Treatment method of emulsion wastewater
A treatment method and emulsion technology, which are applied in water/sewage treatment, chemical instruments and methods, water/sewage multi-stage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of excessive decrease in membrane flux, easy membrane pollution, and low mechanical strength, etc. Achieve the effect of avoiding secondary pollution, improving removal efficiency, and improving biodegradability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
experiment example 1
[0043] Experimental example 1: Comparative experiment of potassium ferrate compound coagulant
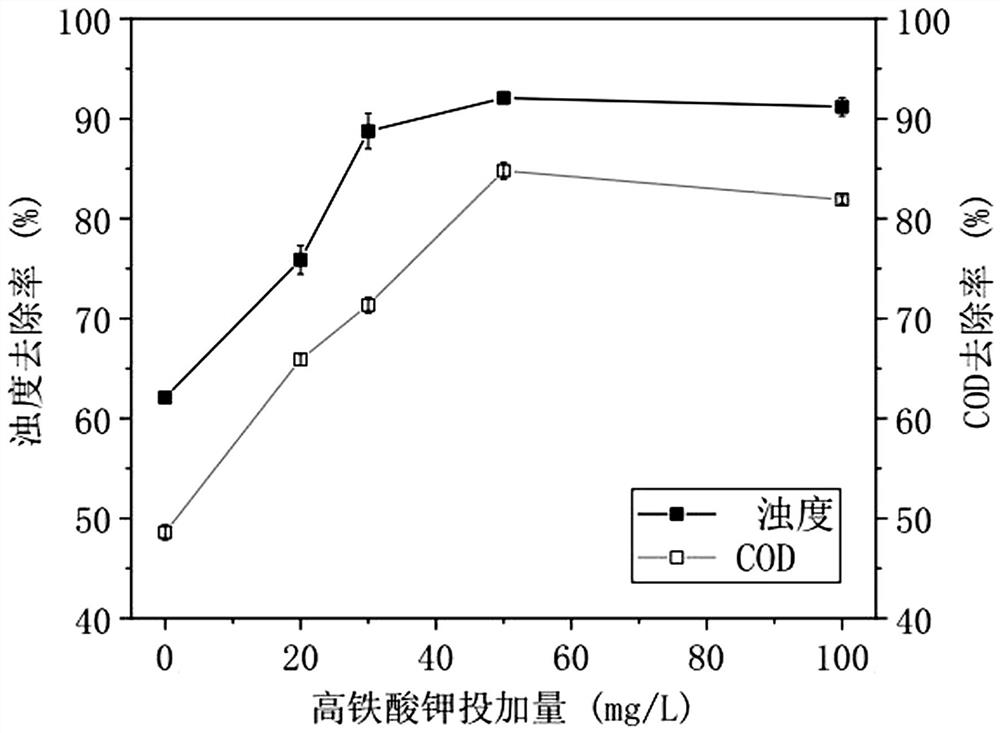
[0044] A. Potassium ferrate compound PAC: Use 1mol / L sulfuric acid and sodium hydroxide solution to adjust the initial pH=7, set the temperature to 30°C, and add PAC to the wastewater under the condition that the dosage of PAC is 50mg / L Potassium ferrate (1% solution) is used as coagulant aid, so that the content of potassium ferrate in the water sample is 0, 20, 30, 50, 100 mg / L respectively.
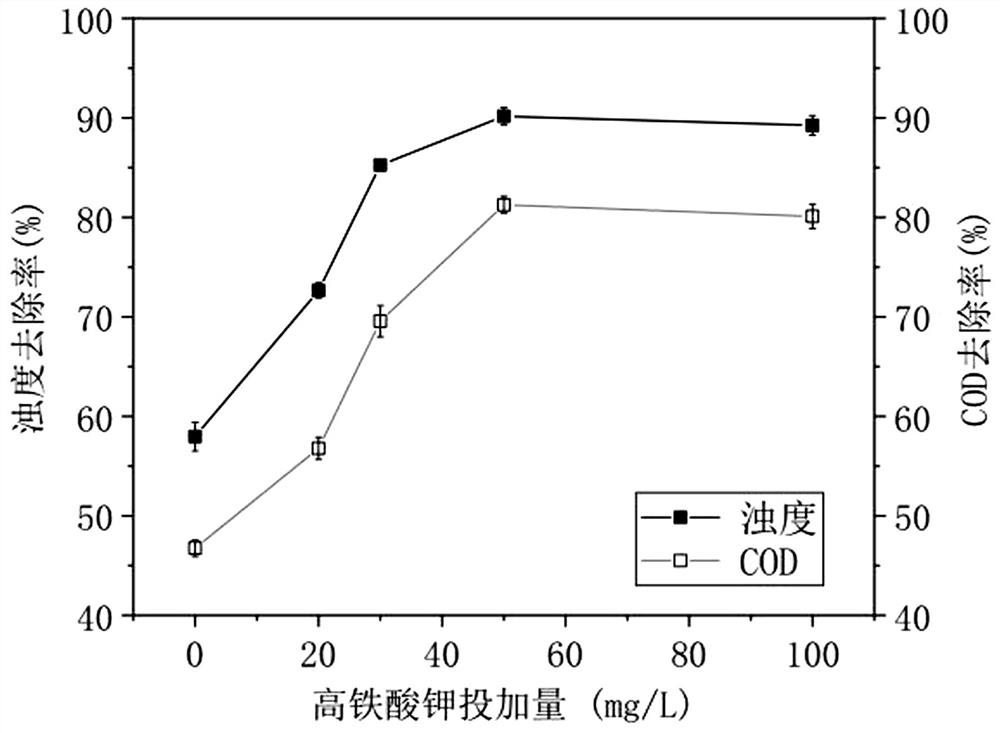
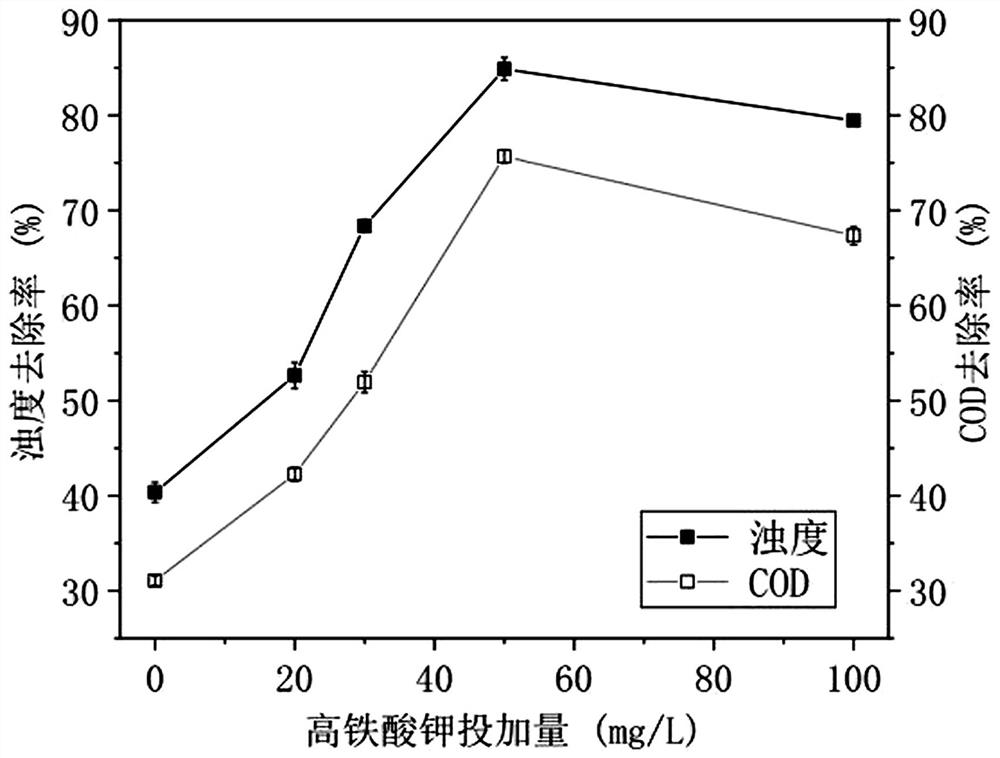
[0045] The effect of the dosage of potassium ferrate on the removal of pollutants is as follows: figure 1 shown. From figure 1 It was found that as the dosage of potassium ferrate increased from 0 to 50mg / L, the removal rate of CODCr and turbidity of the solution increased rapidly from 48.6%, 62.1% to 84.8%, 92.07%, respectively. Table 1 shows the effect on the removal efficiency of emulsion wastewater when only PAC is added, and Table 2 shows the effect on the removal efficiency of emuls...
experiment example 2
