion distance, small damage, and responsive The effect of mild conditions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Embodiment 1: Preparation of zinc phthalocyanine-nanometer zinc oxide photosensitive antibacterial material
[0023] 1. Zinc oxide nanoparticles are prepared by pre-precipitation technology: in this technology, under constant speed stirring conditions, 0.05mol zinc nitrate is completely dissolved in 50mL distilled water at room temperature and continued to stir for 3 hours, and then added to the solution Ammonium hydroxide was slowly added dropwise until the white precipitate was no longer formed; then the pH was adjusted to 9, and after stirring for 3 hours, the precipitate was washed 4 times with distilled water to reduce the pH of the filtrate to 7, and then boiled for 10 minutes, and finally in Calcining at 500°C for 1 hour to obtain zinc oxide nanoparticles;
[0024] 2. Dissolve β-monocarboxyl substituted zinc phthalocyanine in DMSO to make a solution with a concentration of 50μuM, then take 10ml, add 10mg of zinc oxide nanoparticles, ultrasonicate for 5 minutes an...
Embodiment 2
[0025] Embodiment 2: antibacterial performance test
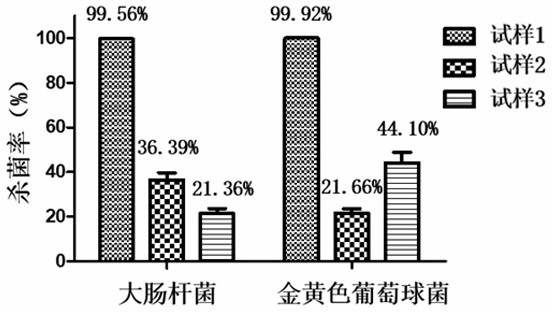
[0026] The experimental strains were Gram-positive Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC 6358) and Gram-negative Escherichia coli (ATCC 8739). Adaptive adjustments are made to the requirements of the test, and the specific steps are as follows:
[0027] The zinc phthalocyanine-nanometer zinc oxide photosensitive antibacterial material (sample 1) and nano zinc oxide (sample 2) prepared in Example 1 were diluted with PBS to a ZnO concentration of 100 mg / L respectively, and the zinc phthalocyanine (sample 3 ) was diluted with PBS until the concentration of zinc phthalocyanine was consistent with the concentration of zinc phthalocyanine in (sample 1), then 20 μl of each sample solution and PBS (control) were added to a 96-well plate, and then 180 μl of bacterial solution was added (10 6 -10 8 CFU / ml), then incubate in a 37°C incubator for 1 hour, then use sterile PBS to dilute each group into different concentration gradients, take 10...
Embodiment 3
[0032] Example 3: Detection of Active Oxygen Generation Ability
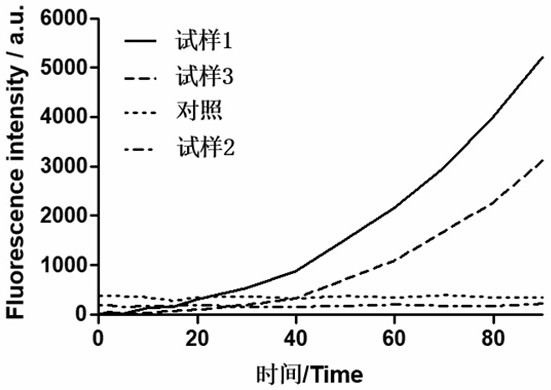
[0033] Get the zinc phthalocyanine-nano zinc oxide photosensitive antibacterial material (sample 1), nano zinc oxide (sample 2), zinc phthalocyanine (sample 3) prepared in Example 1, through quantitative determination and the zinc phthalocyanine in sample 1 Consistent concentration) and PBS (control) 20 μL each into a 96-well plate, then add 180 μL of PBS each, and add active oxygen detection reagent, and then each group is irradiated with a light source with a wavelength of 670nm and a power of 25mw, and the detection is performed every 1 minute. Solution fluorescence intensity. The experiment was repeated 3 times.
[0034] The result is as figure 2 It can be seen that the active oxygen generation ability of zinc phthalocyanine-nano-zinc oxide photosensitive antibacterial material is much higher than that of zinc phthalocyanine and nano-zinc oxide.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com