Thin-layer chromatography identification method forwild chrysanthemum medicinal material and formula granule and application
A technology of formula particle and thin layer identification, which is applied in the directions of material separation, analysis of materials, preparation of test samples, etc., can solve the problems of single identification component, unable to reflect the quality and functional components of wild chrysanthemum medicinal materials as a whole, and achieve the operation Simple, good application prospect, good commercial value effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] A thin-layer identification method for wild chrysanthemum medicinal materials and formula granules, comprising the following steps:
[0034] a. Take chlorogenic acid, mongoside, 4,5-di-O-caffeoylquinic acid, 3,5-O-dicaffeoylquinic acid, luteolin, luteolin reference substance, Add 80% concentration of methanol to make a solution containing 1mg per 1mL as the reference solution.
[0035] b. Add 1 g of wild chrysanthemum as reference medicinal material, add 15 ml of 80% methanol, ultrasonicate for 15 minutes, filter, and the filtrate is used as the test solution.
[0036] c. Take 1 g of the sample to be tested, add 15 ml of 80% methanol, ultrasonicate for 15 minutes, filter, and the filtrate is used as the test solution.
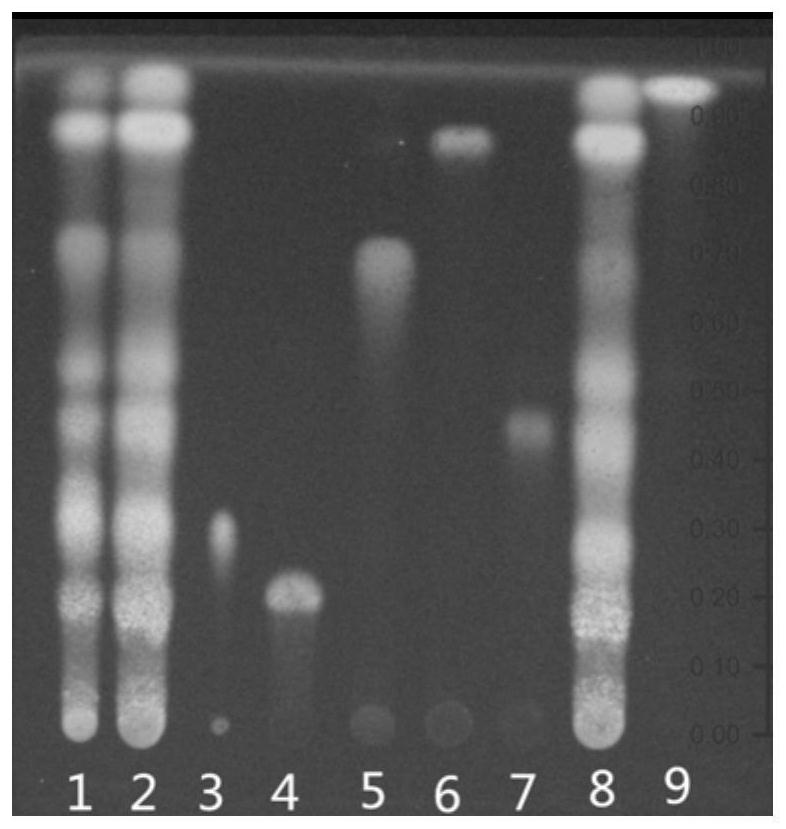
[0037] d. According to the thin-layer chromatography (general rule 0502) test, draw 2 μl of the test solution, 10 μl of the reference medicinal material solution, and 5 μl of the reference substance solution, respectively spot on the same high-efficienc...
