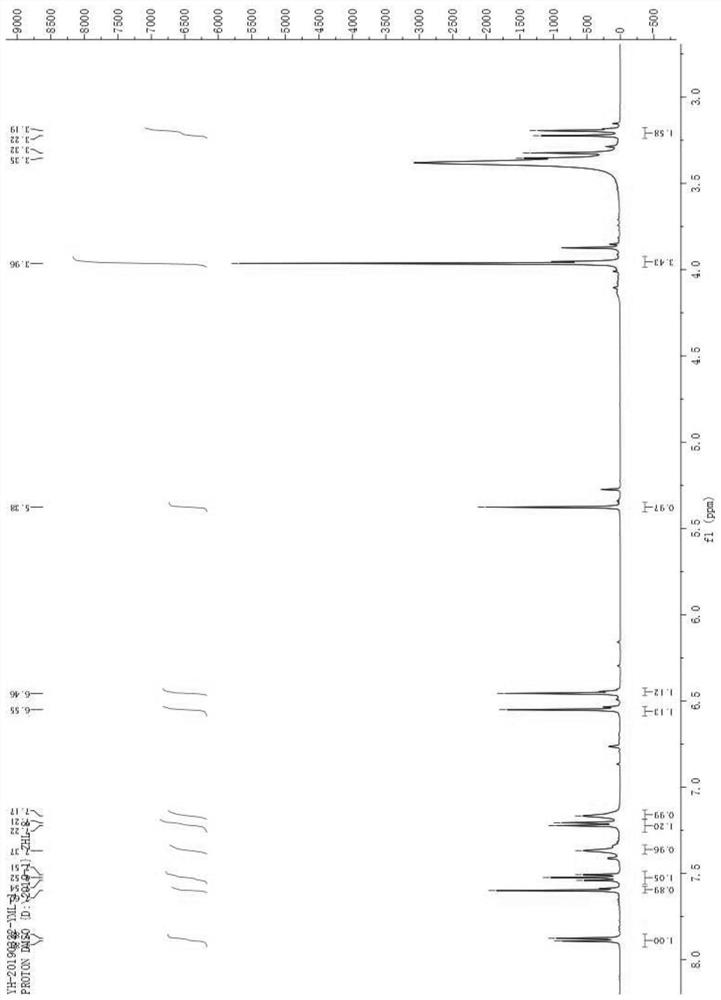
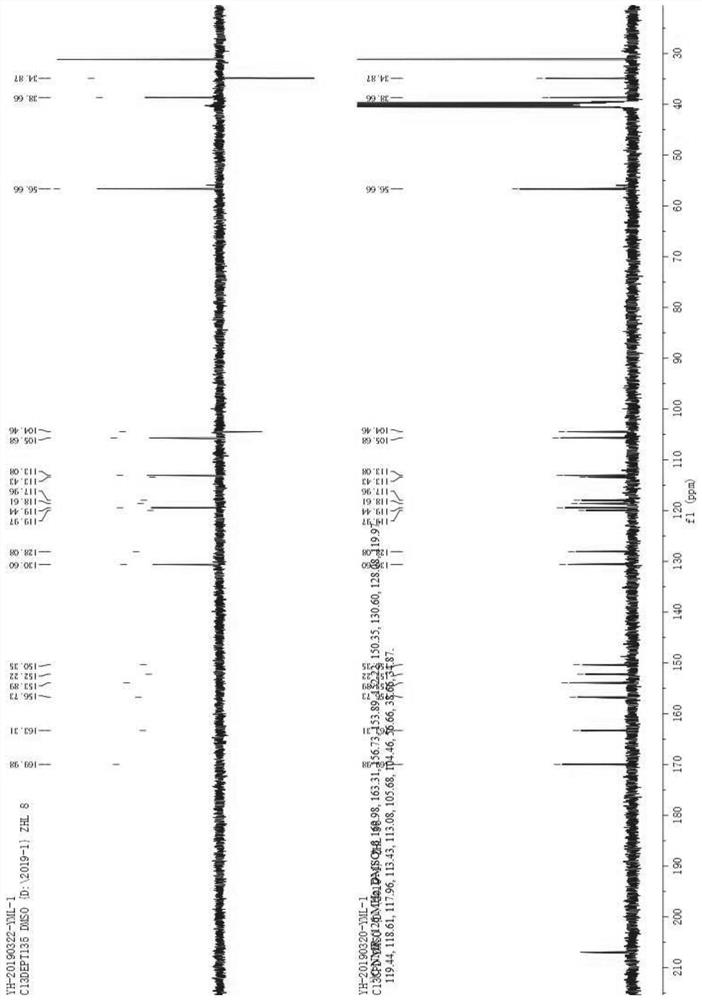
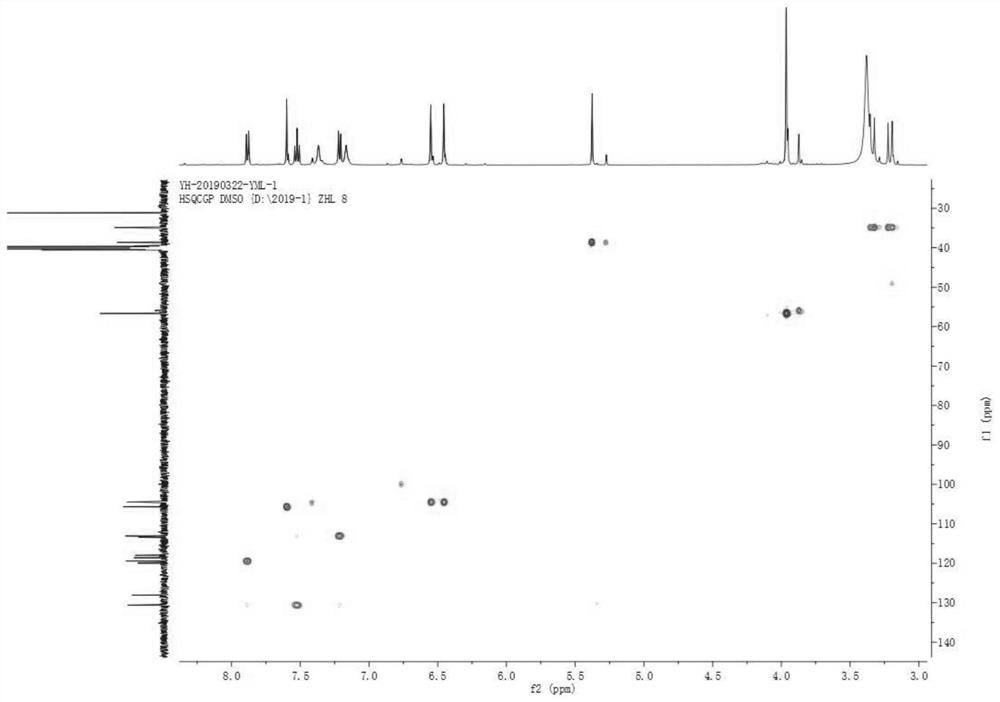
Aristolochic acid derivatives and application
A technique for aristolochic acid and derivatives, which is applied to aristolochic acid derivatives and application fields, can solve problems such as agricultural production loss, and achieve the effect of good application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0063] Embodiment 1: Determination of antibacterial activity of aristoloxazine C in vitro
[0064] Preparation of antibacterial test sample: take a certain amount of compound, and use 5% (volume fraction) methanol to prepare the compound into a test drug solution with a mass concentration of 100 ppm for antibacterial test.
[0065] Activation culture of bacteria: the test bacteria were taken out from the refrigerator at 4°C, inoculated into centrifuge tubes of LB liquid medium, and activated at 37°C for 12 hours.
[0066] Preparation of bacterial suspension: Take a small amount of activated test bacteria and add it to an appropriate amount of liquid LB medium, incubate at 37°C for 8-12 hours, take 2ml of bacterial suspension in a cuvette to test its absorbance, dilute the bacterial solution to 0.5 μg Turbidity (absorbance at 600nm wavelength is 0.08-0.13), and then diluted 200 times with liquid medium, and mixed. At this time, the concentration of the bacterial solution was a...
Embodiment 2
[0072] Embodiment 2: Aristoloxazine C pot bioactivity assay
[0073] The control of tobacco bacterial wilt is carried out by pot experiment method, and the control of kiwifruit canker is carried out by living tissue method.