[0066] Experimental example 2: Single factor experiment in the coagulation and sedimentation stage: add 100mL emulsion wastewater into the beaker, and use 1mol / L H 2 SO 4 and NaOH solution to adjust the pH. Add the specified amount of coagulant PAC (10% solution) and coagulant aid potassium ferrate (1% solution) successively, and carry out magnetic stirring at a fixed speed at a set temperature. Stir the reaction for 10 minutes, let it settle for 30 minutes, take the supernatant to measure COD Cr and turbidity values. The factors investigated include: initial pH (3, 5, 7, 9, 11), PAC dosage (0, 10, 20, 30, 50, 100 mg / L), potassium ferrate dosage (0, 20, 30, 50, 100mg / L), reaction temperature (20, 30, 40, 50, 60°C), settling time.
[0067] The effect of initial pH on the removal of pollutants by coagulation and sedimentation is as follows: Figure 5 shown by Figure 5 The experimental results determined that in subsequent experiments, the initial pH value was selected as ...
experiment example 3
[0080] Experimental example 3: Electrochemical oxidation stage experiment: inject 500mL of wastewater treated under the optimal conditions in the coagulation and sedimentation process section into a beaker with an effective volume of 500mL, and add 500mg / L Na 2 SO 4 electrolyte to increase the conductivity of the solution. Place the BDD anode and Ti cathode vertically in the beaker, the distance between the plates is 10mm, and the immersion area is 10cm 2 , applying a set current density for galvanostatic electrochemical degradation. During the reaction, the beaker was placed on a constant temperature magnetic stirrer to make the concentration of the reaction solution uniform and the temperature constant; samples were taken regularly to determine the concentration values of CODCr, ammonia nitrogen (NH3-N) and total organic carbon (TOC). The factors investigated include: current density (20, 30, 50, 75, 100mA / cm2), initial pH of the electrolysis process section (3, 5, 7, 9,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com