Embodiment 2
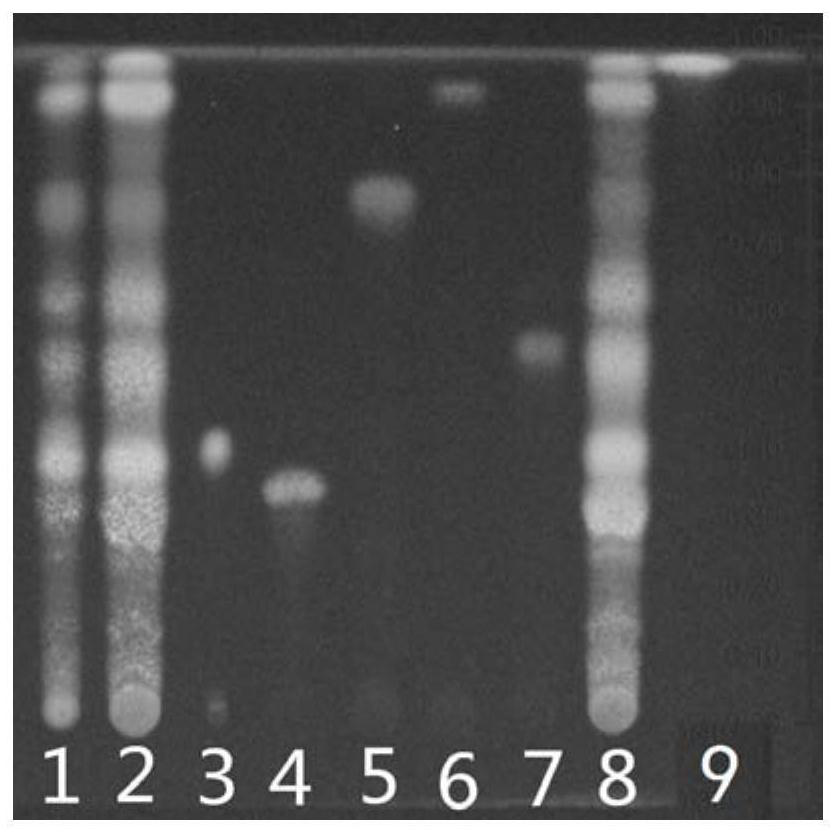
[0039] The basic steps are the same as in Example 1, except that the ratio of ethyl acetate, n-butanol, formic acid and water in the developer is 10:1:1:1. Test results such as figure 2 As shown, the chromatographic separation of the test product and the reference medicinal material is poor at the corresponding positions of the chlorogenic acid and mongoside chromatograms.
Embodiment 3
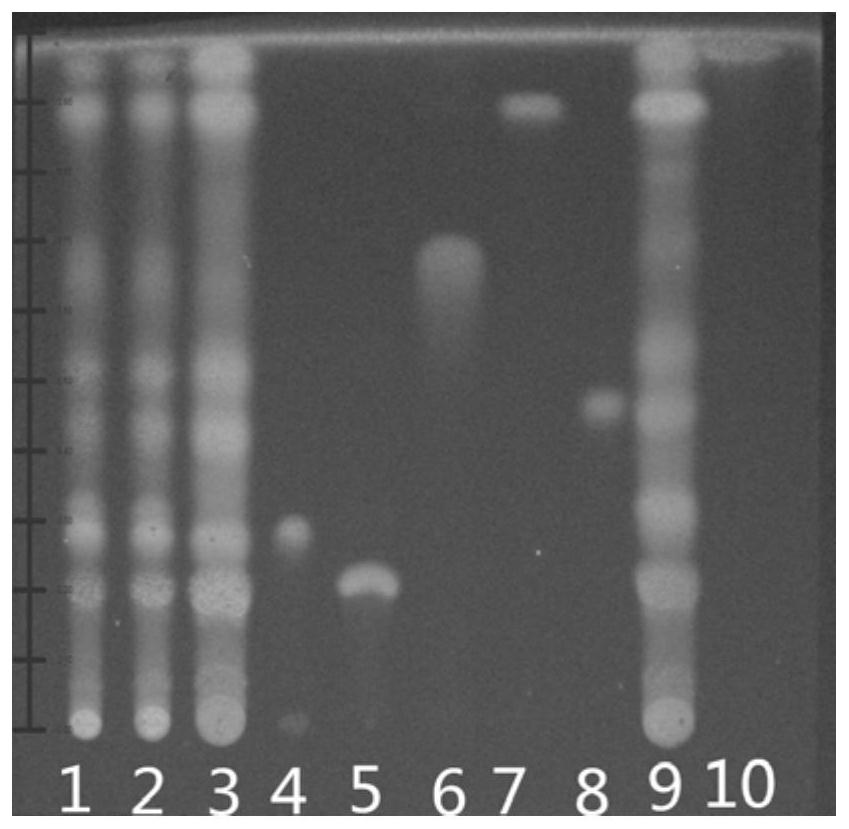
[0041] Take the test sample, reference substance, and reference medicinal material solution of the wild chrysanthemum formula granules, respectively, and point them on the same silica gel G, and use ethyl acetate-n-butanol-formic acid-water as the developer in the ratio of 10:1:0.5:0.5, and develop , take it out, dry it in the air, spray it with 10% sulfuric acid ethanol solution, heat it at 70°C, and inspect it under an ultraviolet lamp (365nm). Such as image 3As shown, the substances corresponding to each label are: 1 and 2 are different batches of wild chrysanthemum formula granules; 3. Wild chrysanthemum control medicinal material; 4. Chlorogenic acid; O-caffeoylquinic acid; 7, 3,5-O-dicaffeoylquinic acid; 8, luteolin; 9, wild chrysanthemum; 10, luteolin. Compared with Example 1, the chromatograms of the test product and the reference medicinal material are not clear at the corresponding positions of the chromatograms of 4,5-di-O-caffeoylquinic acid and luteolin.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com