[0074] Inoculation of pathogenic bacteria: the activated tobacco bacterial wilt pathogen was set to 10 8 cfu / ml suspension concentration, treatment is 10 8 Tobacco irrigated with cfu / ml bacterial suspension; the test compound aristoloxazine C 500mg / L was treated, and the root irrigation (10mL per pot) was applied; at the same time, an equal amount of LB medium was set as a control, and the treated tobacco was placed in the greenhouse for cultivation.
[0075] Cut the freshly picked kiwi branches into small branches of about 15cm, seal the two ends with wax oil, carry out surface disinfection with 75% ethanol, and after drying, use sterilized high-temperature tweezers to create strip wounds in the middle of the branches, spray to activate after 10 8 The...
Embodiment 3
[0086] Embodiment 3: Aristoloxazine C and other fungicide compound in vitro biological activity assay
[0087] This embodiment adopts counting method to measure, and method is described in embodiment 1. 1 in the sample is Aristoloxazine C, and the concentration is listed as the concentration of aristoloxazine C + the concentration of the compound drug. The results of the antibacterial assay are shown in Table 5. The results showed that the combination of aristoloxazine C and various agents had significant inhibitory effects on several pathogenic bacteria.
[0088] Table 5 Antibacterial effects of Aristoloxazine C and representative fungicides on seven pathogenic bacteria
[0089]
[0090]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com